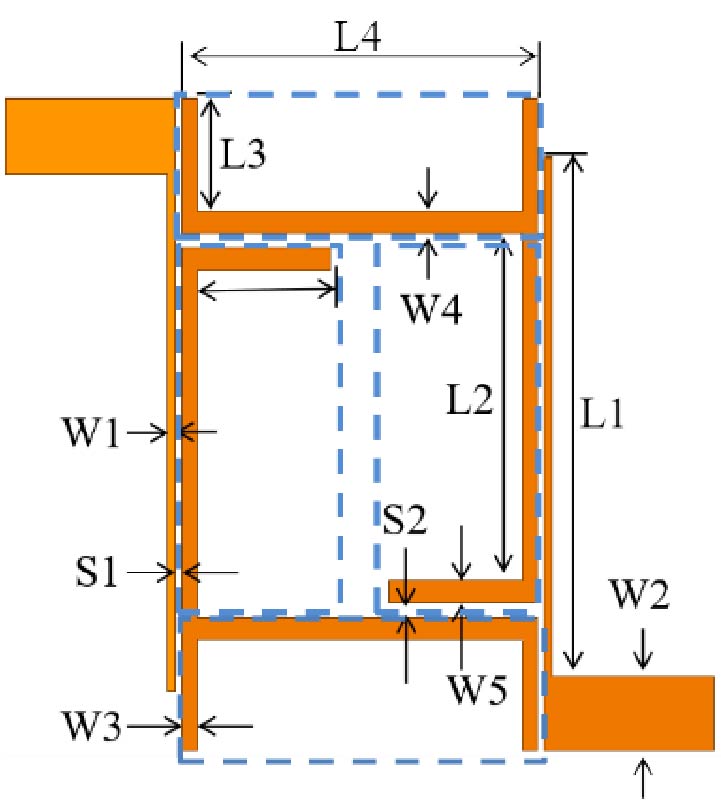
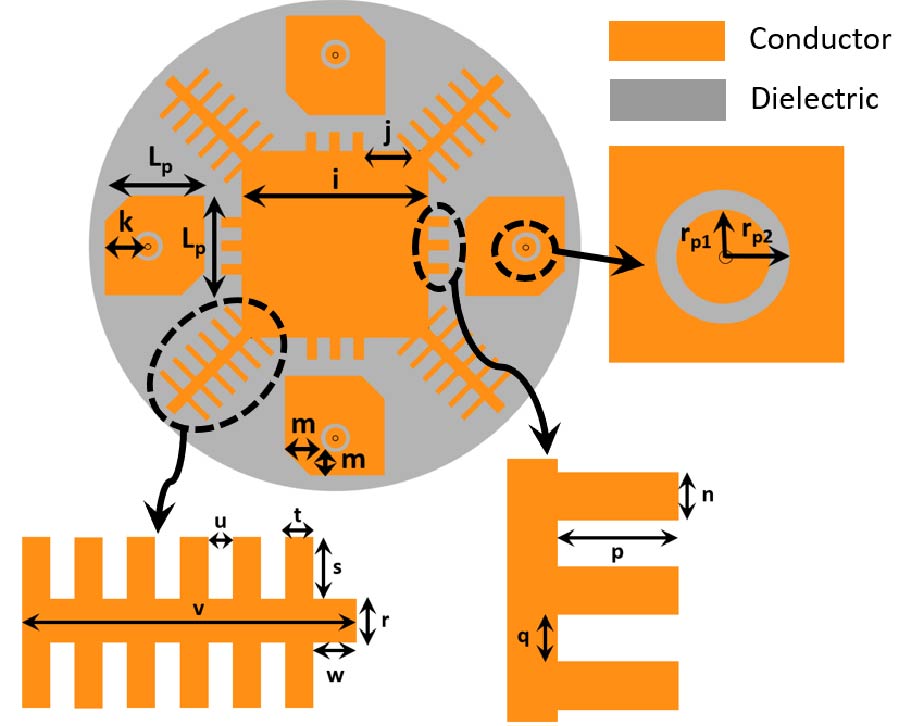
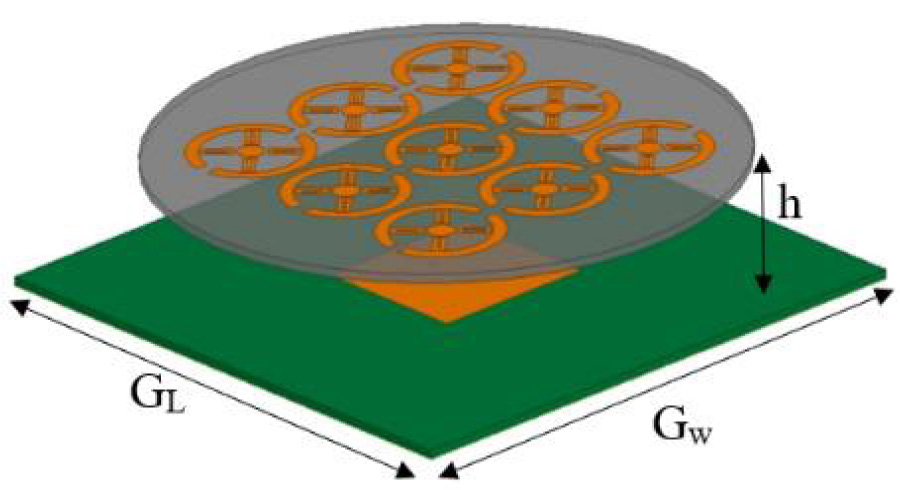
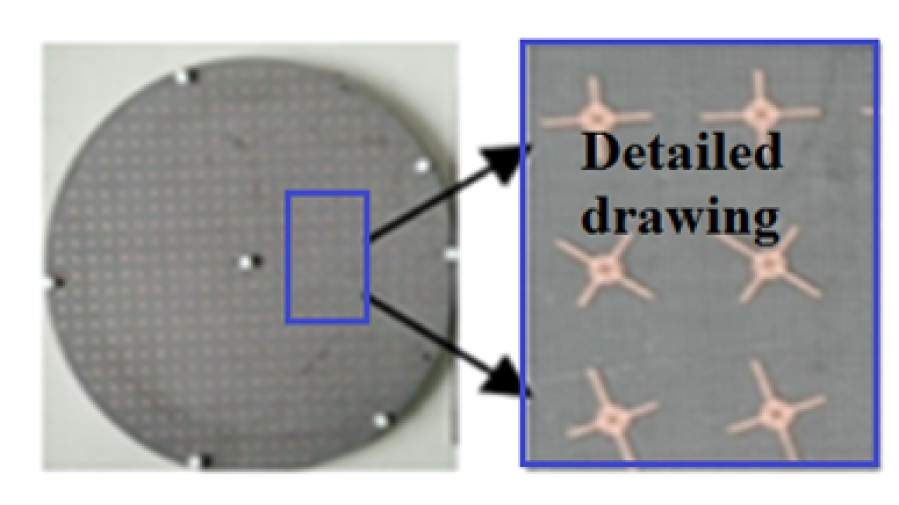
Wideband Multifunctional Bessel Beams by High Efficiency Spin-Decoupled Metasurface for Near Field Applications
Hui-Fen Huang and
Chu-Xin Zheng
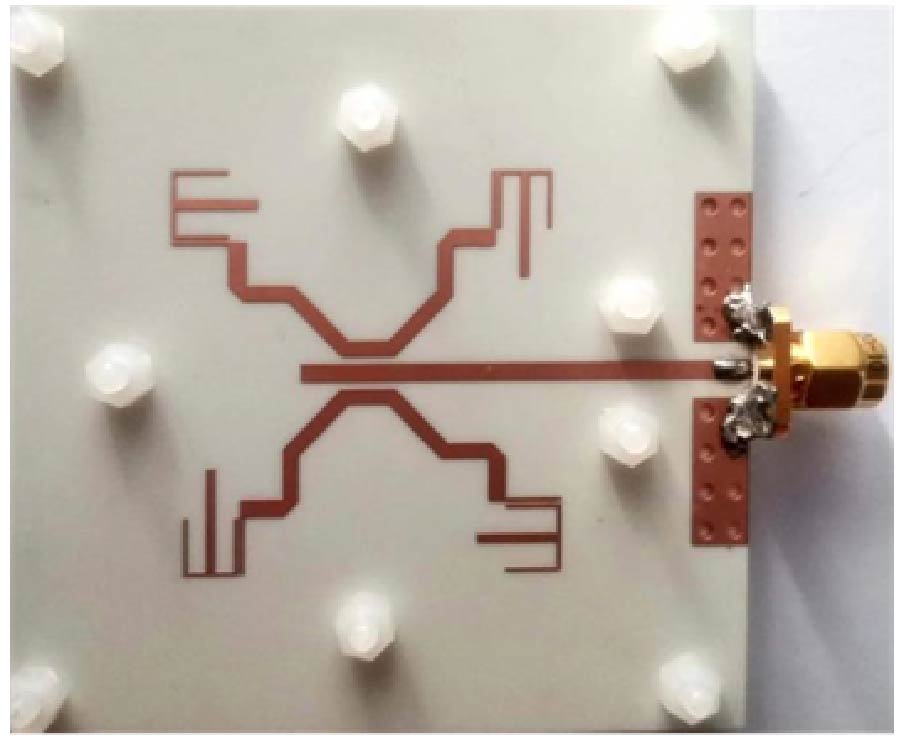
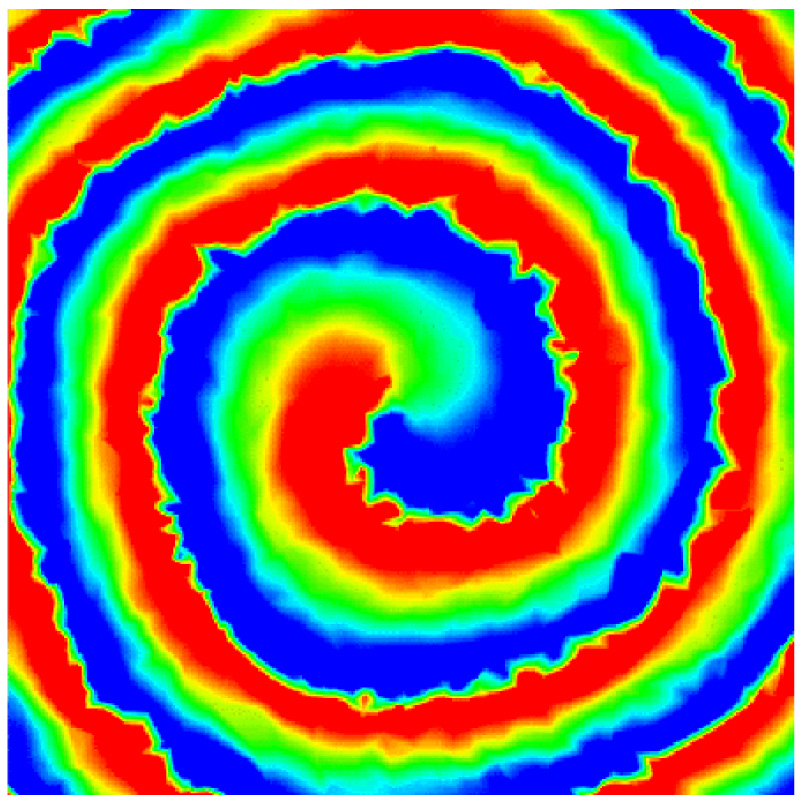
This paper develops a wideband spin-decoupled unit cell to form high efficiency wideband spin-decoupled metasurface (MTS), which can achieve more versatile Bessel beams with independent control of the beam direction, polarization and Orbital angular momentum (OAM) mode for near field applications. The MTS is designed for wideband dual Bessel beams: Beam-I (RHCP, θ1=30˚, φ1=180˚, l=1), Beam-II (LHCP, θ2=30˚, φ2=0˚, l=0), where φ and θ are the azimuth and elevation angles, respectively; l is the OAM mode; and RHCP(LHCP) represents the right (left) hand circular polarization. Compared with conventional phase gradient MTSs, the proposed MTS achieves more versatile functionalities and better performance: wideband (35.3%), dual Bessel beams, circular polarization (CP), high aperture efficiency (AE) 40%, carrying OAM modes, high ratio of non-diffraction distance/aperture size (6.41), high conversion efficiency for Bessel beams (33%), and high OAM purity (78%-99%). Simulated and measured results agree well, and validate the design method. The proposed unit cell can be used to design other high performance multifunctional Bessel beams. The designed Bessel beams have potential applications in dense channel high capacity communication, efficient wireless power transfer, high-resolution imaging, medical treatment.