Design of Cartesian Feedback RF Power Amplifier for L-Band Frequency Range
Mandeep Singh,
Anand Lokesh,
Syed Idris Syed Hassan,
mohd Mahmud and
Mohd Fadzil Ain
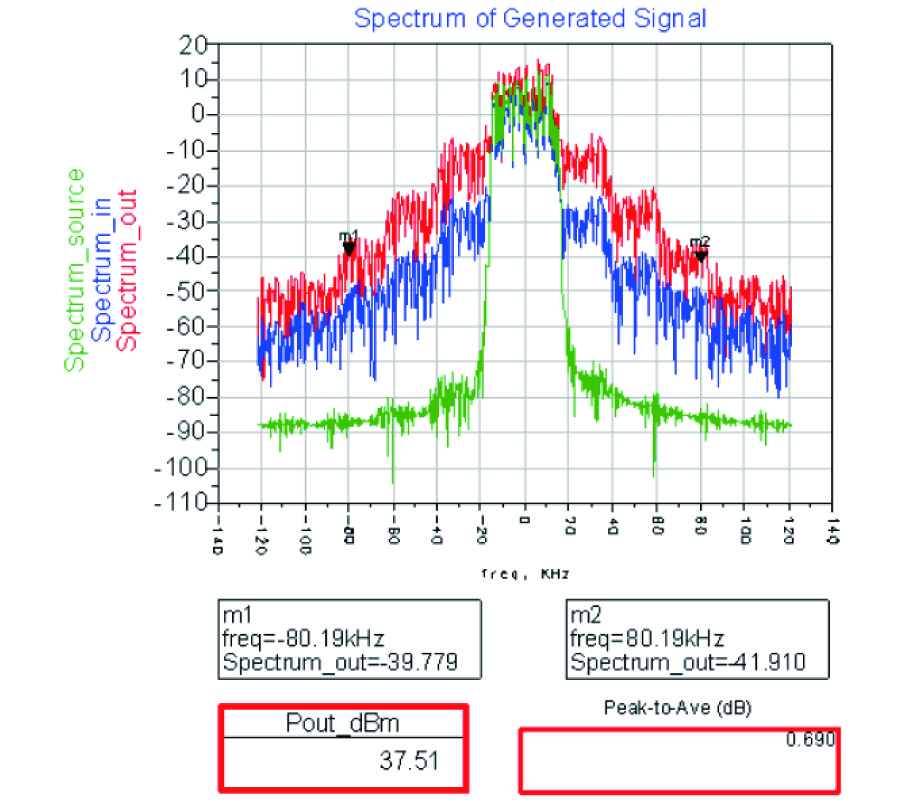
A phase-alignment system is used fully integrate a power amplifier, Cartesian feedback linearization circuitry, and a phasealignment system. The phase-alignment system employs a new technique for offset-free analog multiplication that enables it to function without manual trimming. This paper demonstrates how the phase-alignment system improves the stability margins of the fully integrated Cartesian feedback system. The power amplifier itself, integrated on the same die, operates at 1 GHz and delivers a maximum of 30 dBm of output power into a 50-load. The class AB design for open loop and close loop power amplifier with Cartesian feedback, demonstrated a good linearity of 50 dBc and 80 dBc, respectively. The operating power is 2 W at 1000 MHz frequency.