Design and Implementation of Wearable Antenna Textile for ISM Band
Hasri Ainun Harris,
Radial Anwar,
Yuyu Wahyu,
Mohamad Ismail Sulaiman,
Zuhanis Mansor and
Dwi Andi Nurmantris
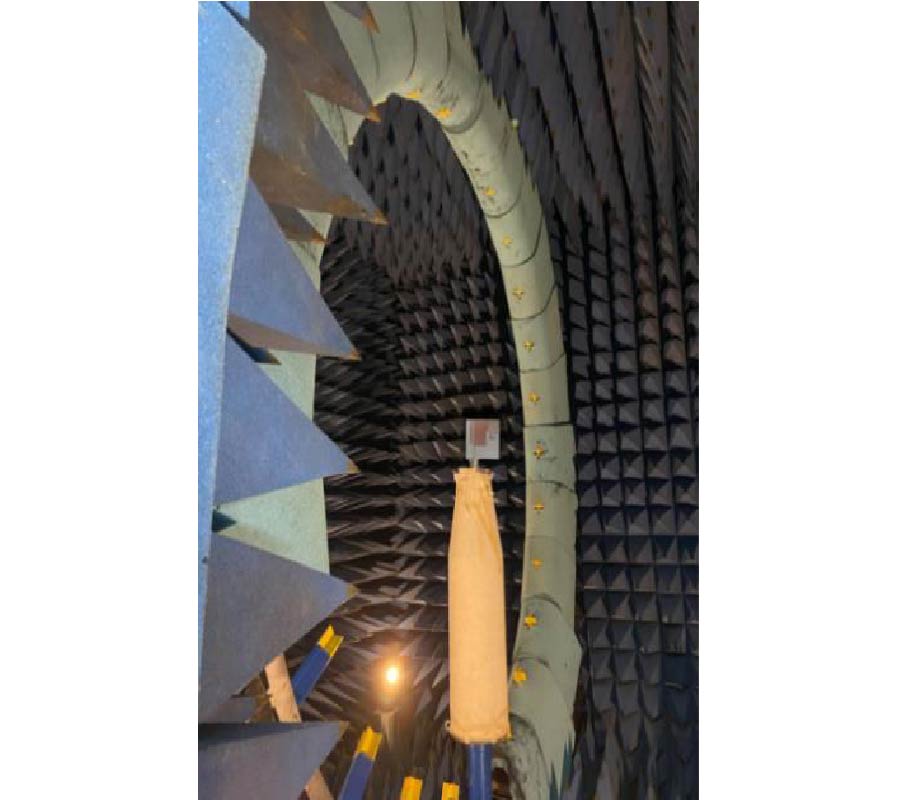
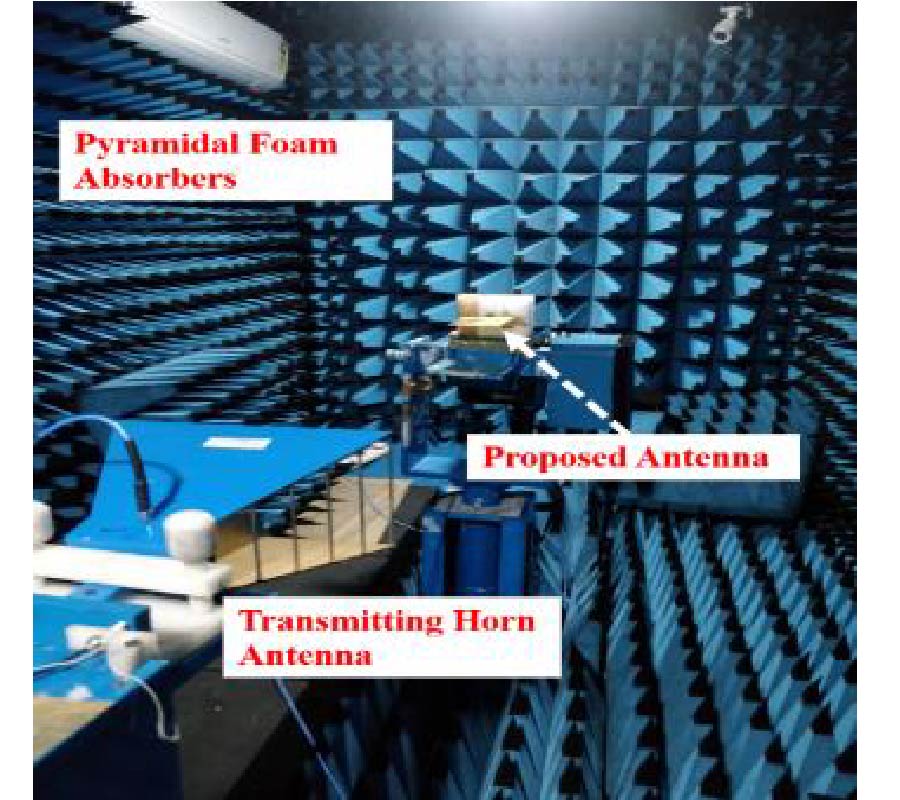
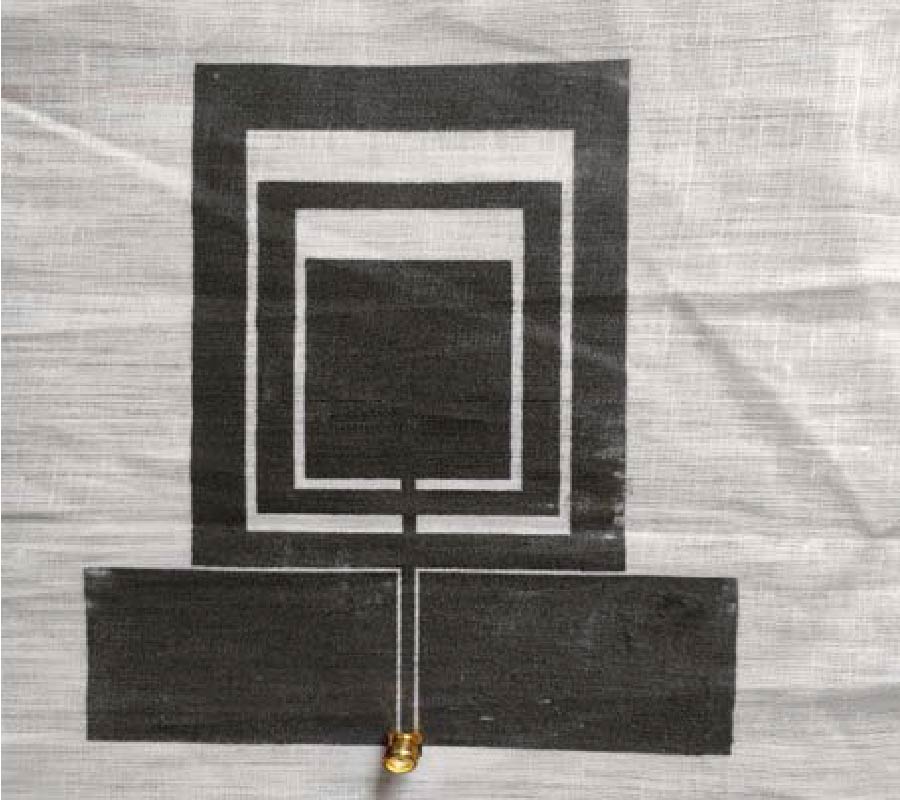
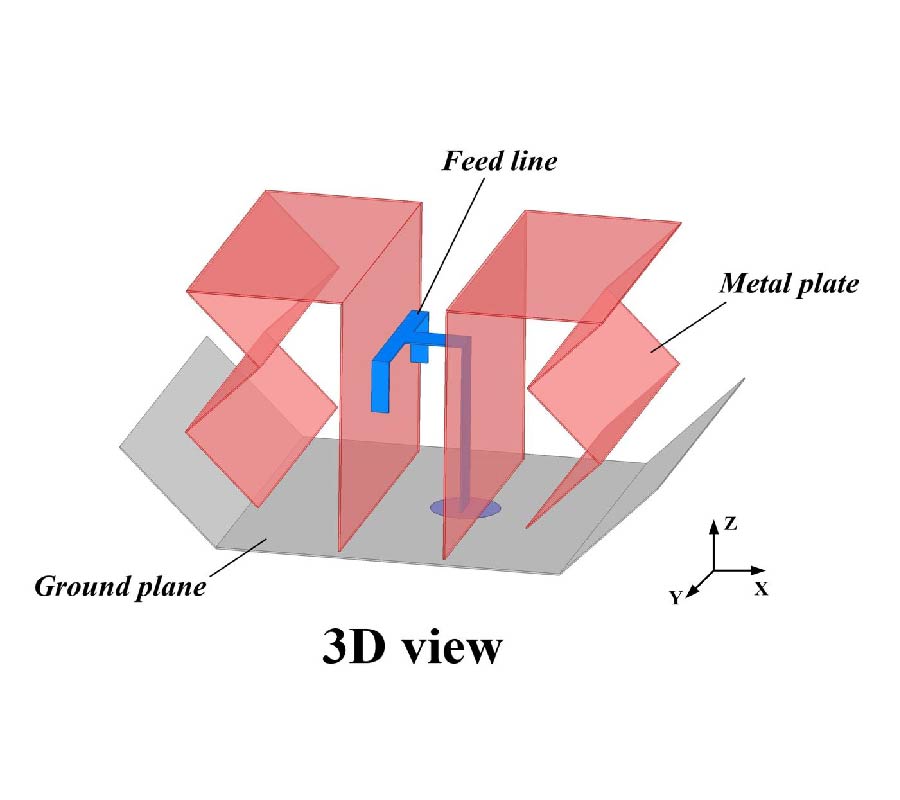
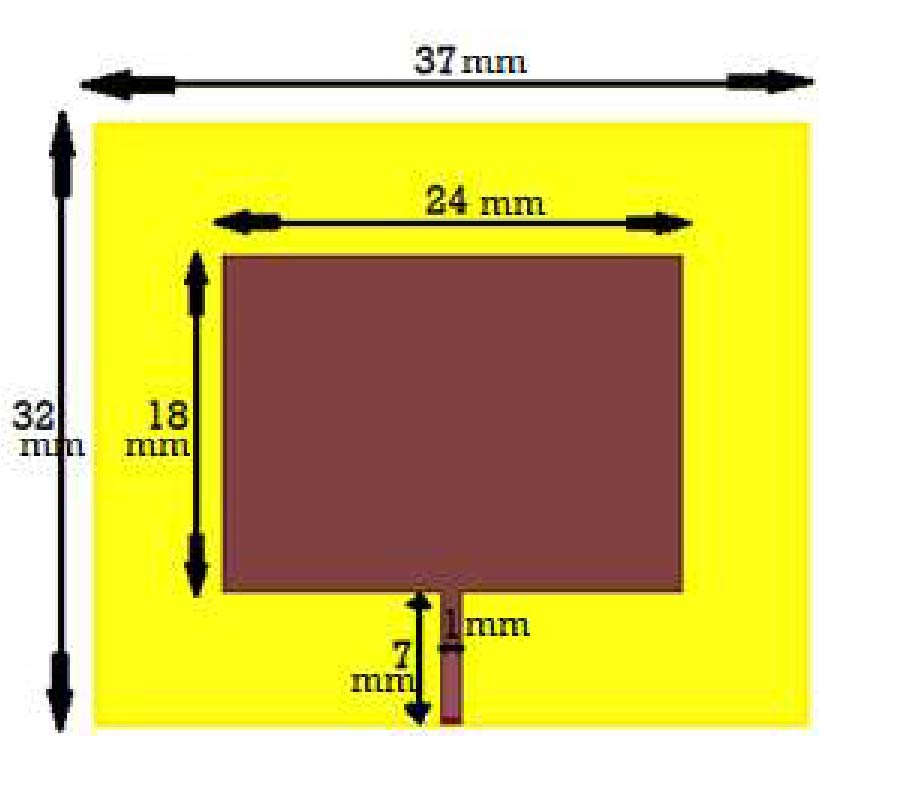
Wearable antenna is one component needed for mid-range communication. It can be integrated into clothing, bags, or any other item worn. This paper presents the structure and performance of a wearable antenna used in place of the ESP8266 Wi-Fi module antenna in dresses. With a higher gain than 2 dBi, this replacement will provide greater signal coverage than the existing Wi-Fi antenna module. The proposed geometry utilizes rectangular patches with the inset feed method in the feedline segment, constructed using copper foil tape, 2.85 mm thick polyester as a substrate with a permittivity (εr) of 1.44, and Defected Ground Structure (DGS) technique. The operating frequency of the proposed antenna is at 2.4 GHz in ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) band. The whole process was used to optimize the structure, fabricated, and measured. As determined by simulation, the proposed antenna's return loss is -13.89 dB, whereas the measured value is -13.253 dB. The measurements scenario for the substitute and existing antenna are divided into two categories: line-of-sight (LoS) and non-line-of-sight (NLOS). Each of them experiences vertical and horizontal position of antenna. In LOS conditions, the vertical position has an average coverage of 9.84 meters more than the antenna module and the horizontal position is 13.84 meters. In NLOS conditions, the horizontal position has an average coverage of 9.22 meters more than the EP8266 antenna module, which in the vertical condition is about 17.06 meters. The obtained data successfully demonstrated that the proposed antenna could significantly increase the coverage of the ESP8266 module.