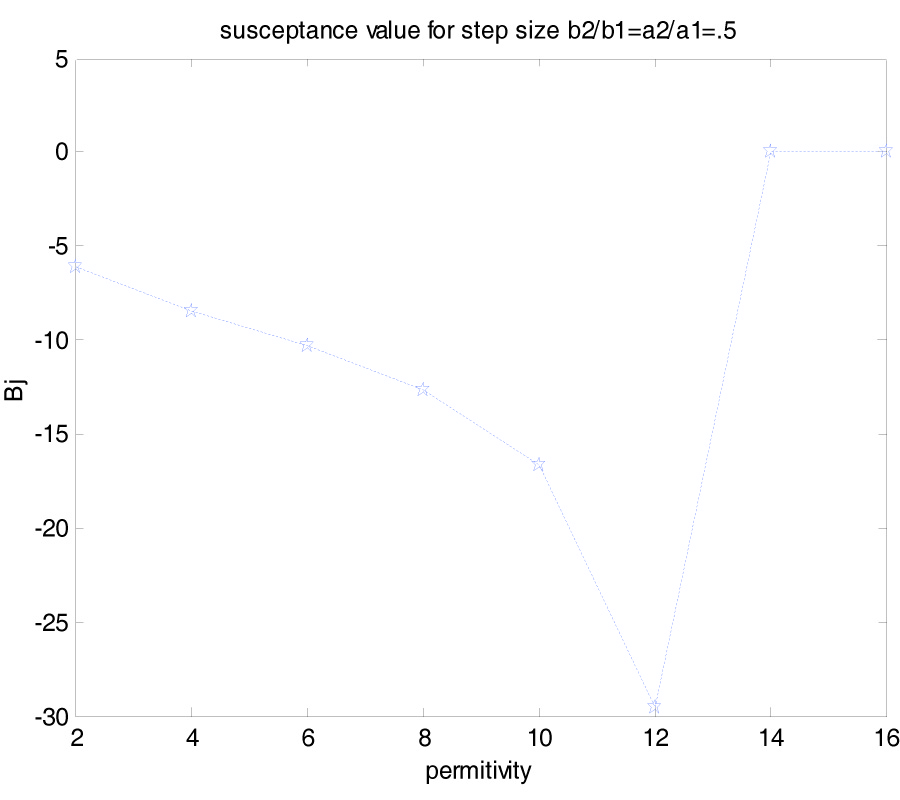
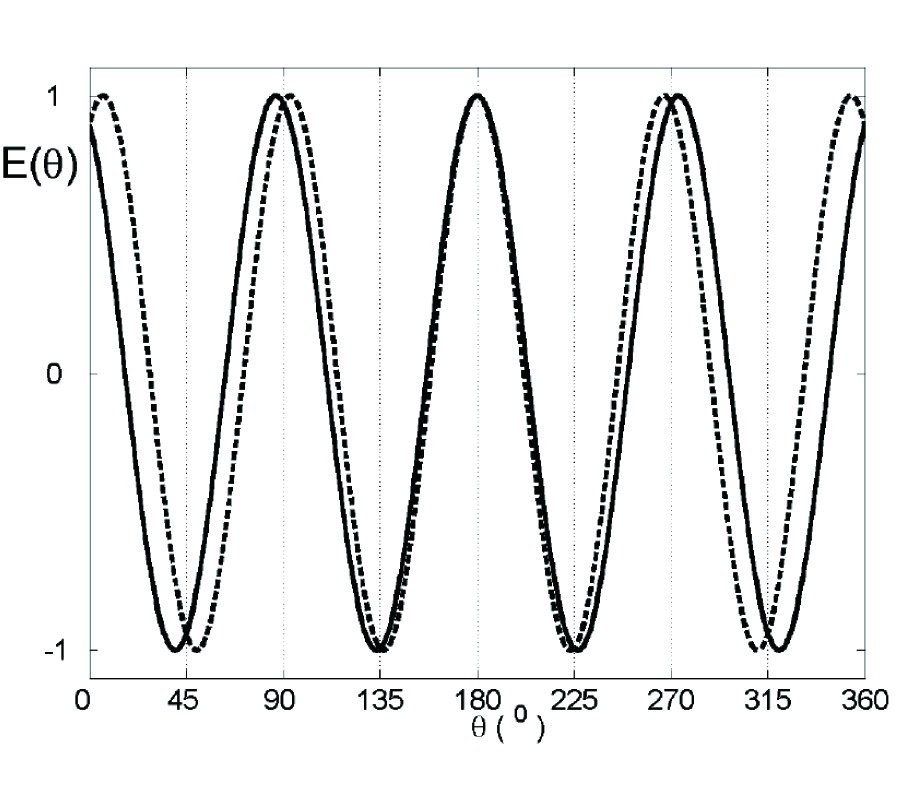
2008-11-18["PIER_181_24111001.png","PIER_182_25012003.png","PIER_183_25052305.png","other\/special_issue_13.png"]
On the Size of Left-Handed Material Lens for Near-Field Target Detection by Focus Scanning
By Gang Wang
Yu Gong
Hongjin Wang
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 87, 345-361, 2008
Abstract
Two focus-scanning schemes, viz. lens-fixed scanning scheme and lens-combined scheme, are proposed for near-field target detection and imaging. Specific lens size must be determined for future lens building in order to achieve desired imaging resolution and convenient data acquisition. Influence of LHM lens size on the performance of two different focus-scanning schemes are investigated and compared by simulating the detection of a perfect electric conductor target of diameter of 2 mm. Numerical simulations indicate that the lens-combined scanning system using thick LHM lens of thickness of two wavelengths requires at least a length of one wavelength to achieve resolution better than 0.4 wavelengths, while the lens-fixed scanning system requires a lens of lengthof approximately 3 wavelengths. When a thin LHM lens is used, high imaging resolution is not a consequent result for the focus-scanning approaches, although thin lens generally yields high focusing resolution. Some guidelines on the selection of length and thickness of flat LHM lens are reported.