2025-07-05 Latest Published
By Sandeep Kiran Vattiprolu
Pullagura Rajesh Kumar
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 112, 121-133, 2025
Abstract
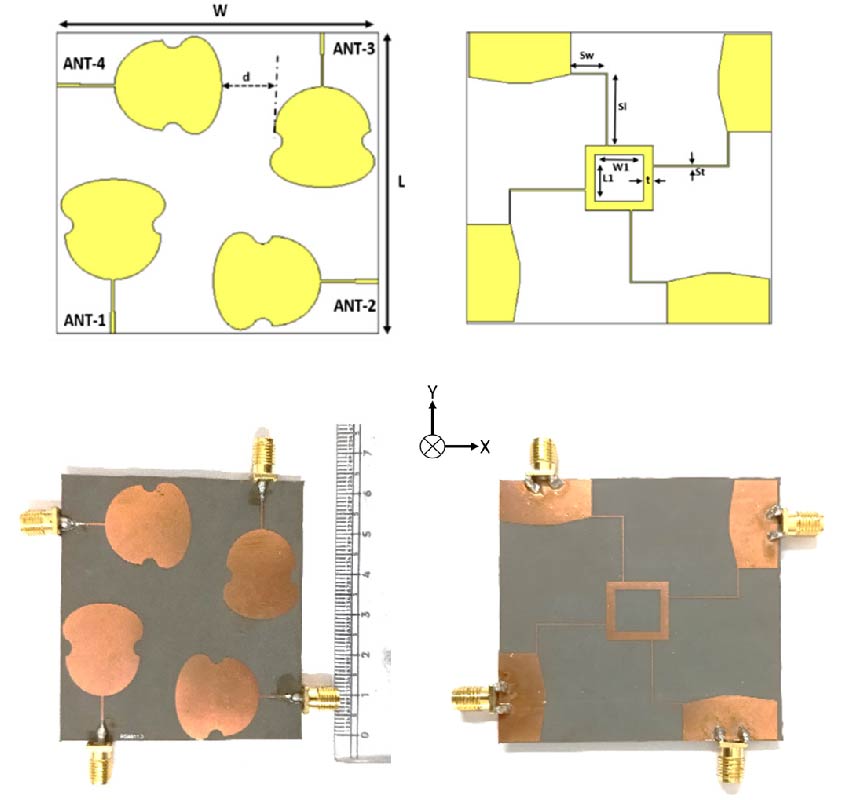
This paper presents the design of a four-element conformal Multi-Input Multi-Output (MIMO) antenna system for Ultra-Wideband (UWB) applications. It is implemented on a flexible RT Duroid 5880 substrate with a relative permittivity of 2.2, a loss tangent of 0.0009, and a thickness of 0.25 mm. It employs a stepped microstrip line-fed guitar-shaped antenna as a single antenna element. The single antenna element is then arranged orthogonally around the four edges of a 63 × 63 mm2 substrate to create a 4-element MIMO system. The four antennas, designated as Ant-1 to Ant-4, have their ground planes connected through L-shaped stubs. The prototypes of single antenna element and 4-element MIMO are built to compare the simulation and measurement findings. The single antenna element is tested under flat, X-bend, and Y-bend cases. It achieves -10 dB impedance bandwidth from 3.14 GHz to over 10.6 GHz, a maximum group delay deviation of 2 ns, and a system fidelity factor greater than 80% in all cases. The 4-element MIMO system was also tested in flat and conformal configurations. It covers a minimum -10 dB impedance bandwidth from 3.5 to 10.8 GHz and exhibits mutual coupling below -18 dB. Its equivalent circuit model is also realized. Its diversity analysis shows an envelope correlation coefficient (ECC) below 0.01, diversity gain (DG) near 10 dB, channel capacity loss (CCL) under 0.4 bits/s/Hz, total active reflection coefficient (TARC) below -10 dB, and mean effective gain (MEG) between -3 dB and -12 dB across the operating band.