2025-12-14 Latest Published
By Tsietsi Condry Ramatladi
Akintunde Ayodeji Alonge
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 116, 65-80, 2026
Abstract
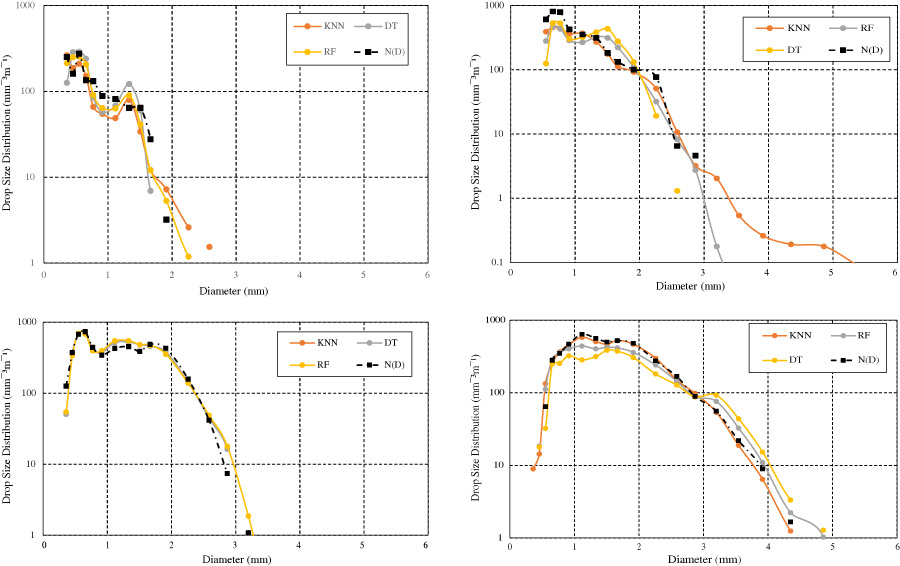
Reliable modelling of rainfall-induced attenuation is crucial for designing and operating high-frequency communication systems, particularly those operating above 10 GHz, in regions with severe rainfall conditions such as subtropical climates. This study offers a comparison of supervised machine learning (ML) models - k-nearest neighbours (KNN), decision trees (DT), and random forests (RF) - against traditional statistical methods such as the lognormal and gamma distributions for estimating raindrop size distribution (DSD) and specific attenuation. Rainfall measurements taken between 2018 and 2019 were obtained from 1-minute disdrometer at the measurement location in Durban, South Africa (29.8651°S, 30.9734°E). The investigated models were then tested across four different rainfall regimes processed from the dataset: drizzle, widespread rain, shower, and thunderstorm. An adaptive tuning method for selecting the best k-value in KNN was introduced to enhance prediction accuracy across various rainfall intensities. Model performances are evaluated using error metrics of root mean square error (RMSE), mean absolute error (MAE), and the coefficient of determination (R2). The results show that KNN outperforms RF and DT, providing the highest accuracy and lowest prediction errors across all rainfall regimes. The confidence interval (CI) analysis confirms that KNN delivers more precise and stable estimates, while RF and DT exhibit greater variability and uncertainty in performance. Additionally, specific attenuation estimations from these ML models are compared at different rain rates with the ITU-R P.838-8 estimations for frequencies up to 100 GHz. These findings highlight the superiority of data-driven model, particularly the adaptive KNN, in capturing complex rainfall microstructures and improving attenuation predictions. This has direct implications for planning and deploying rain-resilient wireless networks in variable climatic regions.