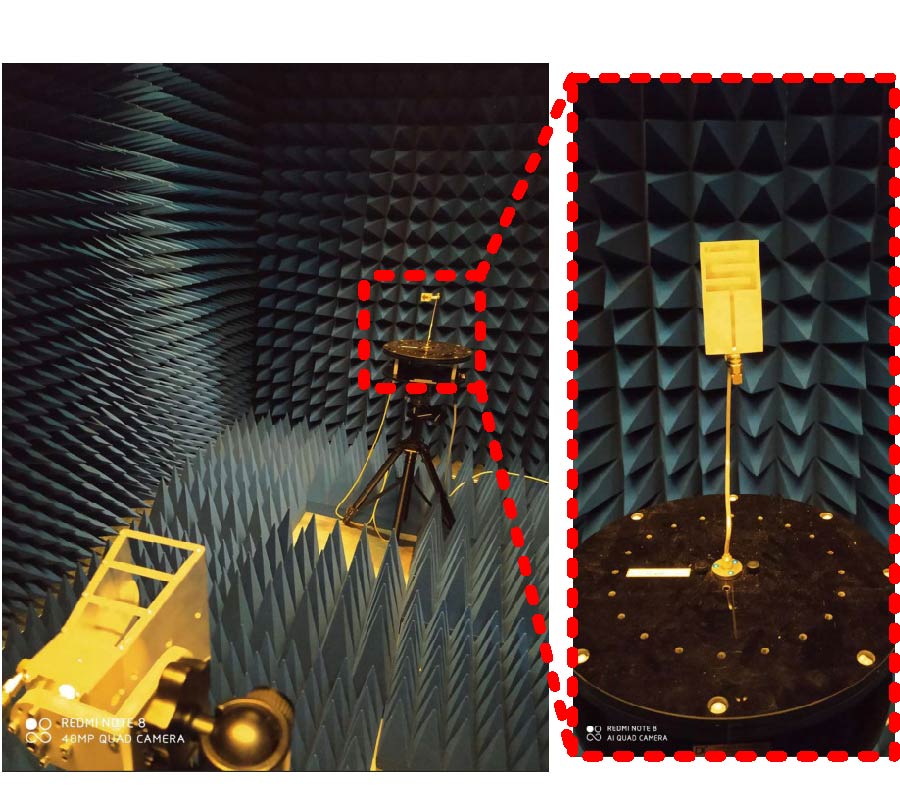
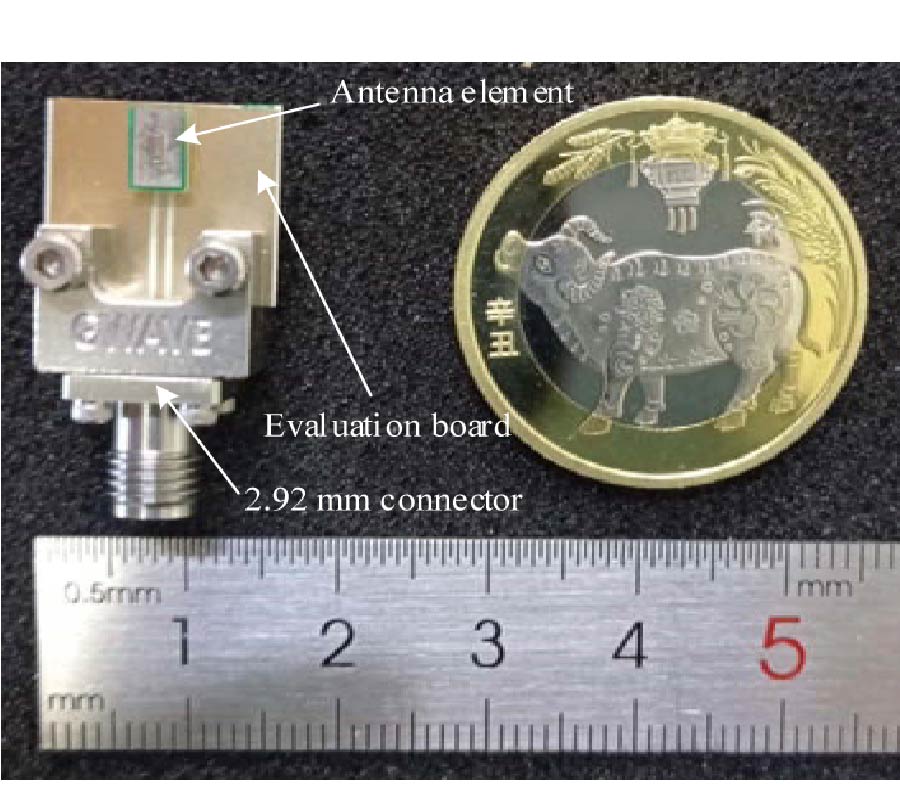
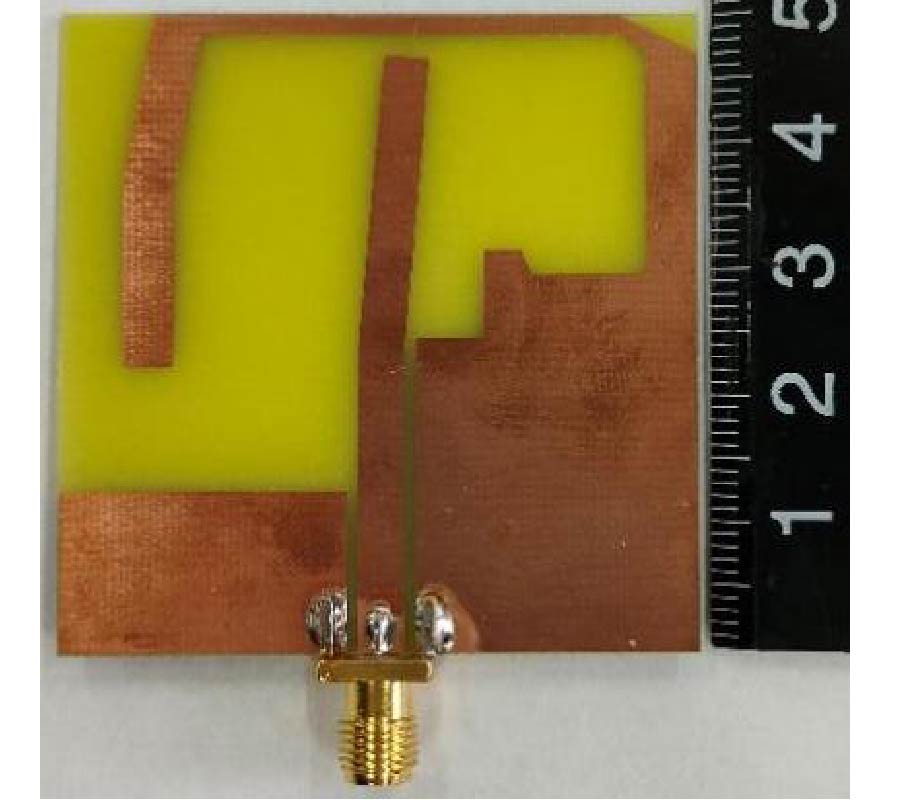
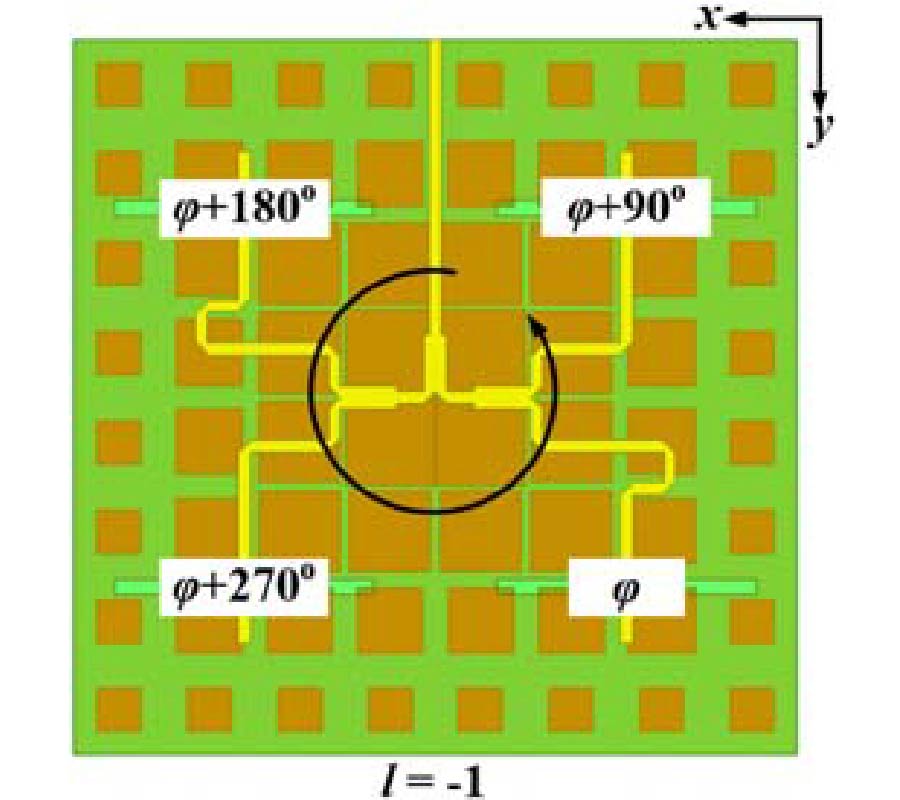
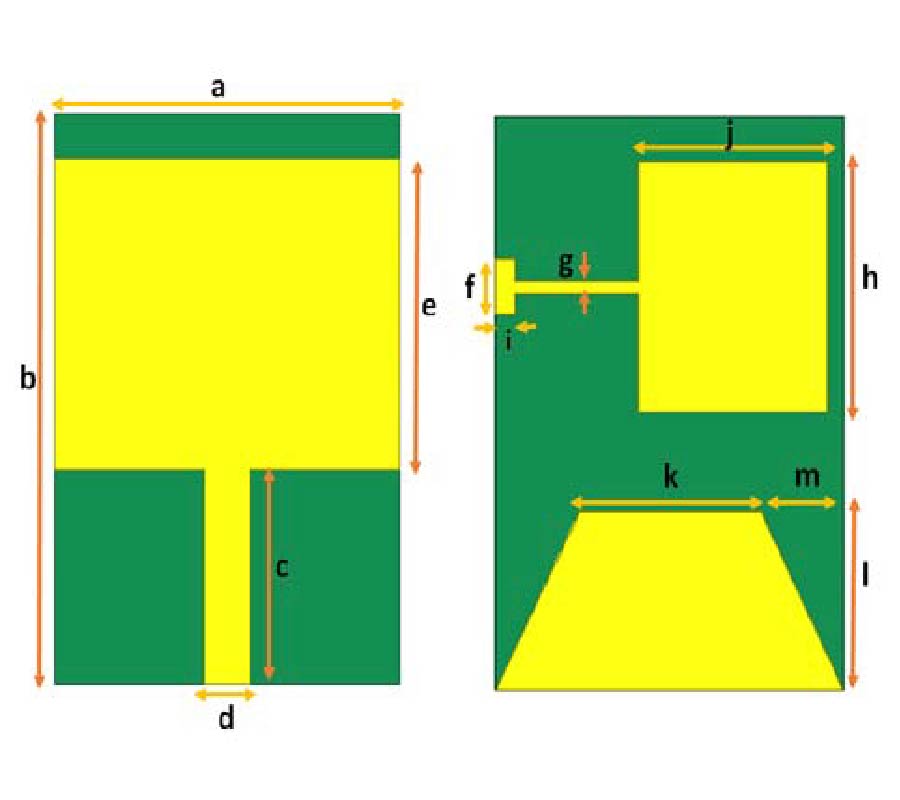
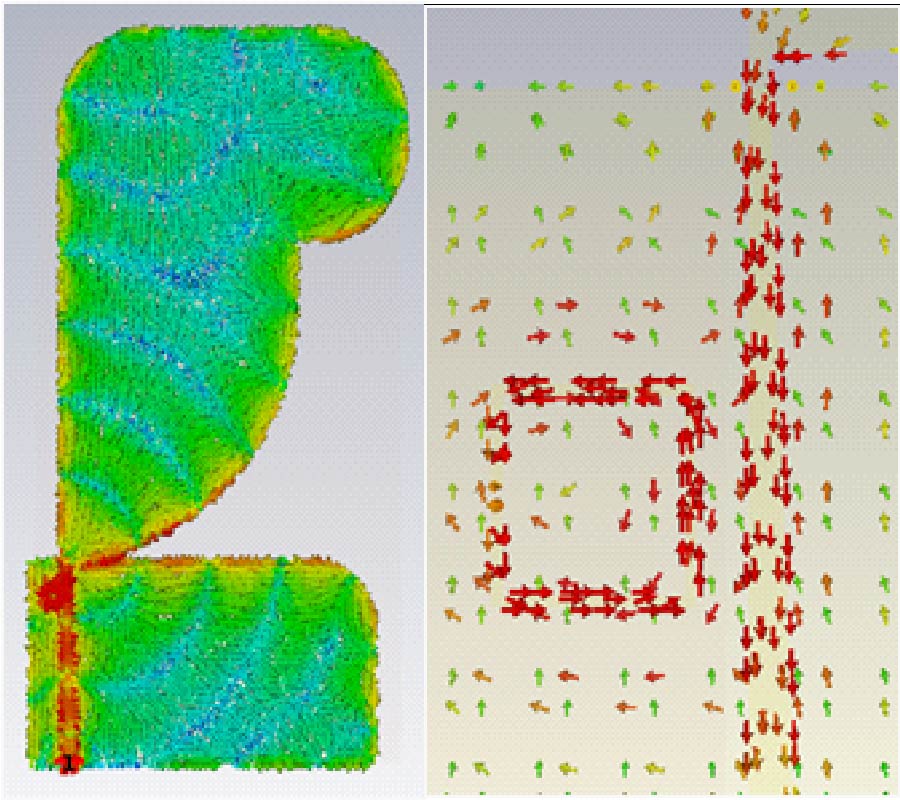
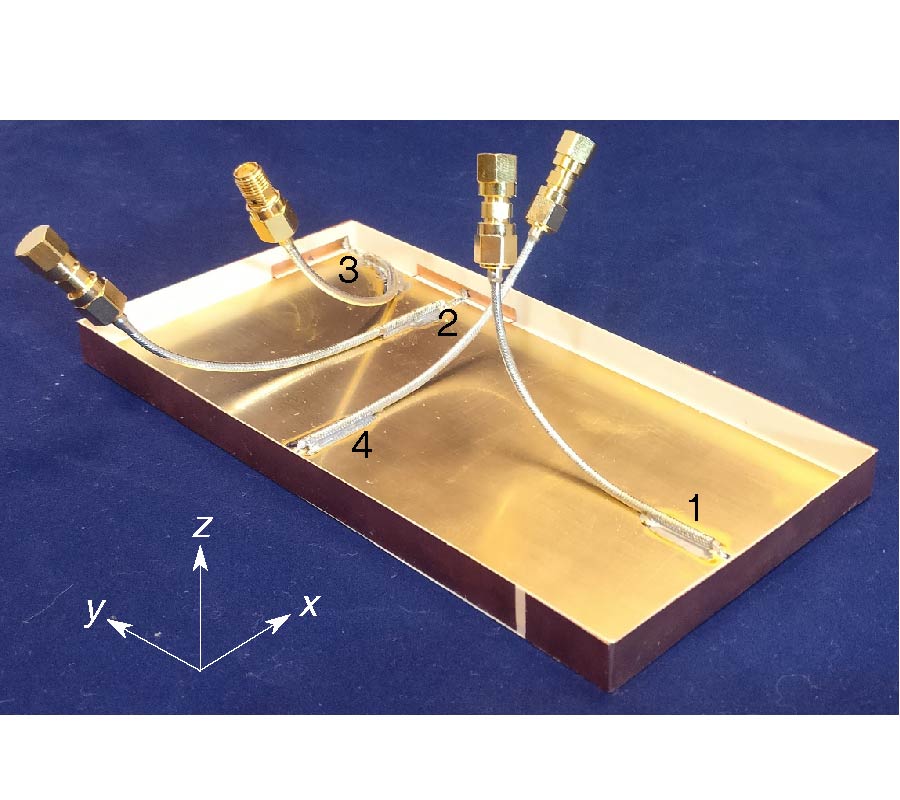
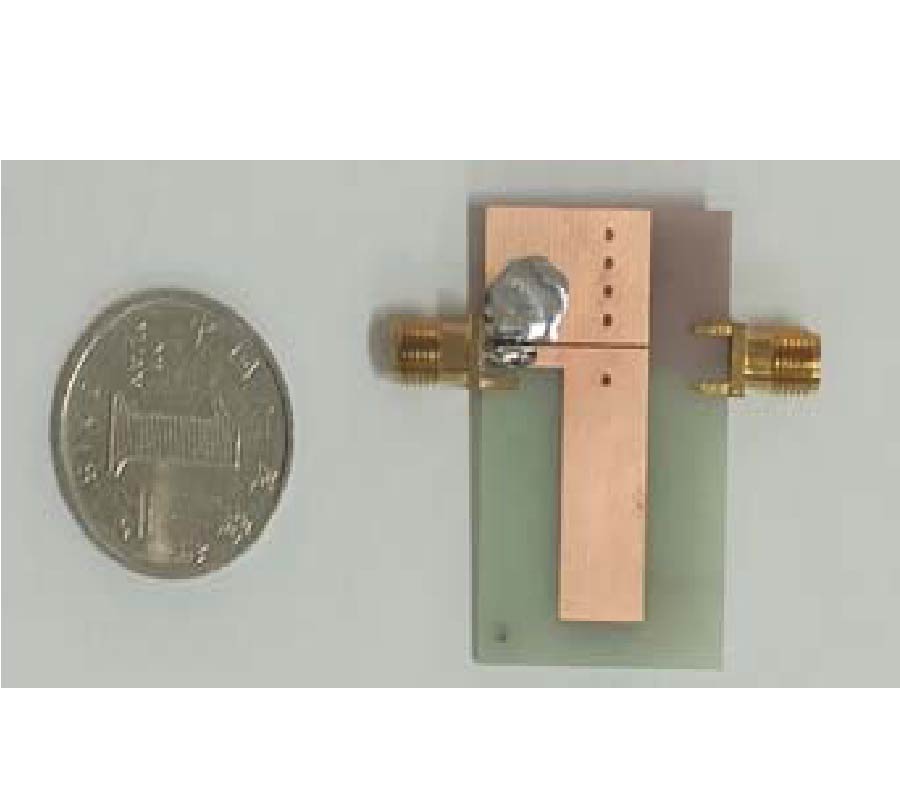
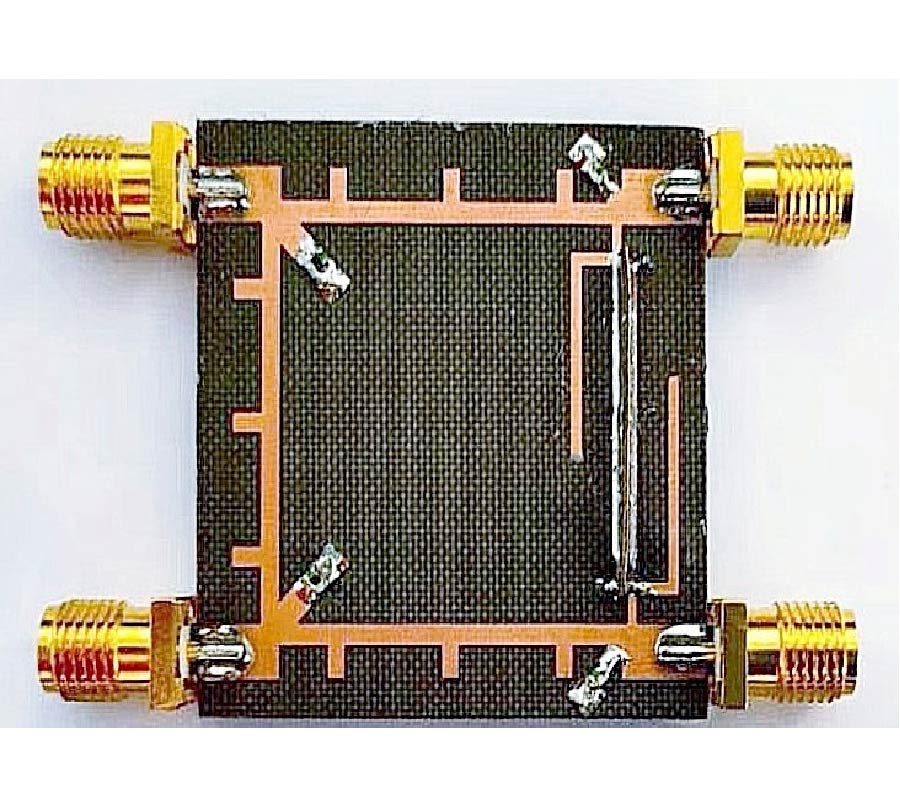
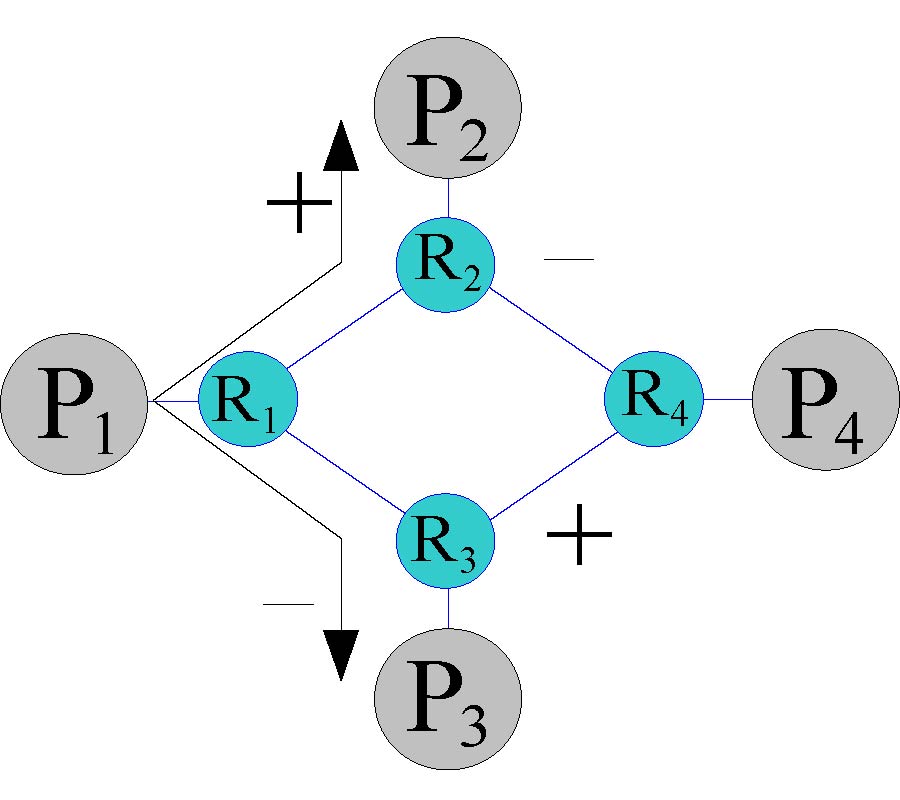
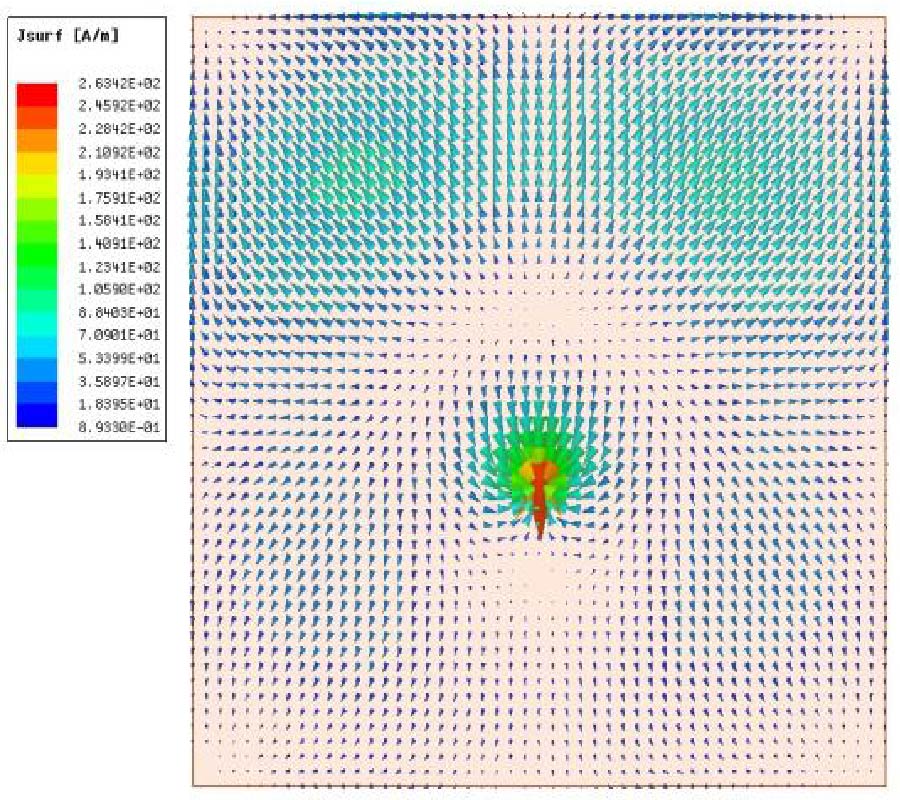
A Sensing Demonstration of a Sub THz
Radio Link Incorporating a Lens Antenna
Ali Ghavidel
,
Sami Myllymäki
,
Mikko Kokkonen
,
Nuutti Tervo
,
Mikko Nelo
and
Heli Jantunen
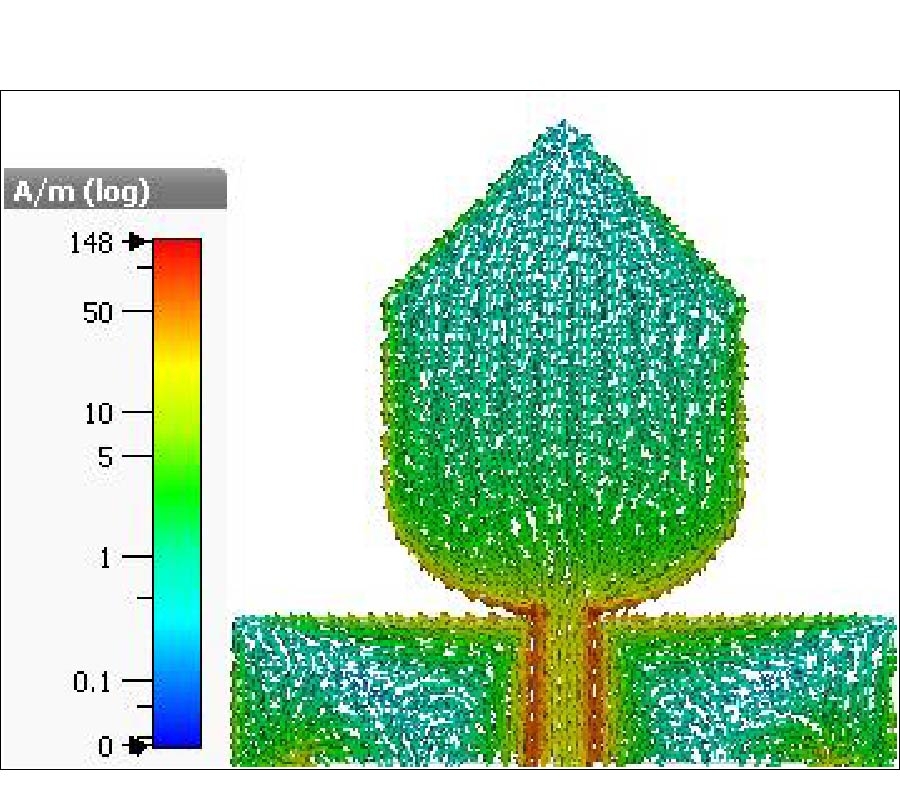
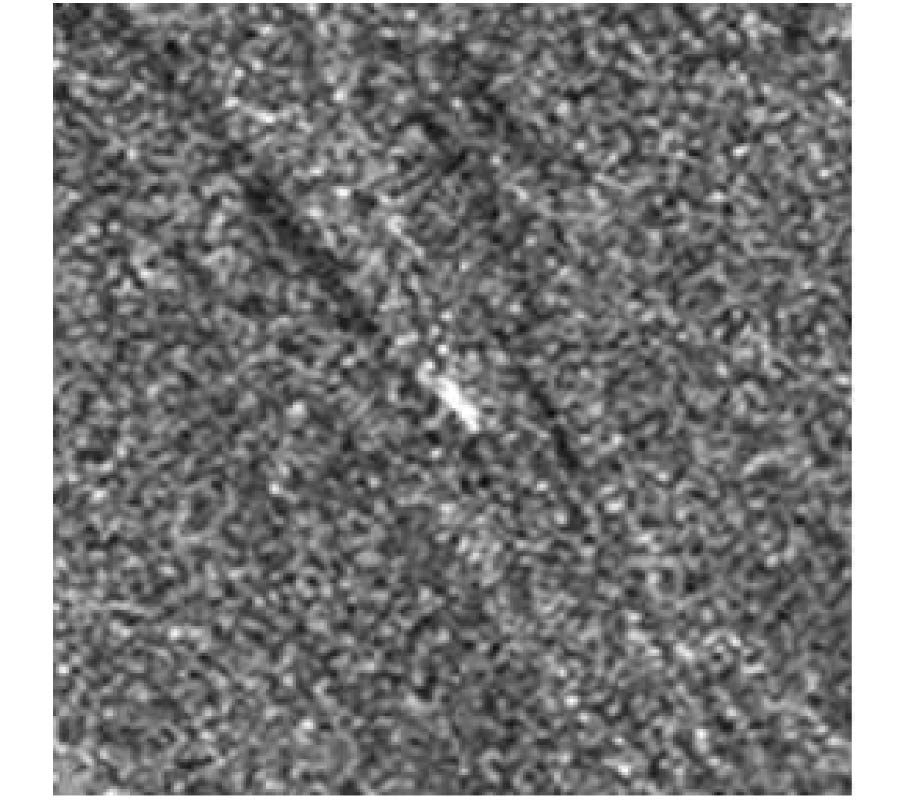
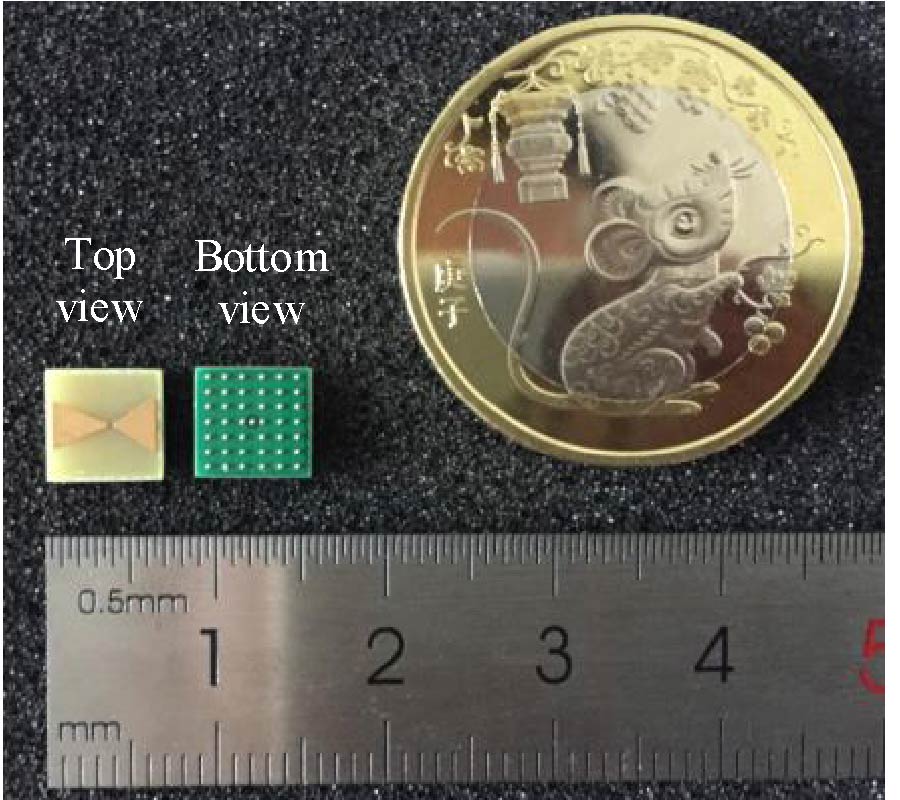
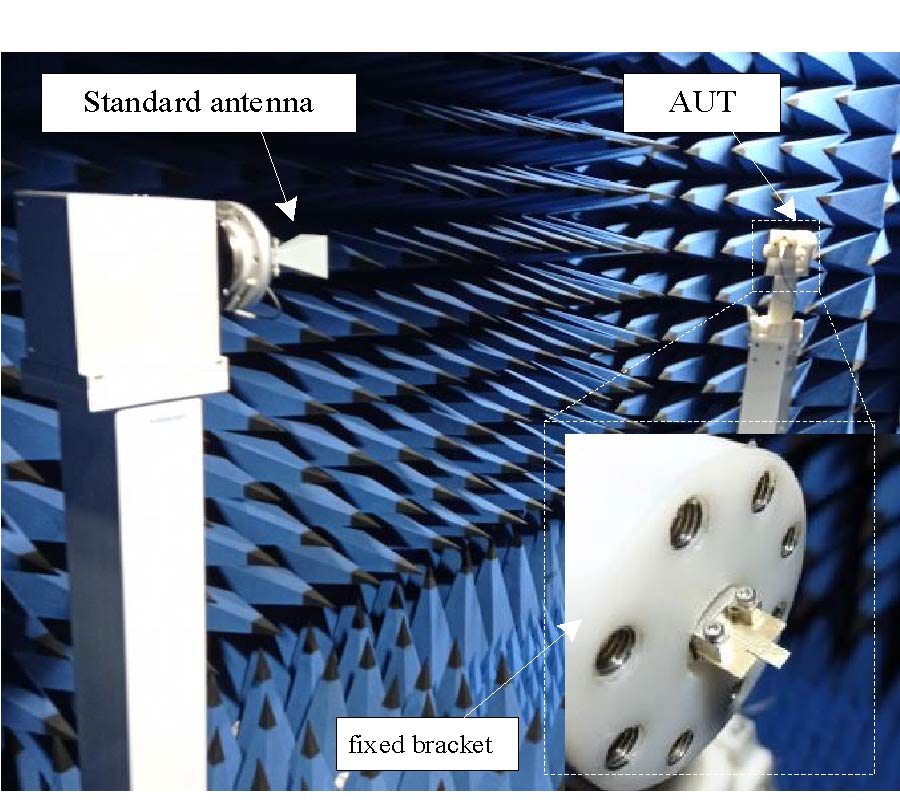
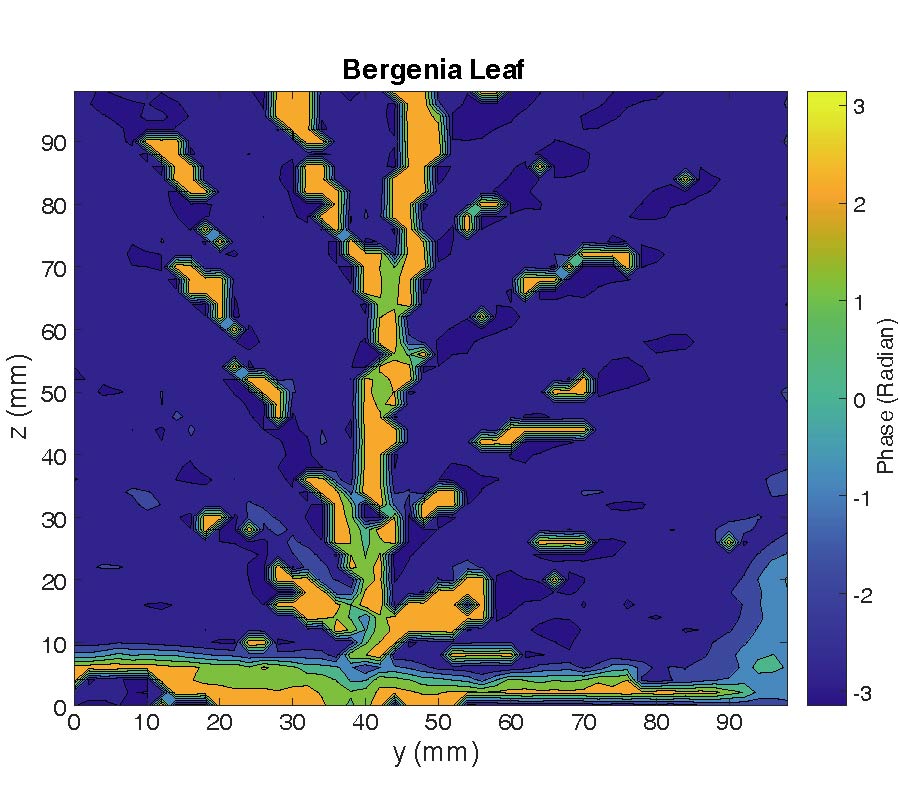
We demonstrate that the future sixth generation (6G) radio links can be utilized for sub-THz frequency imaging using narrow beamwidth, high gain, lens antennas. Two different lenses, a bullet or hemispherical shape, were used in radio link setup (220-380 GHz) for an imaging application. Lenses performed with the gain of 28 dBi, 25 dBi, and narrowed the beamwidths of 1° and 2.5°. Plants were used as imaging objects, and their impacts on radio beams were studied. For assessment, the radio link path loss parameter was -48.5 dB, -53.2 dB, and -57.1 dB with the frequency 220 GHz, 300 GHz, and 330 GHz, respectively. Also, the impact of the radio link distance on the imaging was studied by 50 cm and 2 m link distances. In addition, the 3D image was acquired using the phase component of the image, and it showed the leaf surface roughness and the thickness, which was similar to the measured value.