2021-03-18 Latest Published
By Amandeep Kaur
Praveen Kumar Malik
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 91, 157-173, 2021
Abstract
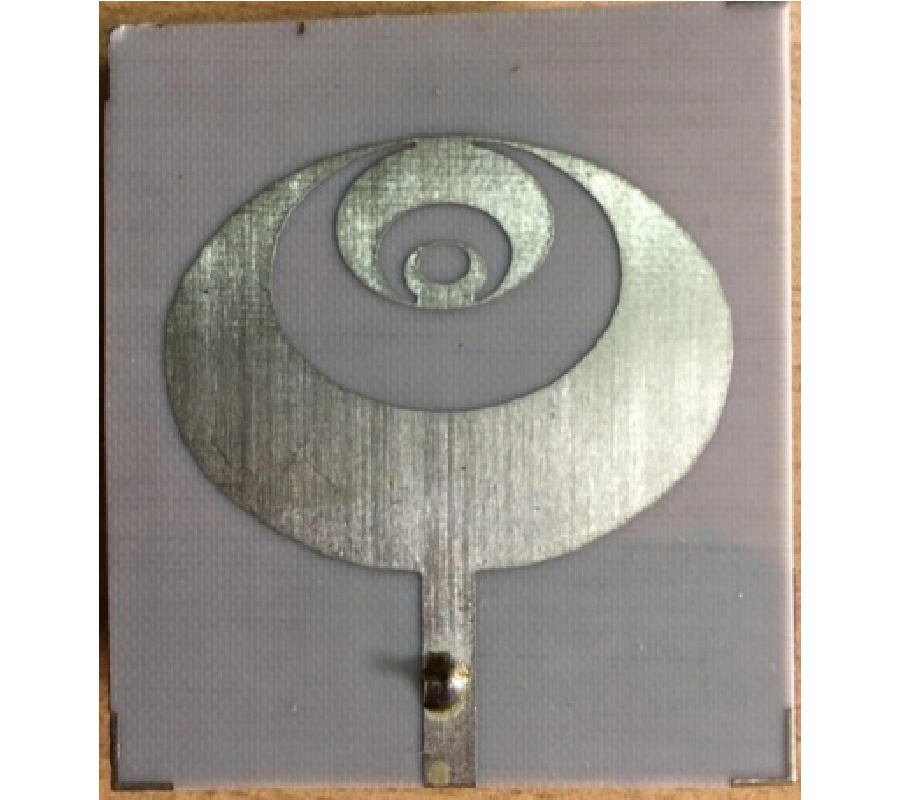
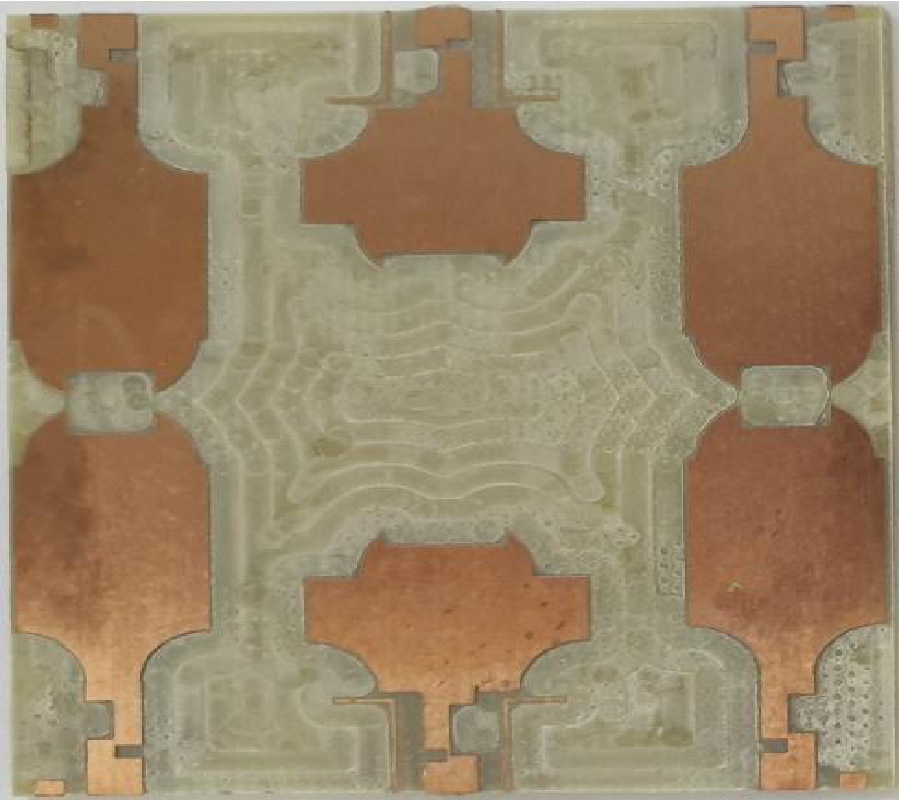
A multiband microstrip antenna is designed for wireless communication application with fractal and defected ground structures. Antenna prototype is fabricated using Rogers RT Duroid 5880 dielectric material on a double layer PCB with dielectric constant 2.2 and thickness 0.8 mm. Through implementing the concept of elliptical shape fractal geometry to microstrip patch antenna, more miniaturization is achieved. Further with defected ground structures, wide impedance bandwidth and gain are achieved. A compact microstrip feedline is used to couple electromagnetic energy to radiator through lumped port. Proposed antenna shows multiband characteristics. Antenna resonates at 2.6 GHz, 6 GHz and 8.2 GHz frequency bands with impedance bandwidth of 410 MHz, 1070 MHz and 4840 MHz. Experimental validation is done to validate simulation results. Antenna operates on different wireless standards like Wi-Fi (2.4 GHz), WLAN (2.4/5.2/5.8 GHz), Wireless Body Area Network (2.3/2.4 GHz), which falls under ISM (Industrial Scientific and Medical) band applications. It also covers communication bands, X-band (8-12 GHz) and S-band (2.3-2.4 GHz).