The Electromagnetic Distribution and Intelligent Signal Extraction of ELF-EM in Hole-Ground Communication
Fukai Li,
Yue Zhao,
Wei Guo,
Jian Wu,
Zan Yin,
Huaiyun Peng and
Kai Liu
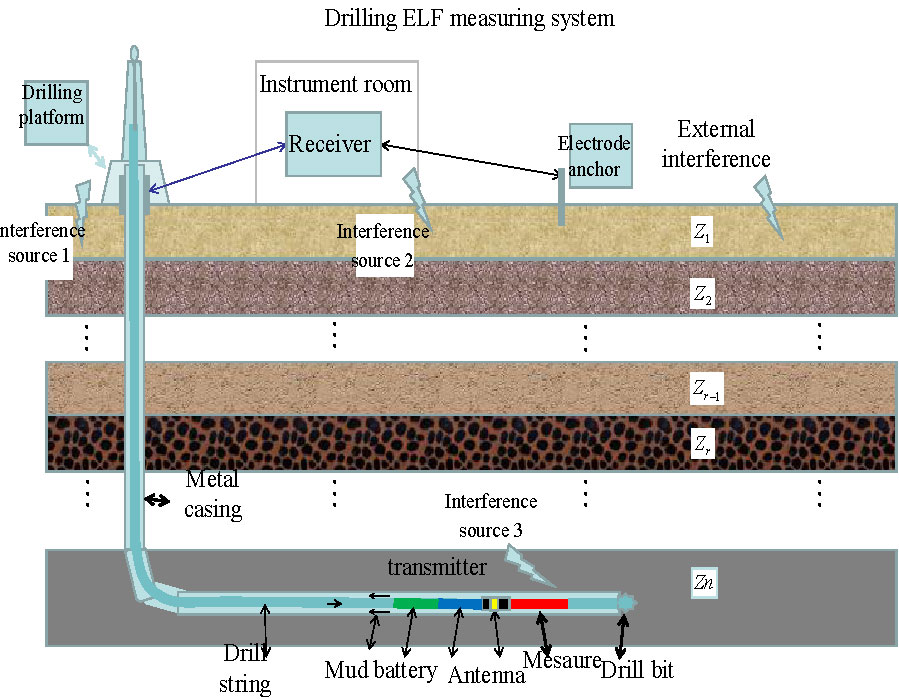
In the field of drilling engineering, innovations in drilling communication(also known as hole-ground communication while drilling) technology are crucial for enhancing exploration efficiency, ensuring operational safety, and optimizing data collection. Extremely Low Frequency electromagnetic (ELF-EM) wave communication transmission technology, with its exceptional penetration capability in formations and low attenuation characteristics, is emerging as a key technology in drilling communications. However, this technology faces challenges such as complex transmission model calculations and difficulty in extracting weak signals from the ground, which hinder its further development. Addressing issues like the inability of conventional models to accurately describe non-uniform media, low frequencies, and near-field open-space conditions in ELF-EM transmission under drilling conditions, as well as numerical dispersion, this paper innovatively conducts a comprehensive and systematic analysis of electromagnetic distribution in extended-reach horizontal wells using the finite element modeling and analysis method. Through software simulations and field tests, the following conclusions are drawn: The induced current on the drill pipe plays a major role in the ground field distribution and the signal received by the system terminal; the horizontal drill pipe in a horizontal well has a certain impact on the ground-received signal, mainly manifesting in that the orientation of the ground-receiving electrode should align with the direction of the horizontal well, and the larger the azimuth difference is from the drilling direction, the smaller the signal reception is; at the surface of the drilling platform, not only can multiple electrodes be used to receive signals, but magnetic sensors can also be employed to receive magnetic component signals. Addressing the issue of extracting communication signals in complex electromagnetic environments during electromagnetic measurement-while-drilling (EM-MWD) operations, a multi-channel intelligent signal extraction method has been designed. This method can improve the in-band signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) by more than 3 to 5 dB and further extend the communication transmission distance compared to single-channel models.