EM Full-Wave Analysis and Testing of Novel Quasi-Elliptic Microstrip Filters for Ultra Narrowband Filter Design
Zuhair Hejazi
,
Maximilian C. Scardelletti
,
Frederick W. Van Keuls
,
Amjad Omar
and
Ayman Sulaiman Al-Zayed
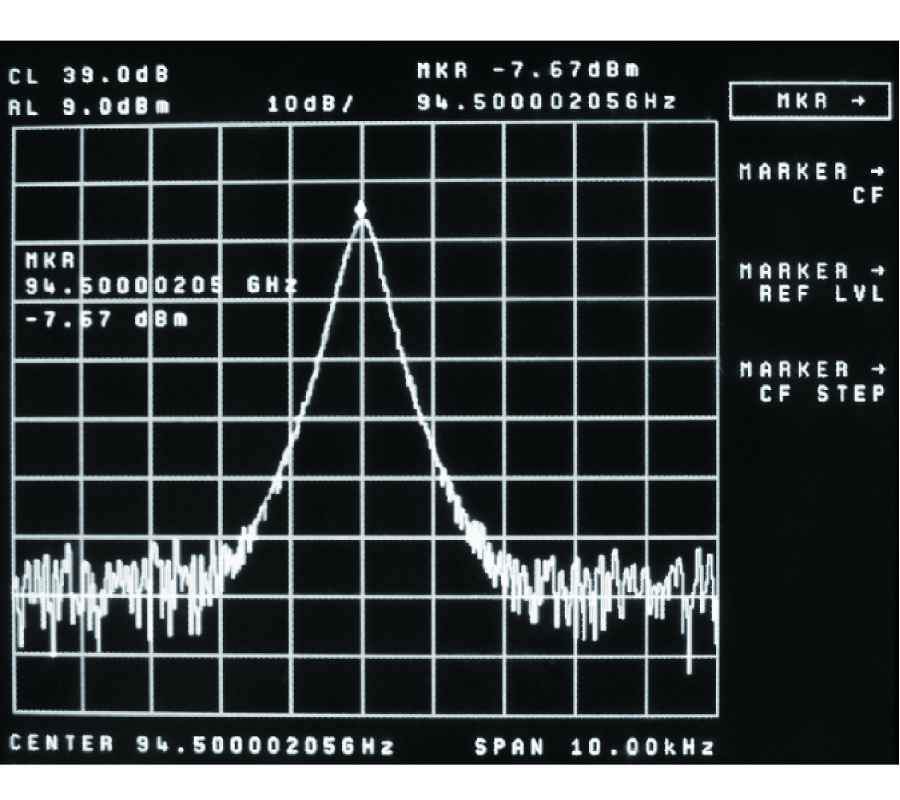
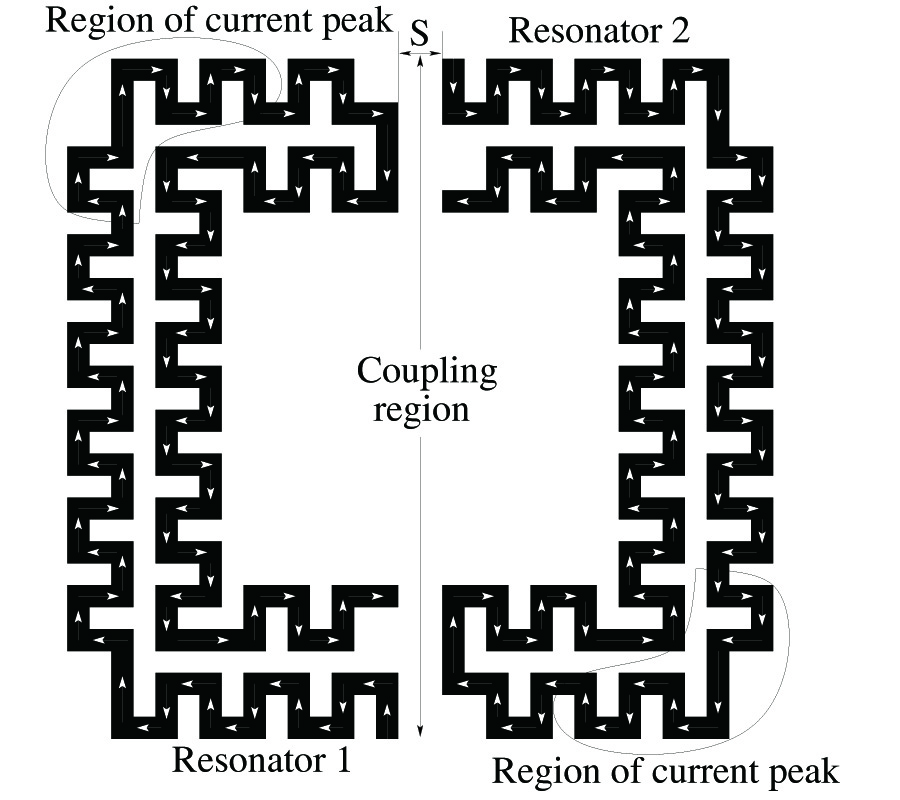
A new class of microstrip filter structures are designed, optimized, simulated and measured for ultra-narrowband performance essential to the wireless industry applications. More accurate model of the coupling coefficient is outlined and tested for narrowband filter design. Two sample filters are fabricated and measured to verify the simulations and prove the concept. The idea behind the new designs is based on minimizing the parasitic couplings within the resonators and the inter-resonator coupling of adjacent resonators. A reduction of the overall coupling coefficient is achieved even with less resonator separation which is a major issue for compactness of such filters. The best new designs showed a simulated fractional bandwidth (FBW) of 0.05% and 0.02% with separations of S = 0.63 mm and S = 0.45 mm, respectively. The measured filters tend to have even narrower FBW than the simulated, though its insertion loss deteriorates, possibly due to mismatch at the interface with external circuitry and poor shielding effect of the test platform. The investigated 2-pole filters are accommodated on a compact area of a nearly 0.6 cm2. An improvement of tens of times of order in narrowband performance is achieved compared to reported similar configuration filters and materials. A sharp selectivity and quasi-elliptic response are also demonstrated with good agreement in both simulations and measurements. In all filters, however, the study shows that the narrower the FBW, the larger the insertion loss (IL) and the worse the return loss (RL). This is confirmed by measurements.