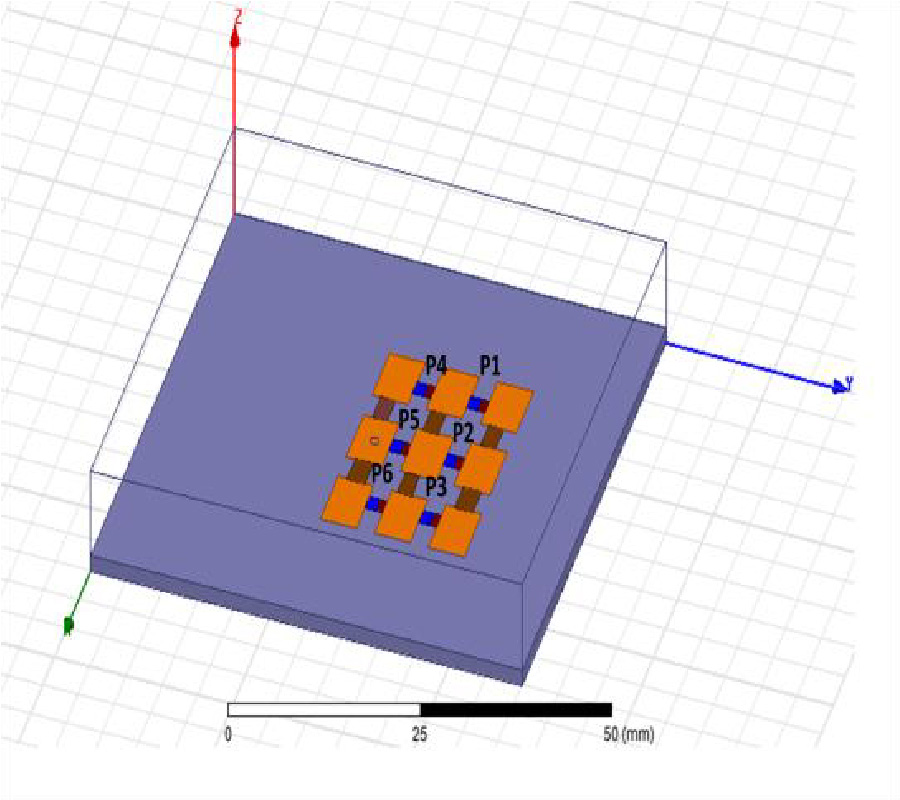
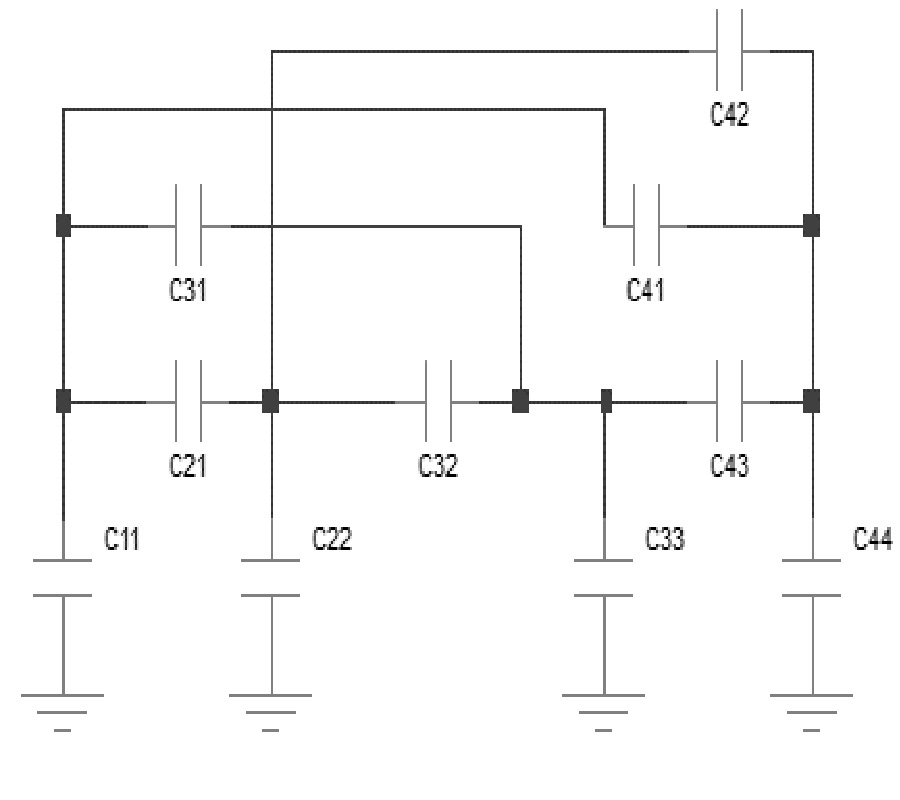
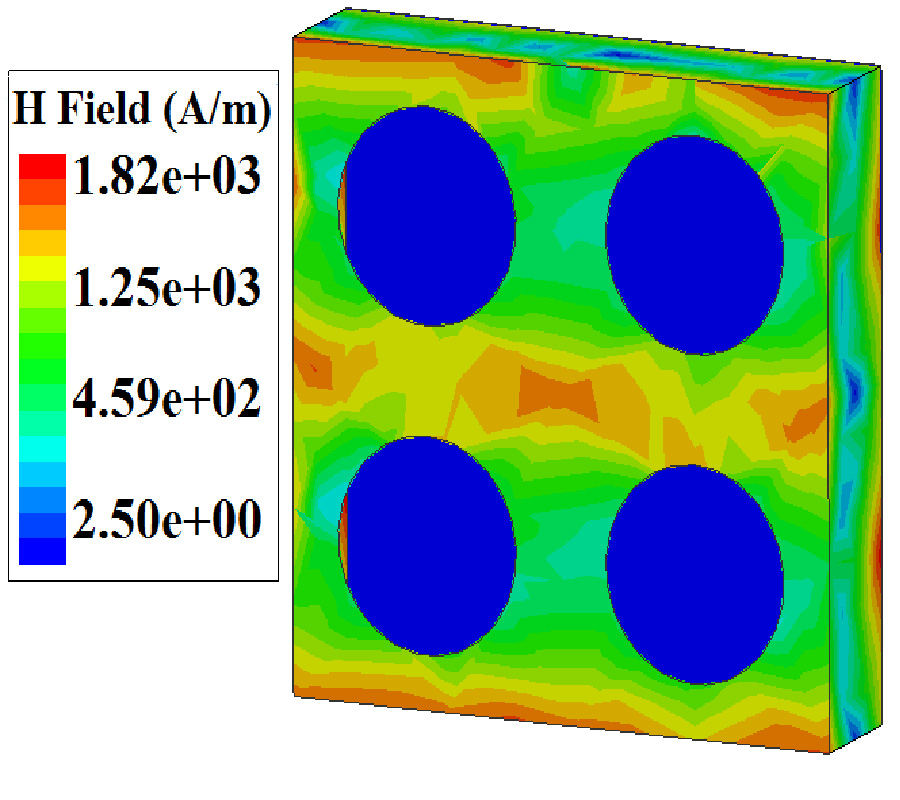
A Compact Microstrip Triplexer with a Novel Structure Using Patch and Spiral Cells for Wireless Communication Applications
Abbas Rezaei
,
Salah Yahya
,
Saman Moradi
and
Mohd Haizal Jamaluddin
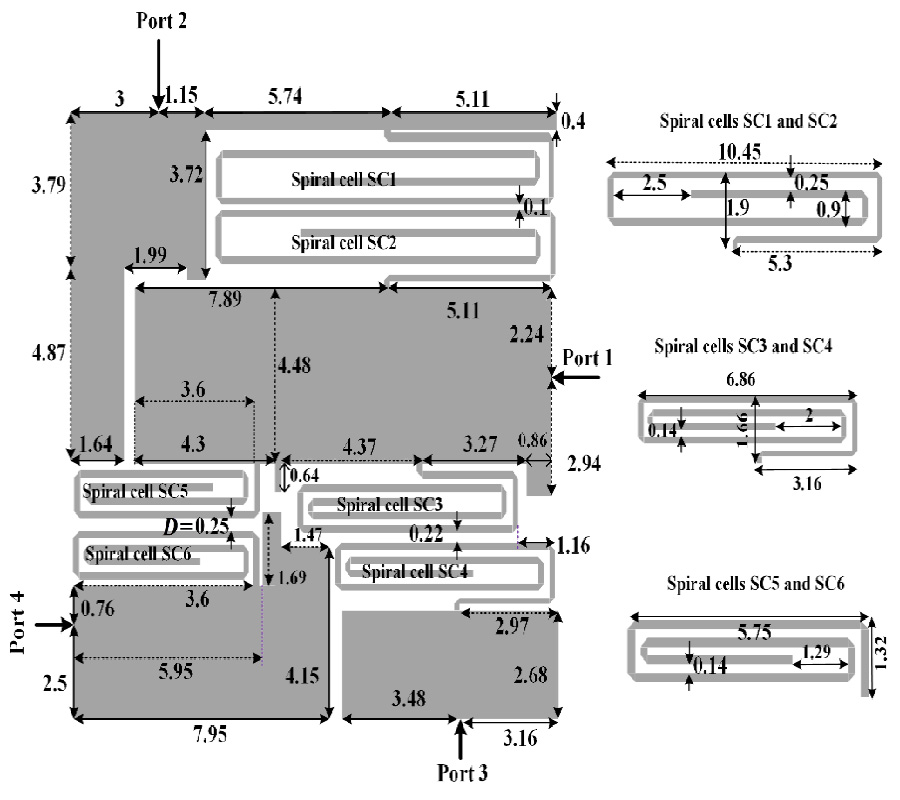
In this work, a novel planar four-port microstrip triplexer is designed and analyzed to operate at 1.9 GHz, 2.5 GHz, and 3.35 GHz for wireless communication applications. The proposed structure consists of a compact patch and spiral cells. The main advantage of this triplexer is its very compact size, with a cross size of only 15 mm×15 mm (0.017λg2). Sharp frequency response at the edges of all passbands, low insertion losses (0.25 dB, 0.4 dB and 0.11 dB), and high return losses (45 dB, 54 dB and 40 dB) in all channels are the other advantages of the designed triplexer. Additionally, the triplexer has reasonable isolations (S23, S24, S34), better than 20 dB. To verify the design method, both EM simulation and measurement results are obtained. The comparison shows that the measured and simulated results are in good agreement, which proves the feasibility of this work.