2024-09-23 Latest Published
By Ahmed Jameel Abdulqader
Jafar Ramadhan Mohammed
Yessar Ezzaldeen Mohammed Ali
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 147, 167-173, 2024
Abstract
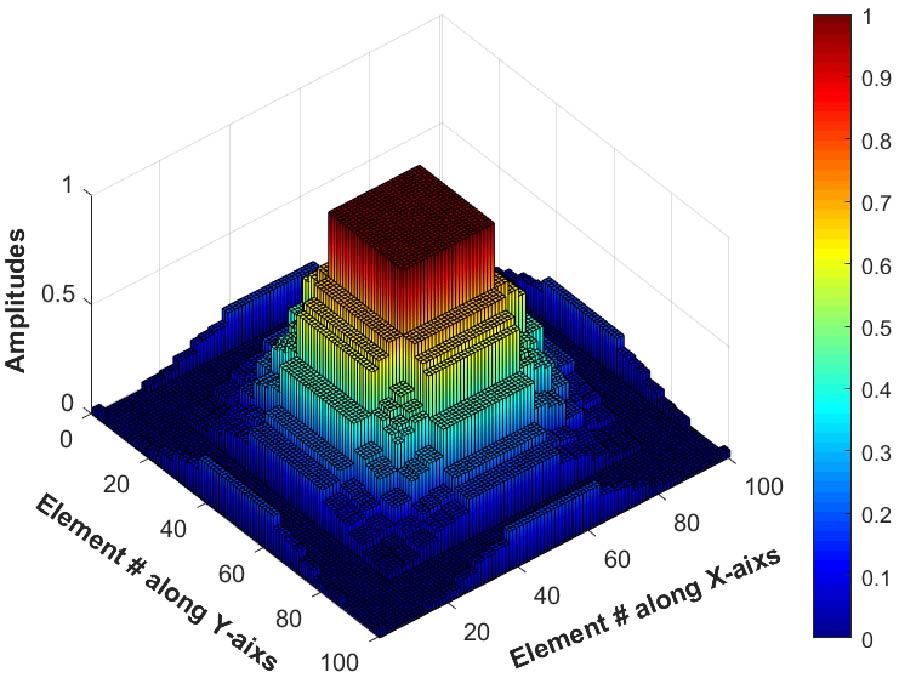
Conventionally, the thinning process in antenna arrays was performed at the element level with random selection after examining all the possible combinations. Thus, the computational time of such thinned methods was relatively high. Reducing the undesirable high computational time is of great interest. In this paper, the thinning process is performed at subarray level rather than element level, thus, the computational time and array complexity were significantly reduced while minimizing the peak side lobe level (PSLL). The optimization process consists of two steps where in the first step the array elements are portioned into a number of nonuniform ascending subarrays, while in the second step some of the least significant subarrays were turned off. Moreover, two schemes were used to portion the array elements. The first one is based on portioning all the array elements into ascending subarrays. This is known as fully nonuniform ascending subarray configuration since the entire array elements were portioned into smaller unequal groups. The second one is based on portioning only part of the elements located at the sides of the array, while leaving the central elements individually without any partition. This is known as partially nonuniform ascending subarray configuration. The genetic optimization algorithm is used to find out optimally which subarrays need to be thinned (or turned off) by setting their excitation amplitudes to zero. The simulation results for a total of 100 elements linear array illustrate that the PSLL, in the full subarray configuration, can be minimized to more than -33 dB by thinning 5 subarrays and the complexity reduction percentage was 72% before thinning and it becomes 82% after thinning. On the other hand, the PSLL in the partial subarray configuration was reduced down to more than -30 dB by thinning 4 subarrays at each side of the array. In this case. The complexity reduction percentage was 52% before thinning, and it becomes 60% after thinning. The number of individual central-elements on both sides of the array was 26, and the number of subarrays on both sides of the array was 22. Furthermore, the idea of the thinned subarrays was successfully extended and applied to the two-dimensional planar arrays of 100 × 100 elements.