Classification of Severe Bacterial Pneumonia Based on CT Images and Deep Learning
Ke Cui,
Dawei Gong,
Xiaobo Chen,
Youzu Xu,
Haiyan Li,
Yefei Zhu,
Julian Evans,
Xin Gong,
Zhenzhan Shi,
Yinghe Xu and
Sailing He
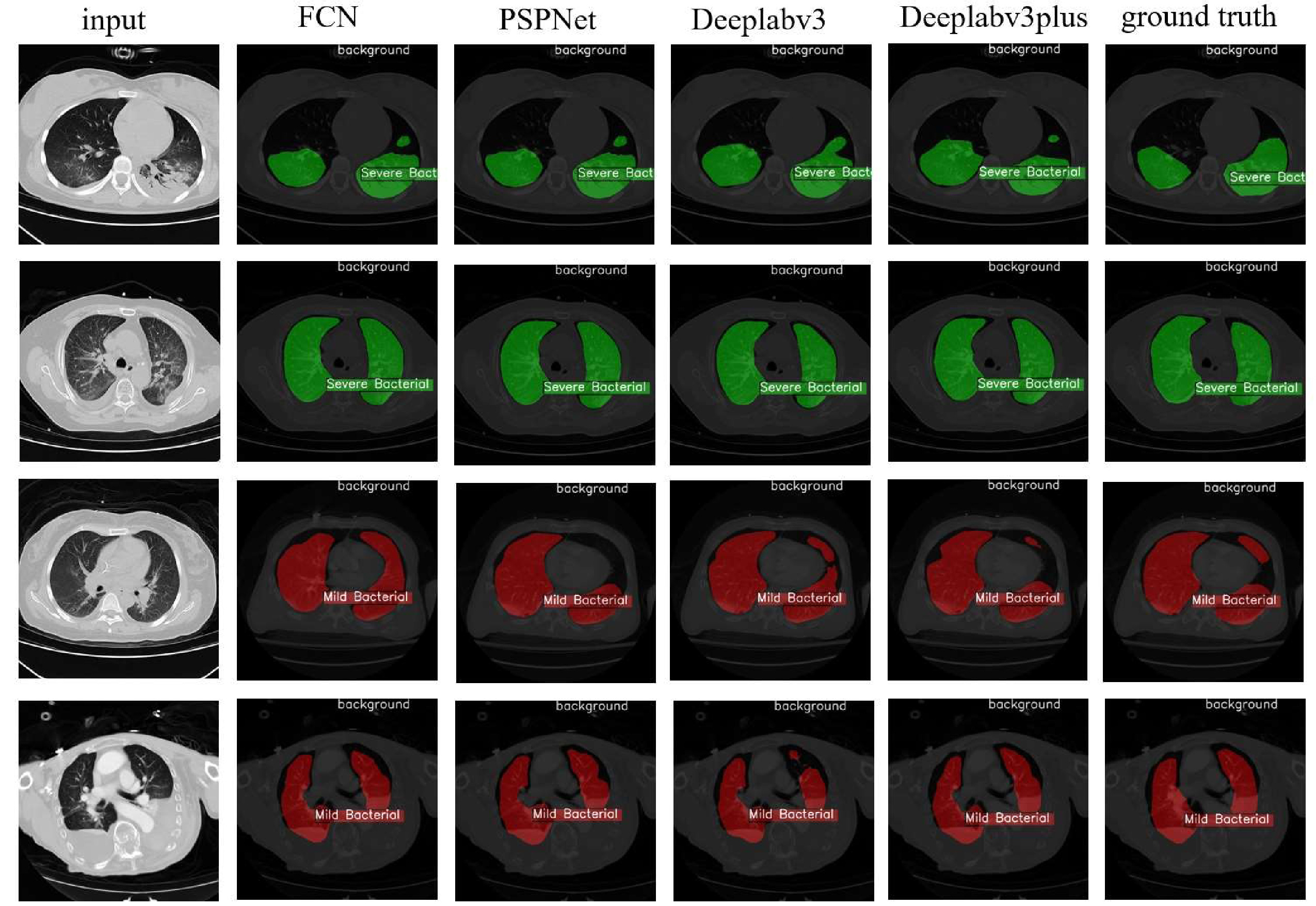
Severe bacterial pneumonia is a serious respiratory disease caused by bacteria, which is mainly transmitted through the respiratory tract. To achieve early recognition of severe pneumonia patients through images, this study collected the CT images of 180 patients diagnosed with bacterial infection in the lungs on the day of emergency admission to a large regional medical center (a Top-Tier (Grade 3 A) hospital). After classification by two deputy chief physicians of the respiratory department, 93 cases of severe bacterial infection were obtained and the rest 87 cases were identified as mild bacterial infection. The CT sequences were then preprocessed and annotated to obtain 599 images with annotated lung infection areas. Together with 107 normal (non-infected) images, these bacterial infection images were randomly divided into a training set of 447 and a test set of 259. In the experiment, four deep learning methods, namely, FCN, PSPNet, deeplabv3, and deeplabv3plus, were used for training and three-class classification (severe bacterial infection, mild bacterial infection, and normal). Deeplabv3plus showed the best performance, with an overall accuracy of 96.91% (including a sensitivity of 95.25%, a specificity of 97.24%, an accuracy of 86.96%, a recall rate of 95.24%, and an F1 score of 90.91%) for severe bacterial infection. Using deep learning technology to diagnose severe pneumonia as early as possible can produce valuable treatment time for patients, thereby significantly reducing mortality and complication rates.