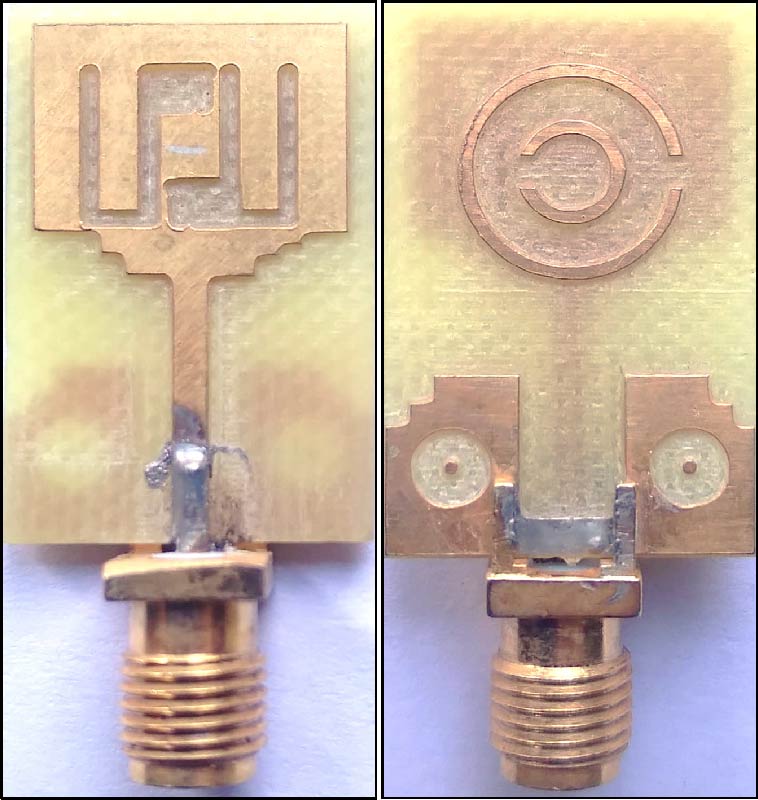
A Proximity-Fed Multi-Band Printed Antenna for Wireless Communication Applications
Ali Jabbar Salim
,
Jabbar K. Mohammed
,
Hussam Al-Saedi
and
Jawad K. Ali
This paper introduces a new triple-band antenna driven indirectly by a feed line for multiple wireless applications. The structure of this antenna is based on the creation of a set of slots and slits on the ground plane mounted on a substrate with relative permittivity of 4.4 and thickness of 1.6 mm. On the other hand, a 50-ohm microstrip feed line has been fixed. It is found that the proposed antenna offers a triple-band fashion with -10 dB impedance bandwidths suitable for most recent wireless applications. The first band extends from 1.6 GHz to 2.8 GHz, which covers LTE bands (1, 2, 3, 4, 9, 10, 23, 24, 25, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 39 and 40), 2.4 GHz-Bluetooth, and 2.45 GHz ISM. The second band extends from 3.38 GHz to 3.6 GHz, which covers most WiMAX applications, while the third band reconciles 5.8 GHz-ITS and 2.4/5.8 GHz-WLAN. A prototype of the proposed antenna has been successfully simulated, fabricated, and measured.