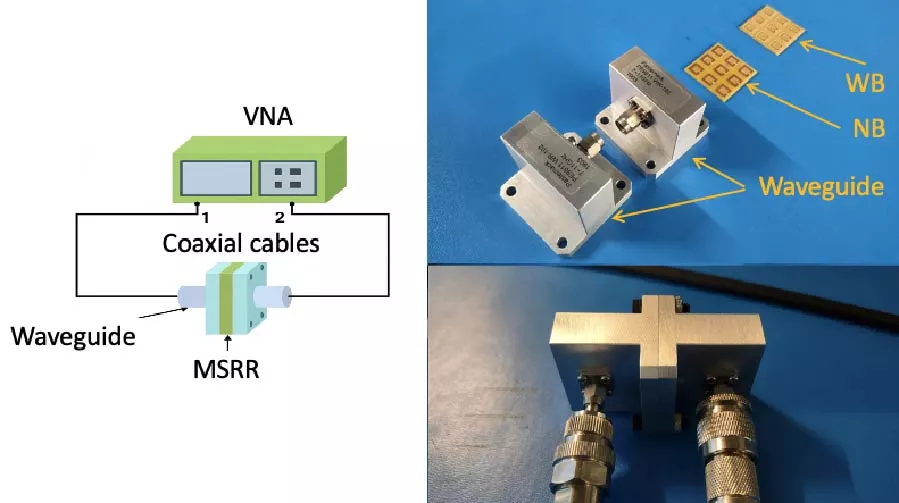
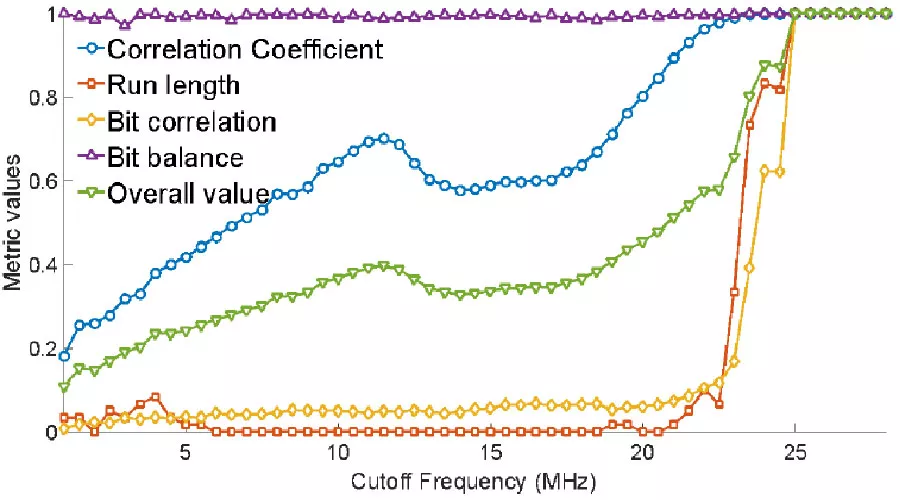
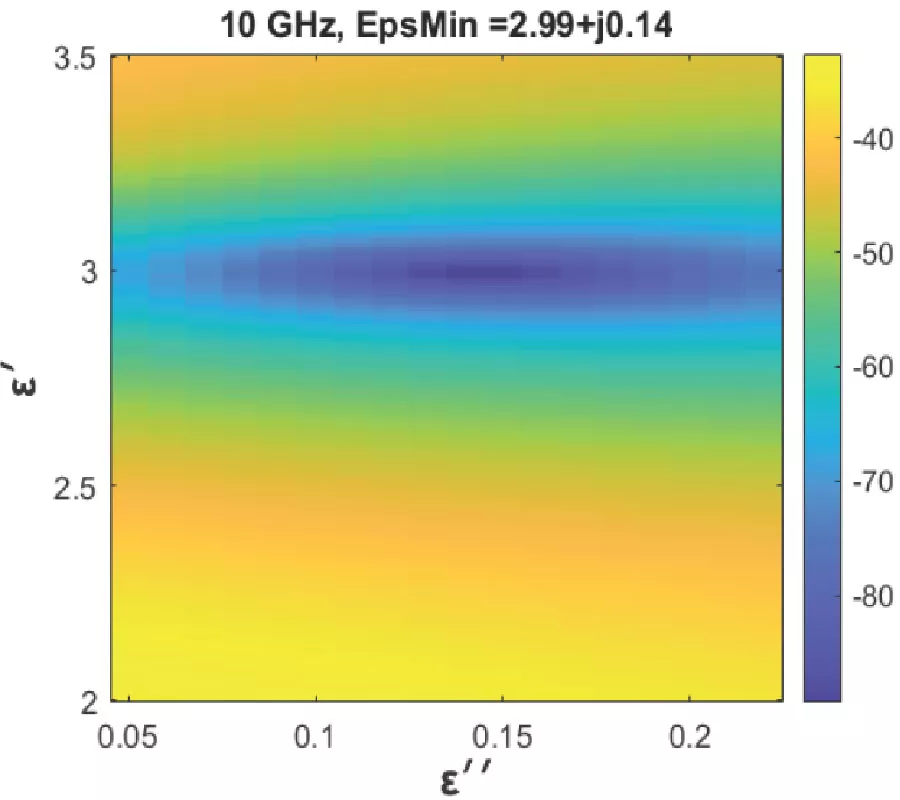
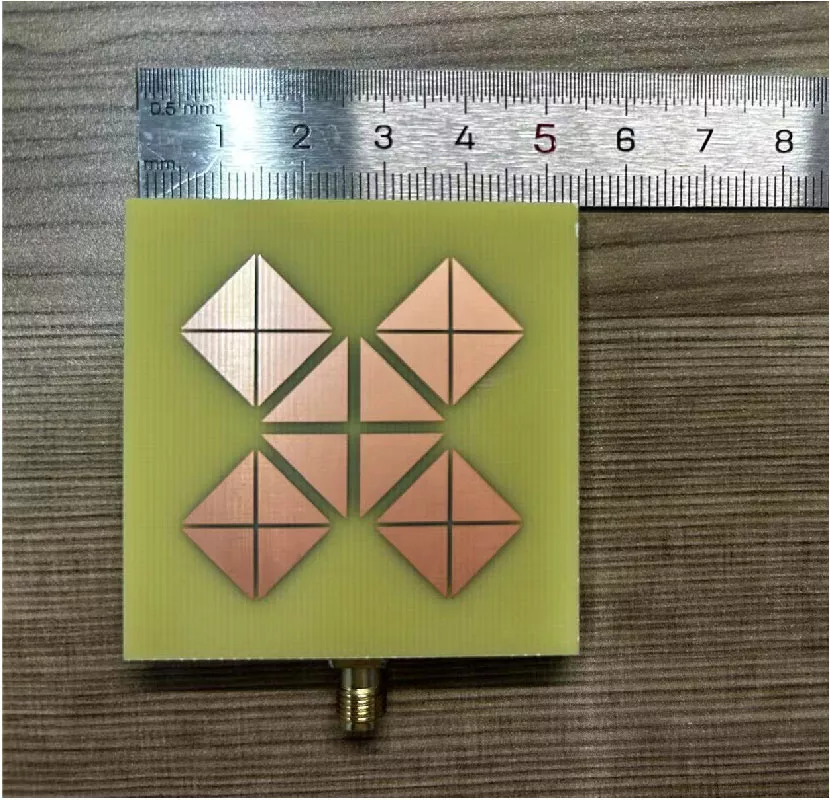
Improving Gain-Bandwidth Product of Modified Split Ring Resonators for 6G Wireless Networks
Al-Moatasem Al-Hinaai,
Anthony N. Caruso,
Travis D. Fields,
Mohamed Z. M. Hamdalla and
Kalyan C. Durbhakula
Metamaterials are emerging as a key enabler for 6G wireless communications, attracting growing attention from industry due to their engineered electromagnetic properties that enable control over wave propagation. Metamaterials have shown promise across diverse applications; however, the desire to achieve 1 TBPS data rates in 6G communications is partially constrained by a major fundamental challenge in metamaterials: achieving gigahertz of instantaneous bandwidth (IBW) values. To address the IBW issue, we designed, fabricated, and tested a fundamental component of metamaterial, i.e., a modified split ring resonator (MSRR), achieving 90% of the targeted 1 GHz IBW and an effective permeability (μeff) close to 25 within the IBW. In addition, the gain-bandwidth product (GBWP) is over 1.5× greater than that of commercial 5G antennas, while maintaining the same aperture size of 1.59λc. We studied and reported the effect of MSRR frequency-dependent μeff on the IBW and GBWP and proposed an optimized MSRR design that achieves 3× the bandwidth of a conventional SRR. Finally, we integrated the proposed MSRR atop a wideband patch antenna, enhancing peak realized gain by 6 dBi.