2025-12-18 Latest Published
By Xuemei Zheng
Ao Gui
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 129, 1-8, 2026
Abstract
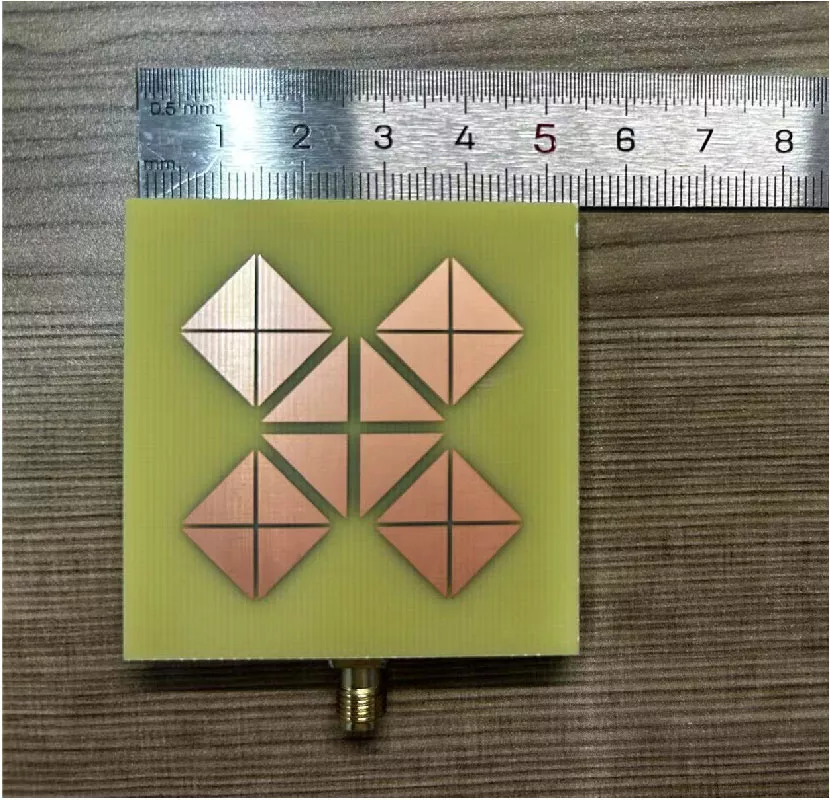
In response to the demand for broadband antennas in satellite communications, this paper sets out the proposal of a broadband circularly polarised metasurface antenna. Based on the theory of characteristic mode analysis of super surface, a pair of characteristic modes with the potential to realize circular polarization broadband are obtained and used as the modes to be excited. At the same time, the metasurface current is analyzed; the position of the floor gap is determined according to the results; and the shape of the floor gap is designed to better stimulate the characteristic mode. Subsequently, the power is transmitted through the microstrip line gap coupling feeding structure to excite the selected mode. Finally, an MTS antenna with dimensions of 0.9λ0 × 0.9λ0 × 0.076λ0 at a centre frequency of 5 GHz was determined. The antenna was modeled using CST, a 3D electromagnetic simulation software, and then physically tested for verification. The experimental findings indicate that the impedance bandwidth of the antenna in question is 4.20-5.83 GHz (relative bandwidth of 32.6%). Furthermore, the 3 dB axial ratio bandwidth is 4.38-5.97 GHz (relative bandwidth of 30.7%).