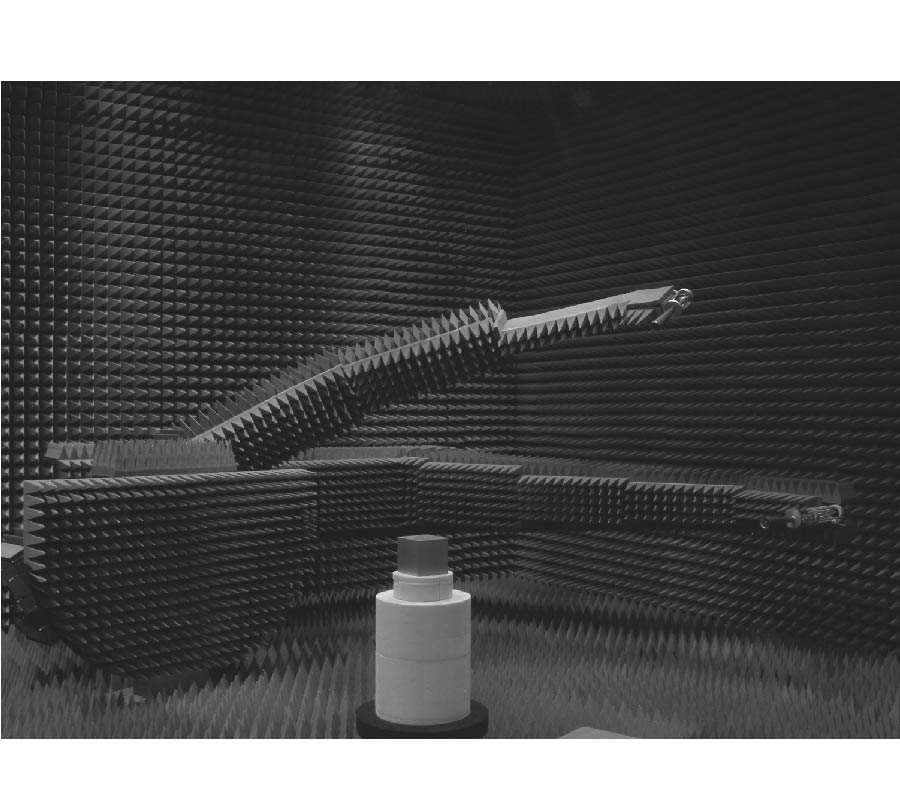
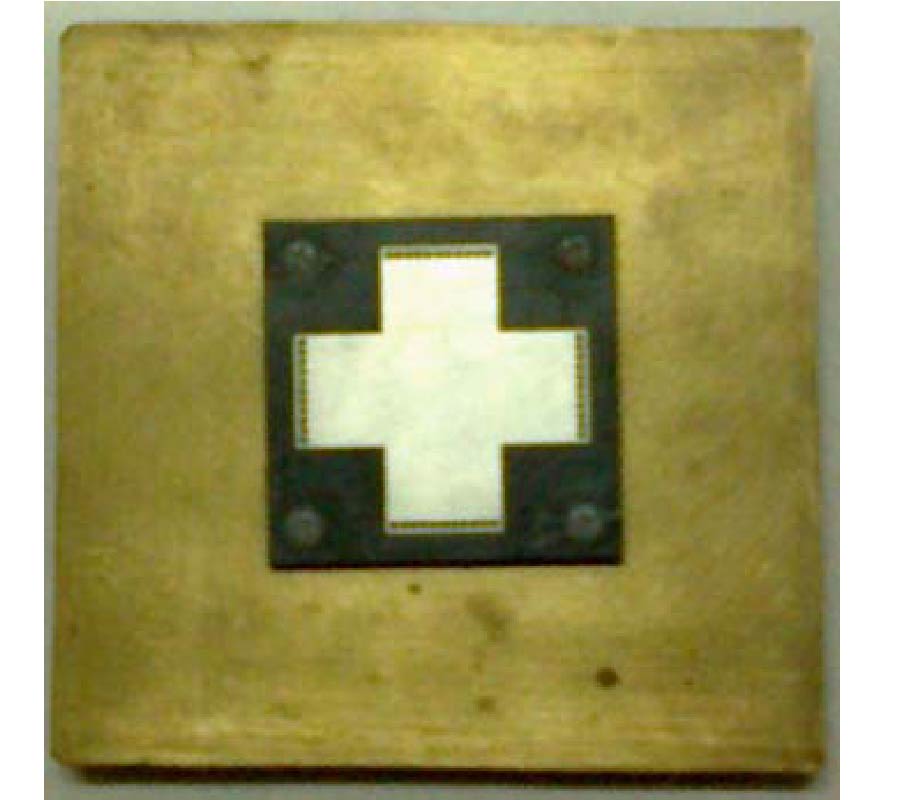
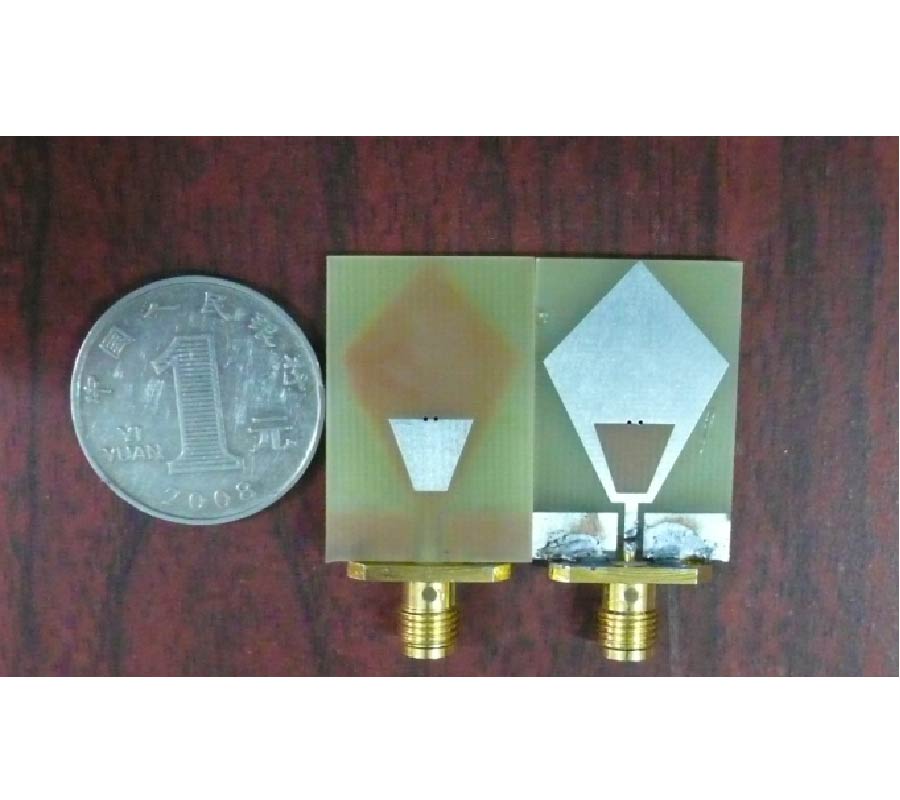
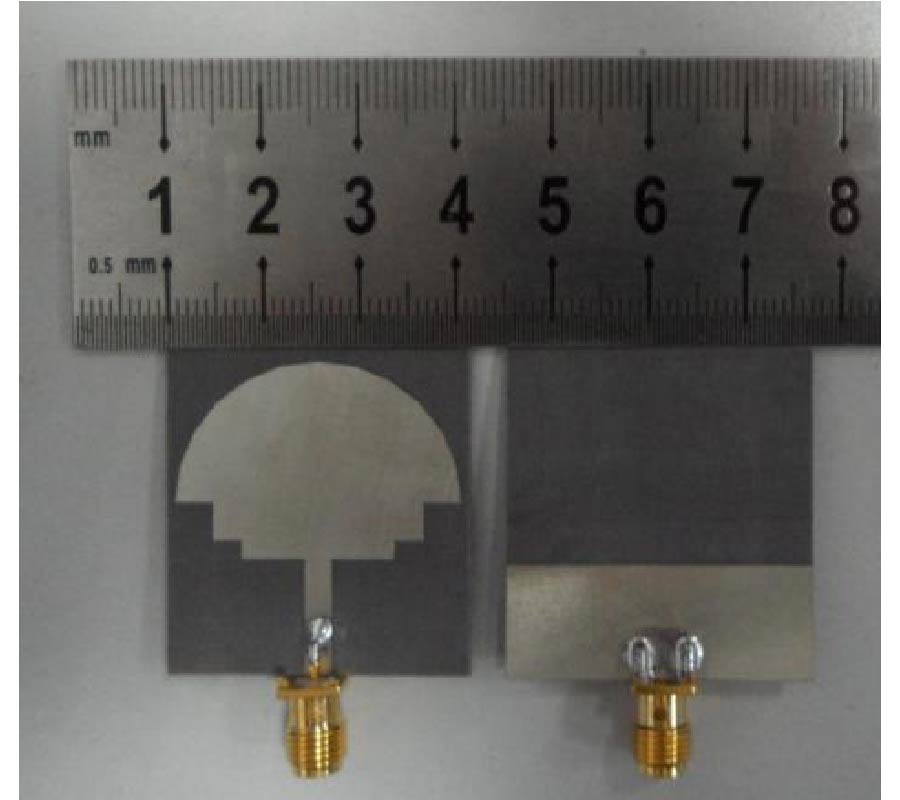
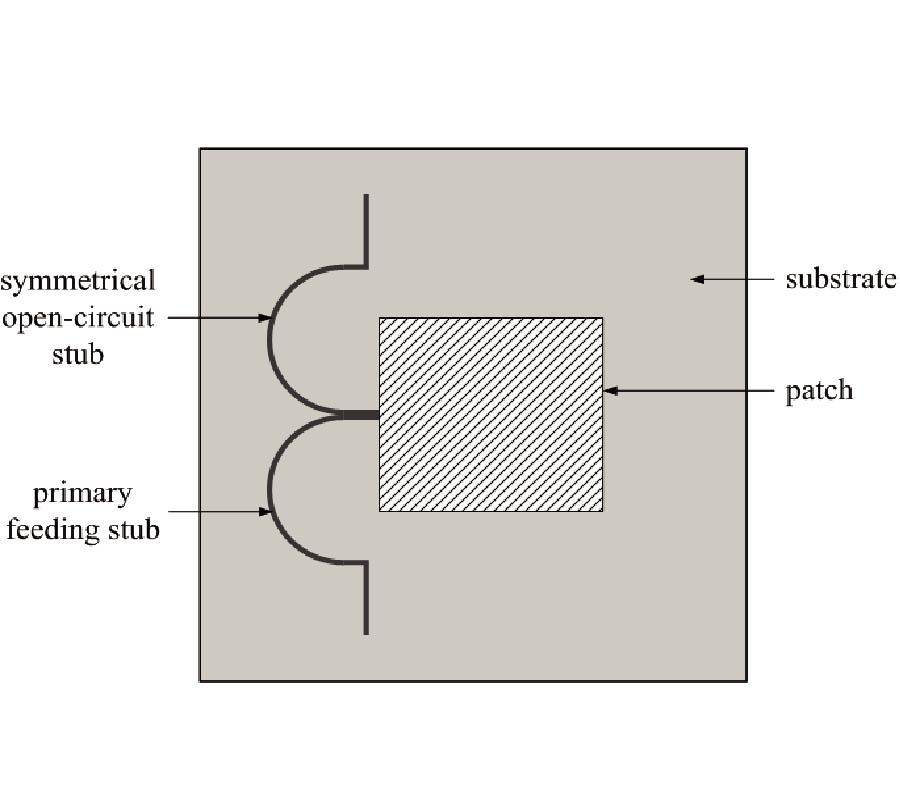
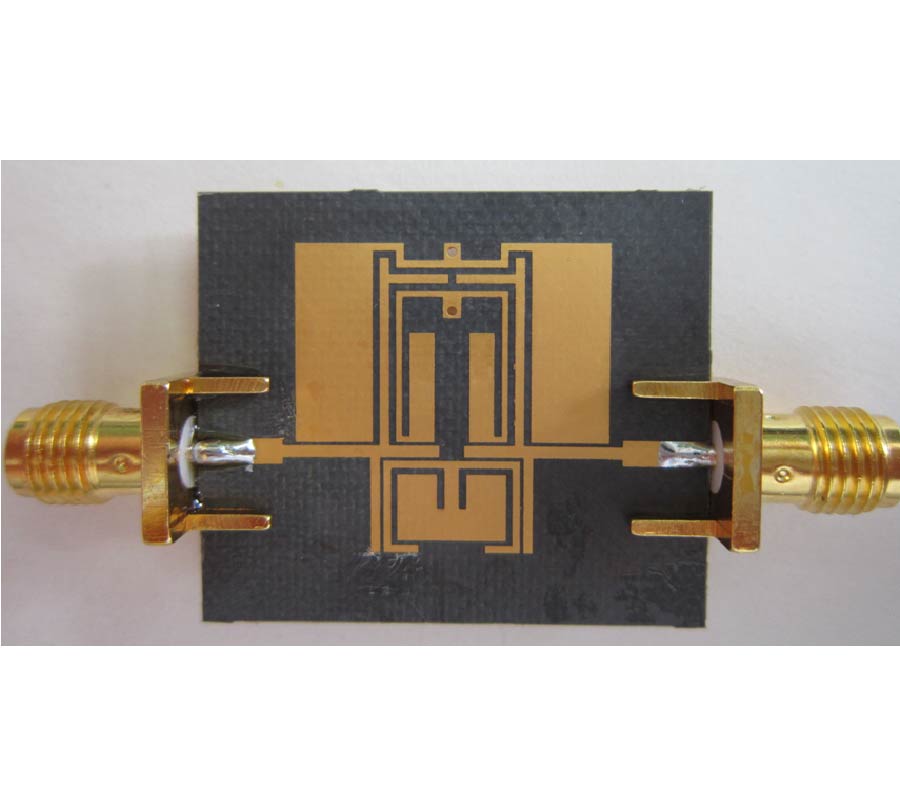
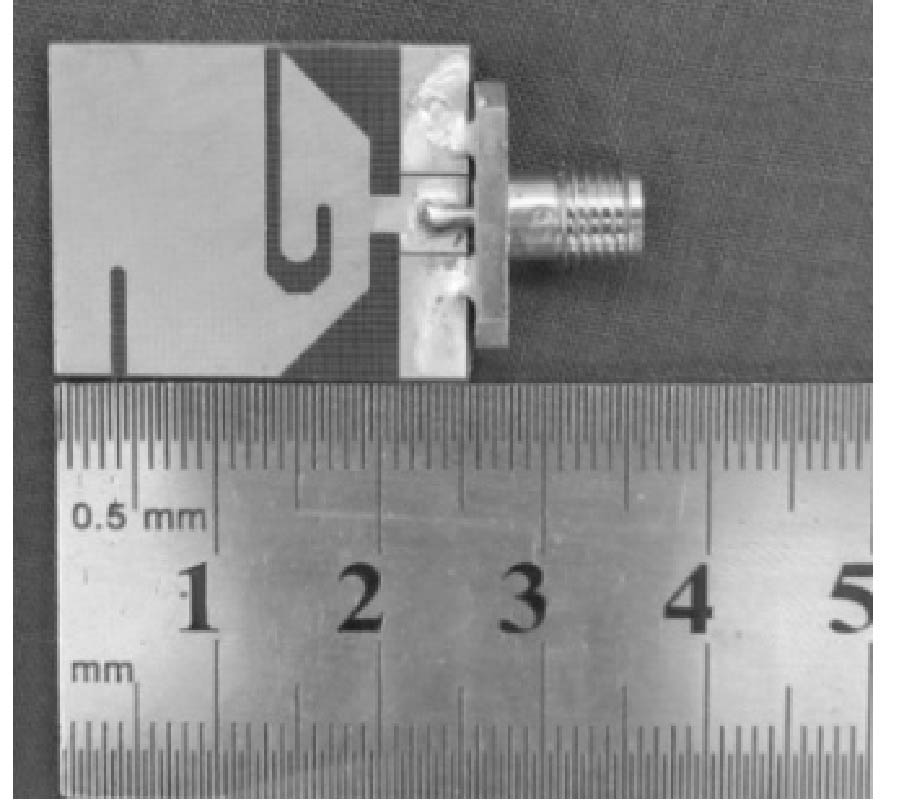
RCS Reduction for a FSS-Backed Reflectarray Using a Ring Element
Li-Shi Ren,
Yong-Chang Jiao,
Jin-Juan Zhao and
Fan Li
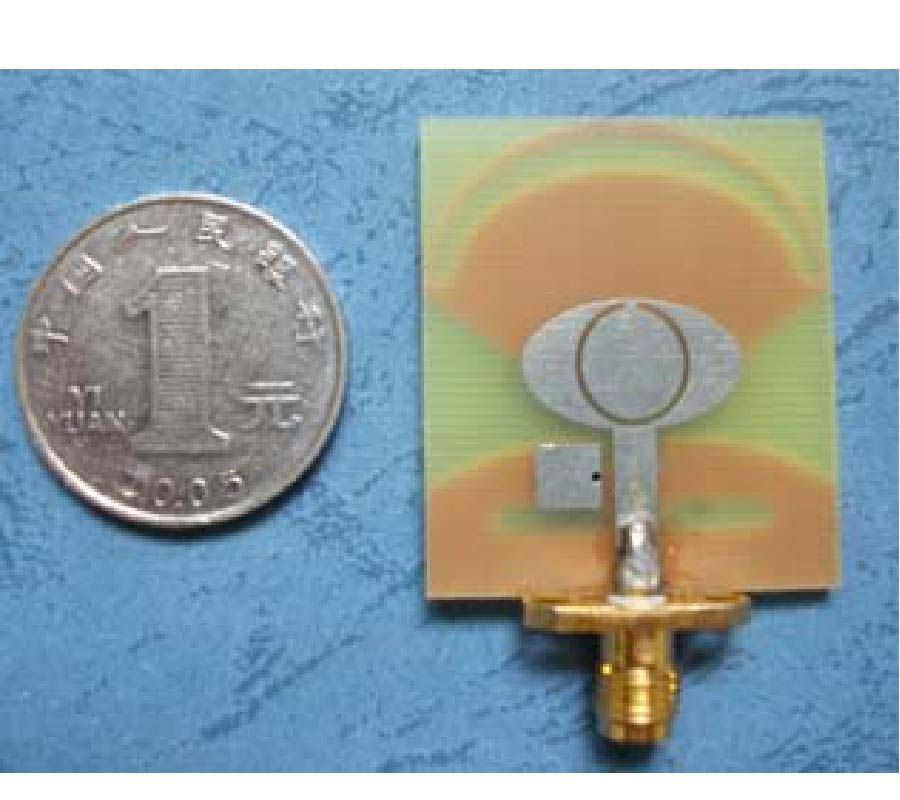
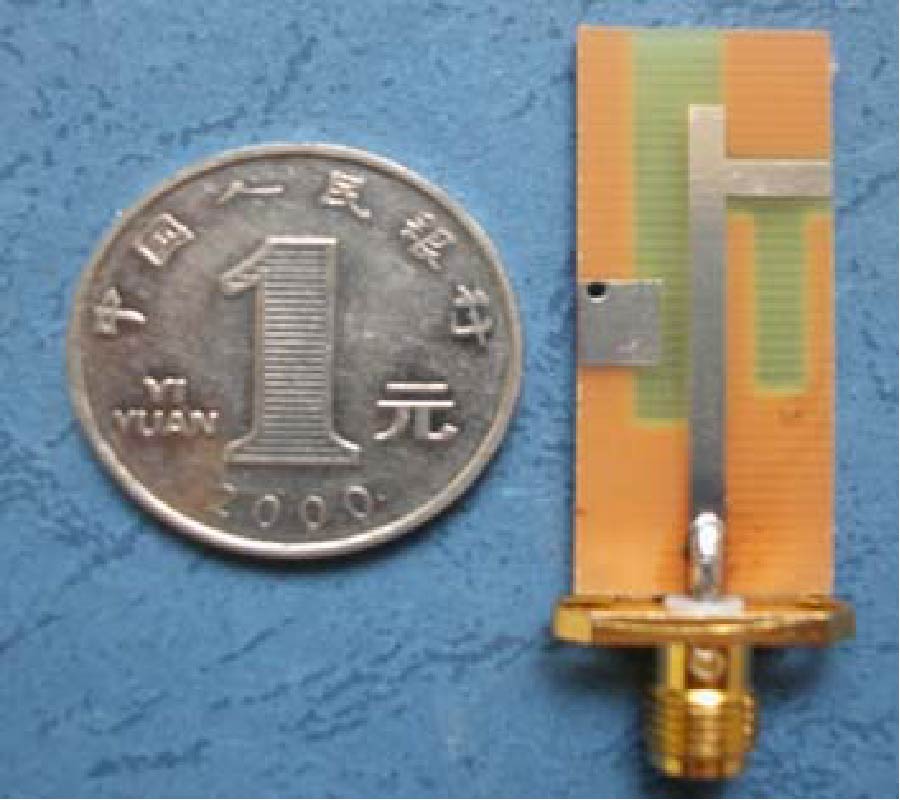
A novel RCS (radar cross section) reduction configuration for a reflectarray antenna, employing the appropriate FSS (frequency-selective surface) as a ground, is proposed. The performance of a reflectarray element backed either by a solid metal ground plane or a frequency-selective surface is compared. To optimize the performance of the designed frequency-selective surface, a parametric study is carried out using Ansoft HFSS. Then, a prime-focus FSS-backed reflectarray is fabricated and tested. The measurements demonstrate that the gain of a FSS-backed reflectarray is about 0.5 dB lower than its counterpart backed by a solid ground plane. The RCS is nearly the same at the operating band of 10 GHz, while out of this band the FSS-backed reflectarray reduces the RCS strongly, especially at 1 GHz with the reduction up to 20 dB. Compared with the RCS reductions obtained in the other papers, the FSS-backed reflectarray using a ring element can also obtain a good result.