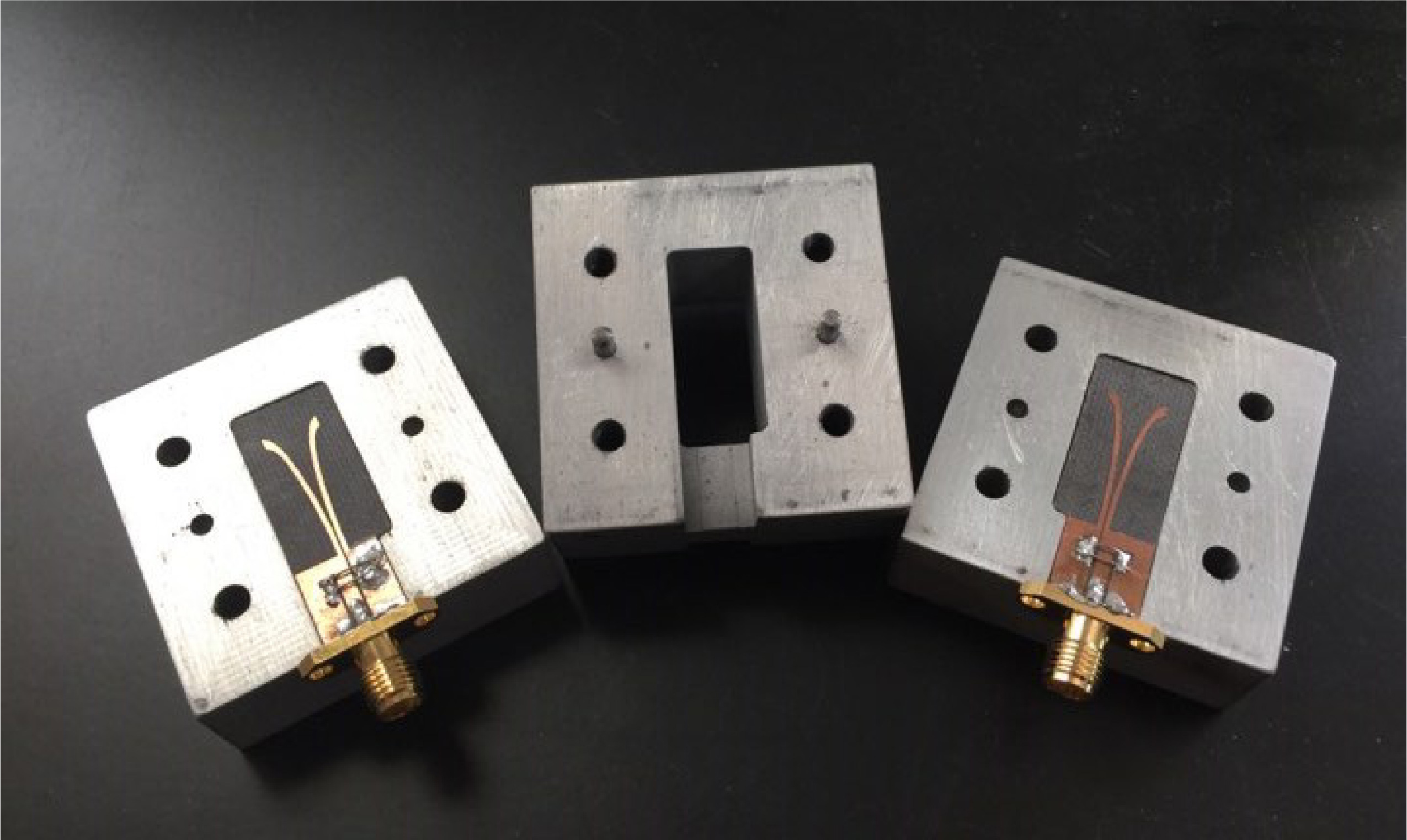
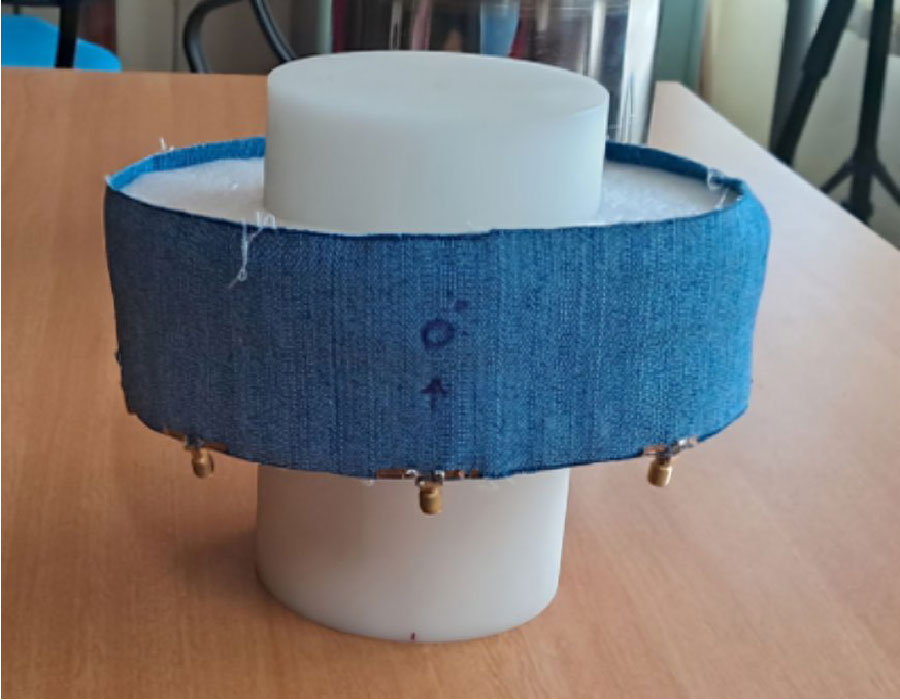
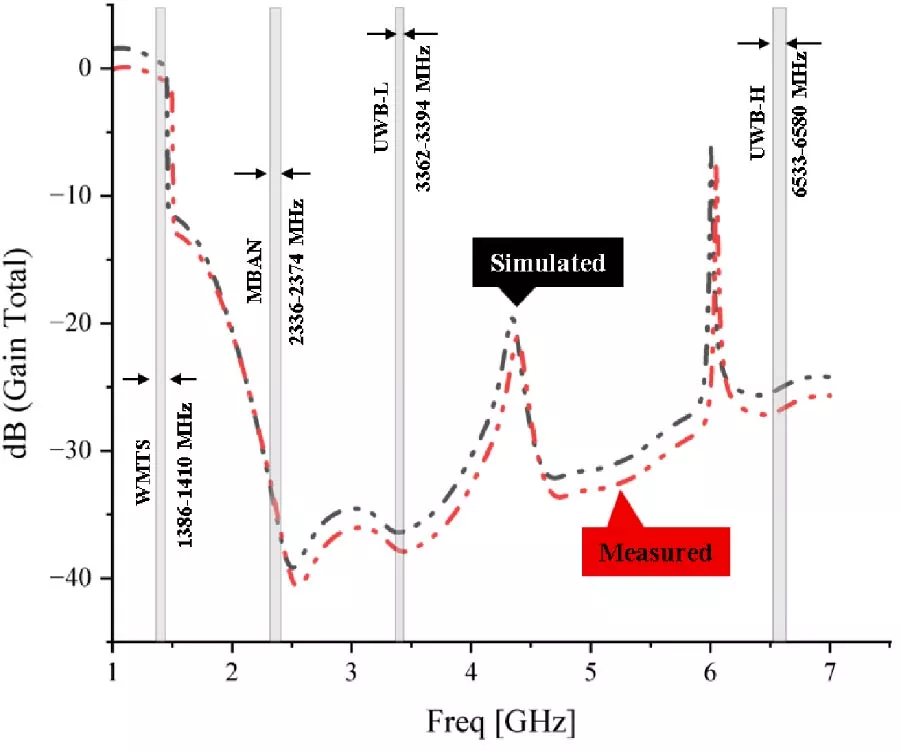
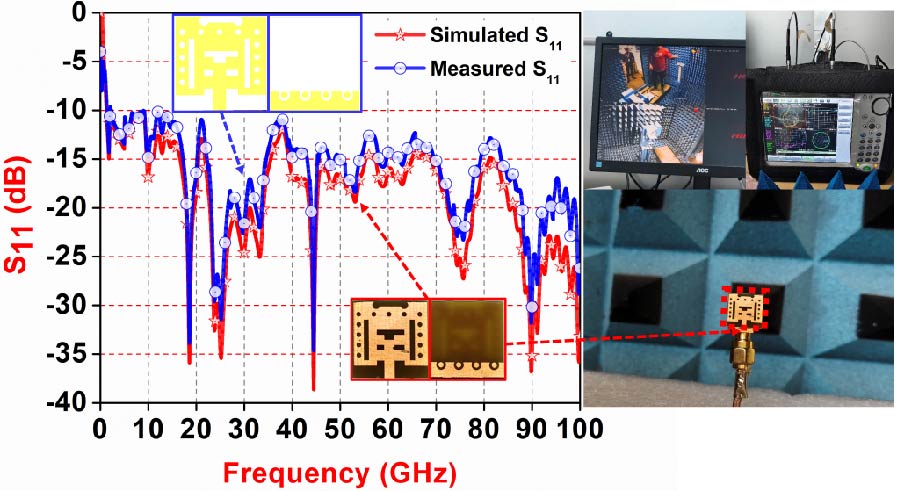
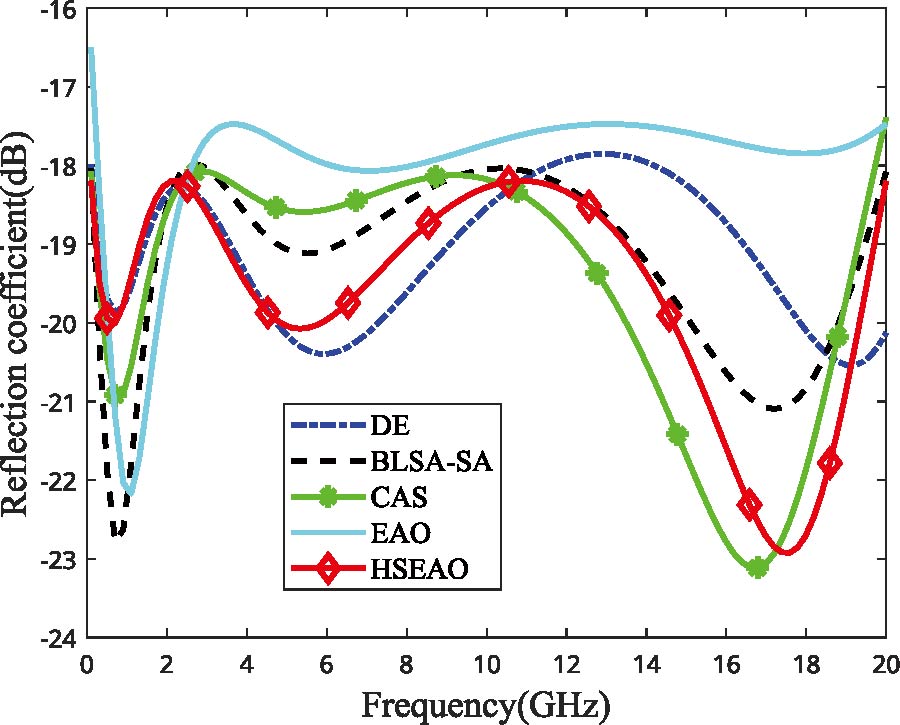
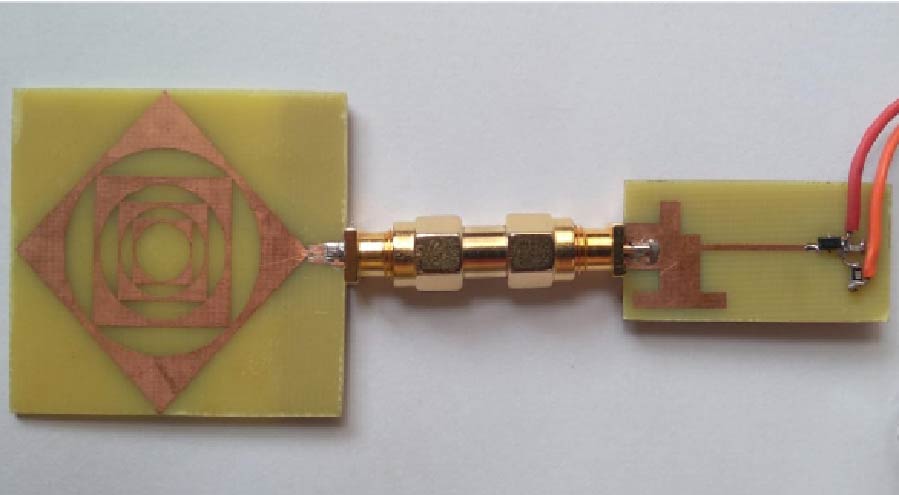
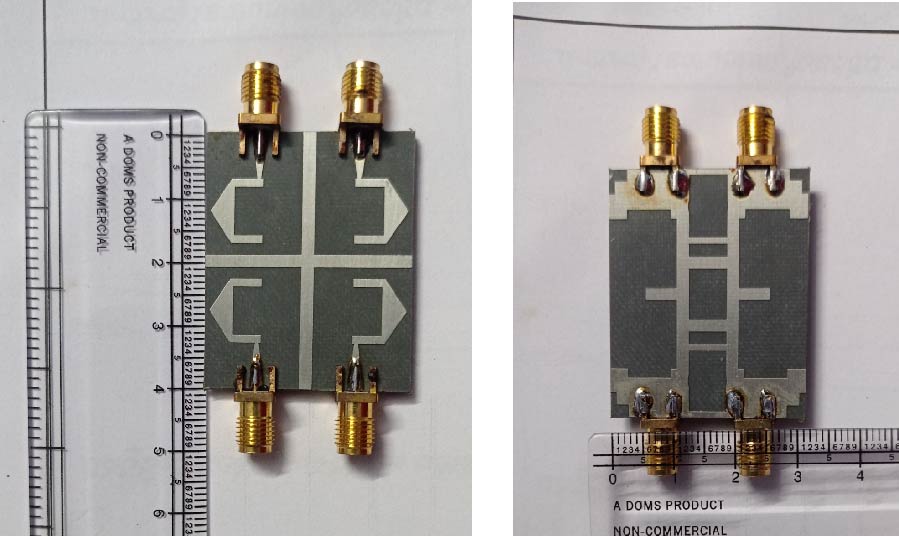
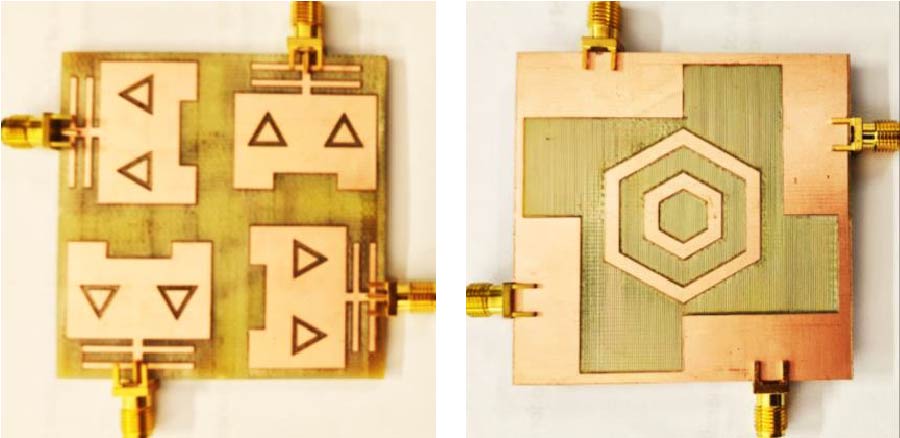
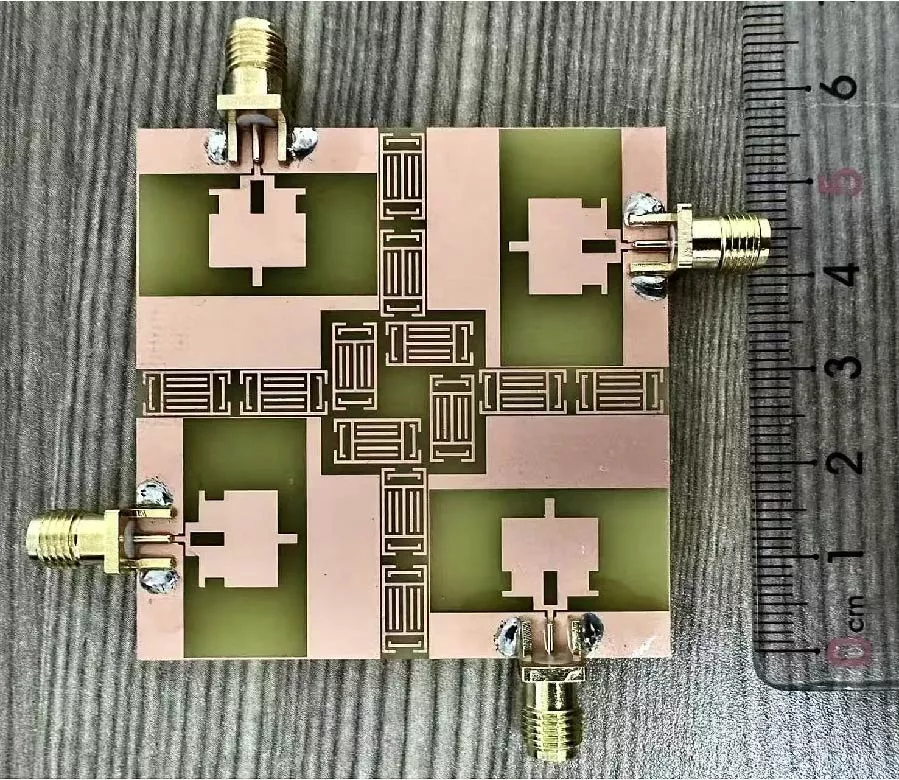
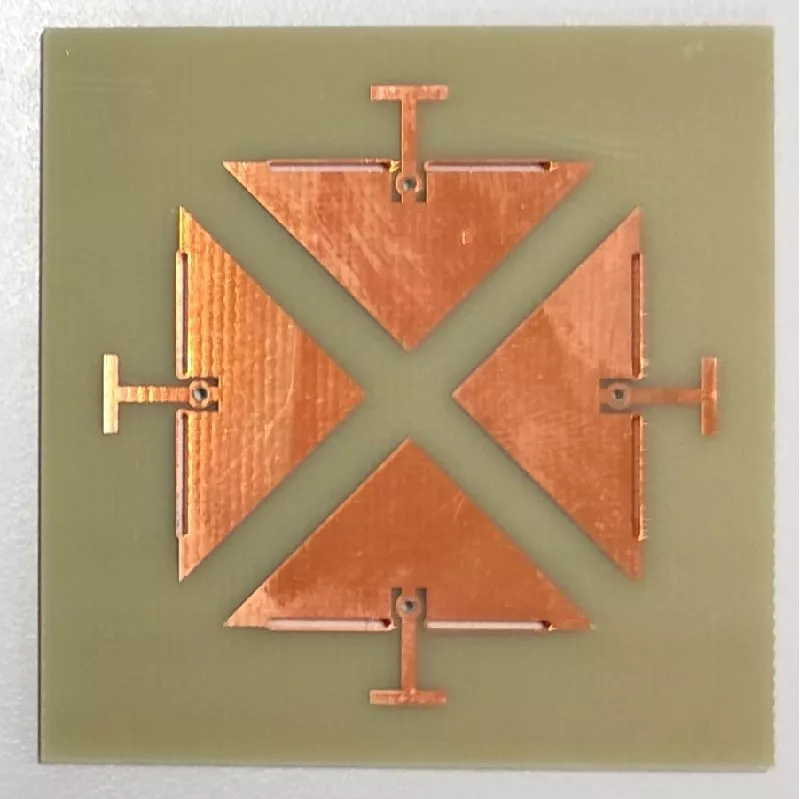
Wearable Multistatic Antenna Configuration on a Denim Substrate for Medical Imaging
Anju Maria,
Thathamkulam A. Anjit and
Palayyan Mythili
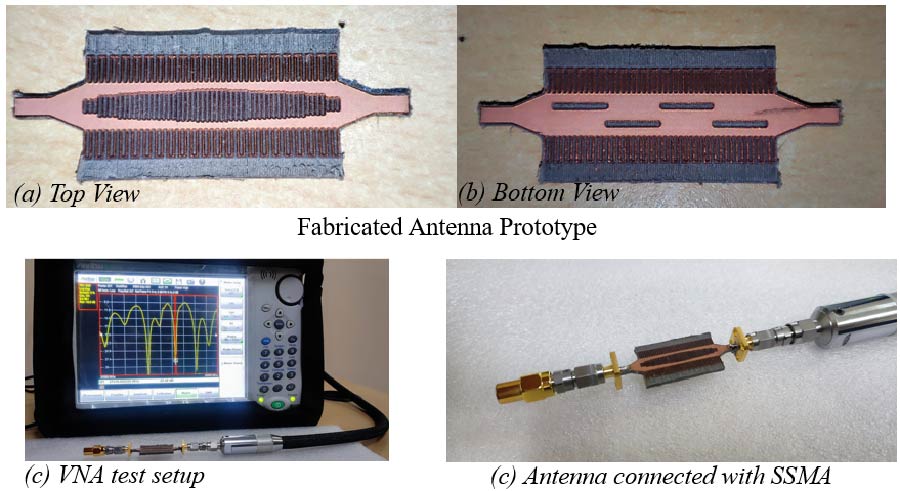
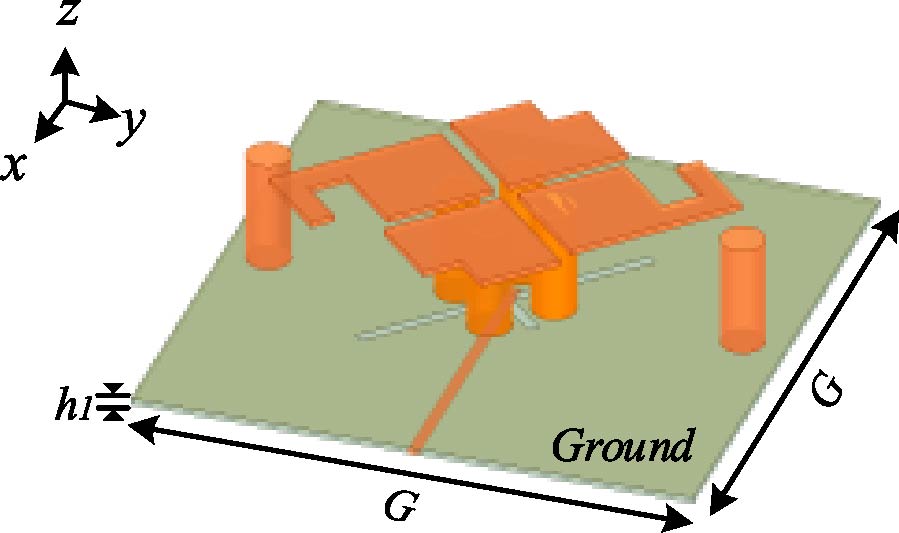
In this work, a multistatic antenna configuration with Compact Textile Wearable Antennas (CTWAs) is proposed for microwave imaging. The setup includes eight CTWA antennas printed on a denim jeans fabric wrapped around the phantom with a foam layer in between. The phantom is made of Delrin and is intended to replicate the breast tissue. It contains three PVC inclusions that mimic the tumors with sizes of 6 mm, 10 mm, and 3 mm. These inclusions are located at the center, near the outer surface, and between the center and the outer surface. The CTWA antennas surrounding the phantom collects the scattered data for further processing. Distorted Born Iterative Method (DBIM), along with the Reweighted Basis Pursuit (RWBP), a convex optimization algorithm, is used to reconstruct the object profile. RWBP is an iterative reconstruction algorithm in the sparse domain capable of extracting the size, shape, location, and dielectric distribution of the inclusions. The experiment is conducted using two different approaches. In one approach, multistatic without rotation, the receiver antenna is fixed at positions 0°, 45°, 90°, 135°, 180°, 225°, 270°, and 315°. In the other approach, multistatic with rotation, the receiver antenna is rotated in steps of 9° about the center of the phantom to achieve angles in between. In the multistatic configuration without rotation, the inclusions of 10 mm, 6 mm, and 3 mm were detected with errors of 0.125, 0.35, and 0.433, respectively, While in the case of multistatic configuration with rotation, the inclusions were detected with errors of 0.070, 0.066 and 0.03 respectively. The results obtained are compared with the previous studies available in the literature. These results demonstrate that the proposed wearable multistatic antenna configuration is suitable for medical imaging applications, enabling better target detection, localization, comfort, and flexibility.