A Flexible Foldable Broadband Metamaterial Absorber Fabricated by Intaglio Printing Technology
Ye Dong
,
Zhangyou Yang
,
Siqi Zhang
,
Rongrong Zhu
,
Bin Zheng
and
Huan Lu
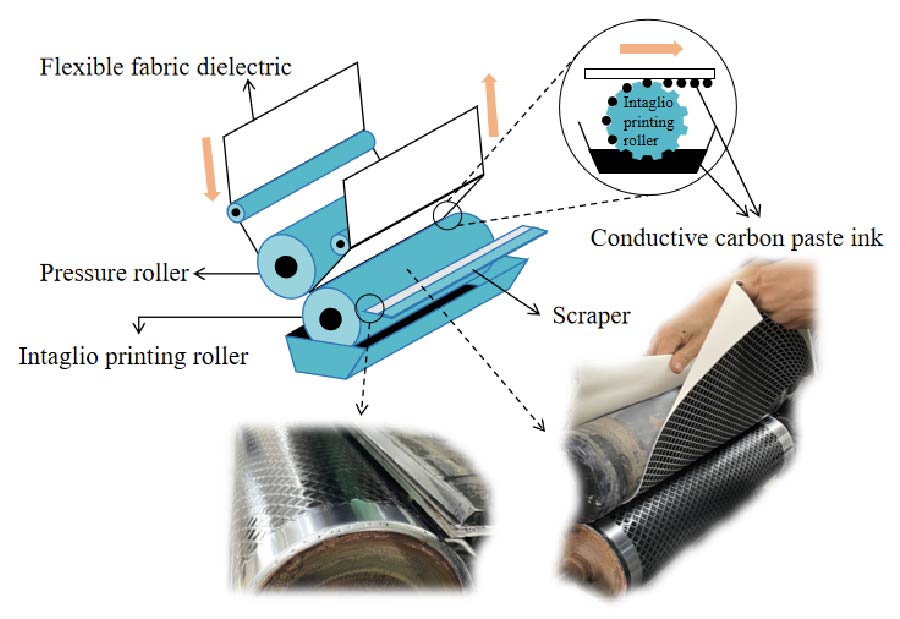
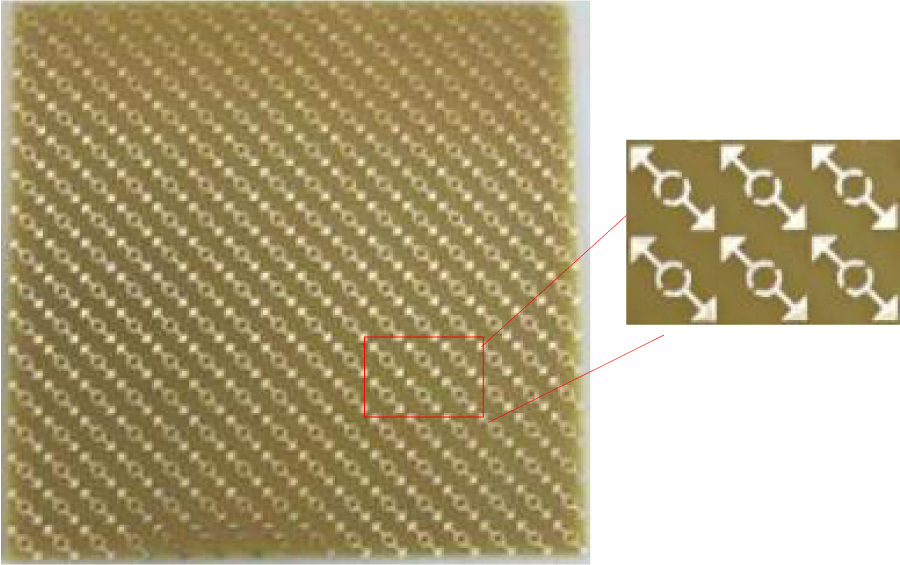
Absorbing materials can absorb incident electromagnetic waves effectively and have important research value in radar fields. However, the current absorbing materials are mostly affected by the thickness and flexibility of the dielectric substrate, and they have shortcomings such as being not thin, not flexible, not folding, and not conformal with the protection target, which is not conducive to practical application. In this paper, we propose a flexible absorbing material that can be folded freely for wearable and practical engineering applications, which is composed of a conductive carbon paste ink resistance film layer, a flexible fabric dielectric substrate and a metal backplane. When the incidence angle is less than 30°, more than 90% absorption performance can be achieved at the operating frequency of 9.5-11.5 GHz with polarization insensitive characteristics. Simulated and experimental results prove the effectiveness of the structure. Our work provides the groundwork for the commercialization of future meta-devices such as wearable invisibility cloaks, sensors, optical filters/switchers, photodetectors, and energy converters.