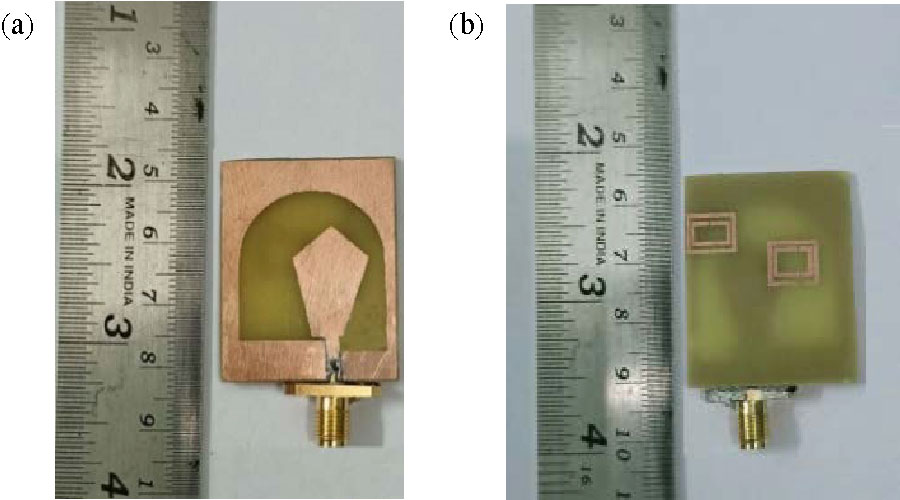
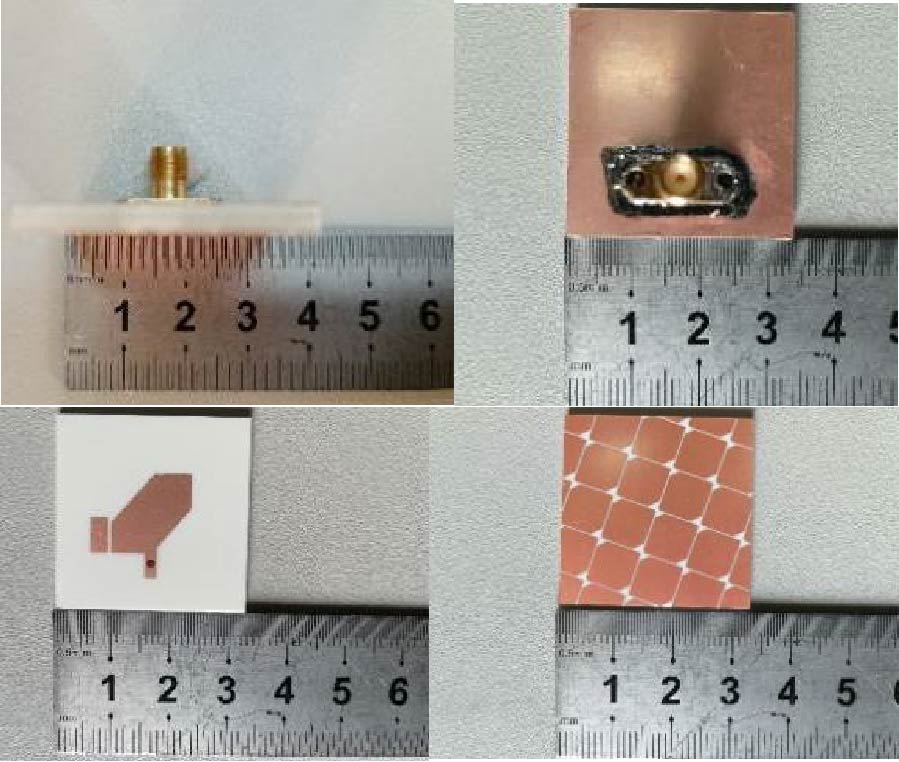
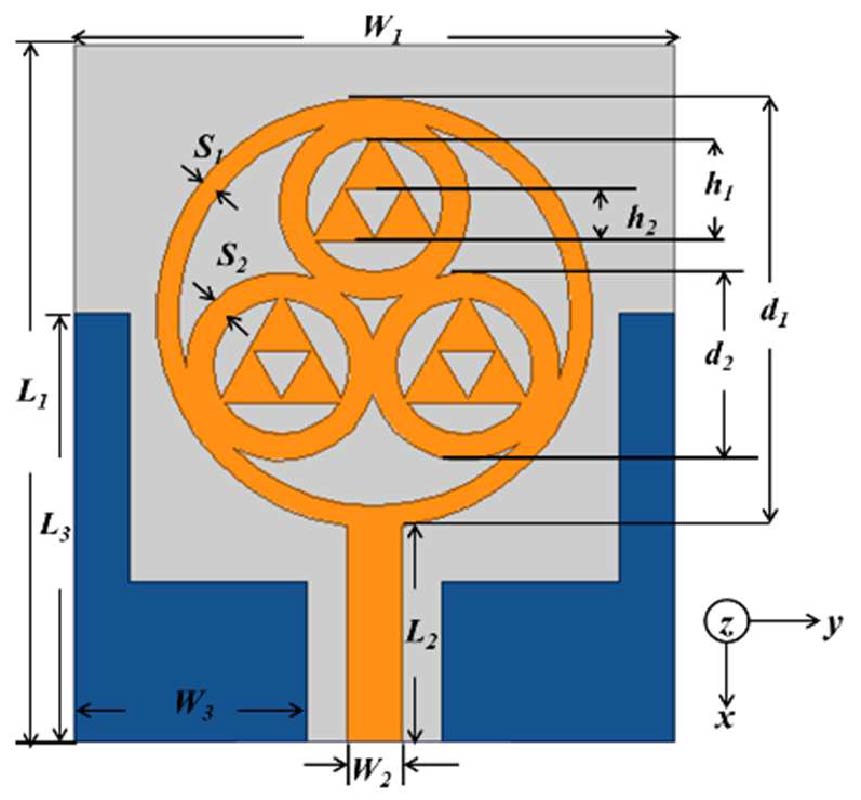
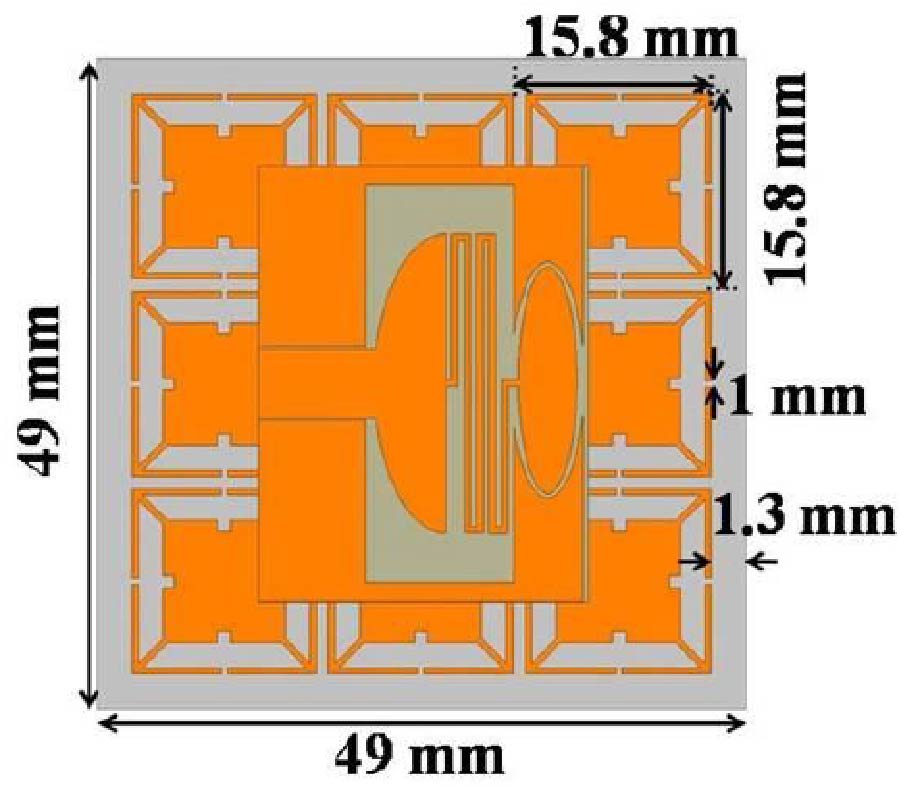
Enhanced Prediction of Metamaterial Antenna Parameters Using Advanced Machine Learning Regression Models
Prince Jain,
Prabodh Kumar Sahoo,
Aymen Dheyaa Khaleel and
Ahmed Jamal Abdullah Al-Gburi
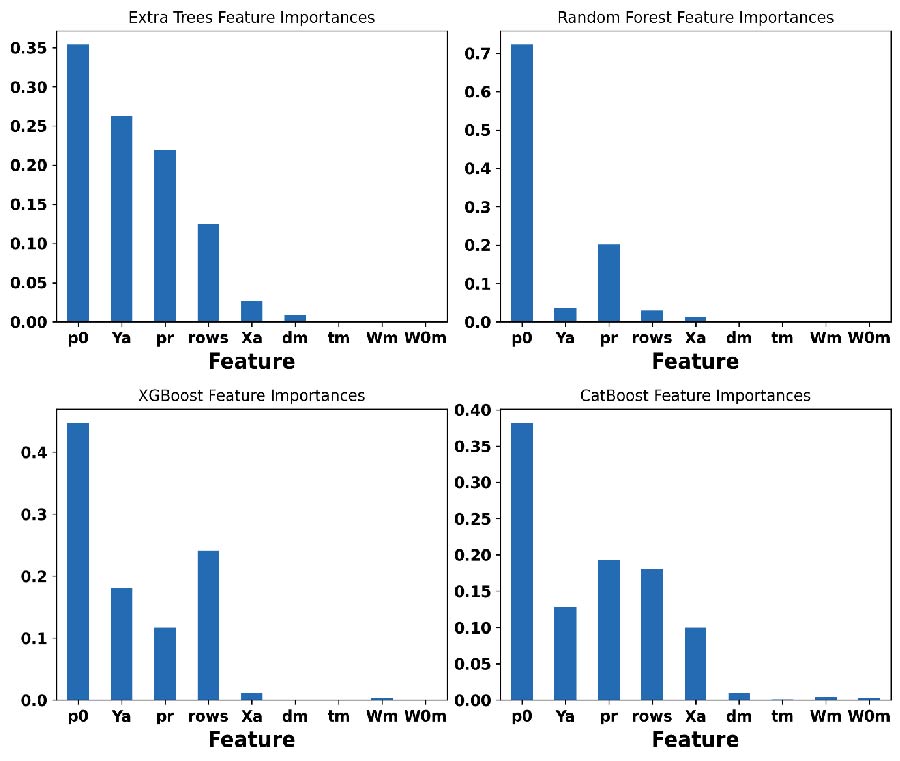
The integration of machine learning (ML) regression models in predicting the parameters of metamaterial antennas significantly reduces the design time required for optimizing antenna performance compared to traditional simulation tools. Metamaterial antennas, known for overcoming the bandwidth constraints of small antennas, benefit greatly from these advanced predictive models. This study applies and evaluates four ML regression models - Extra Trees, Random Forest, XGBoost, and CatBoost - to predict key antenna parameters such as S11, gain, and bandwidth. Each model's performance is assessed using metrics like Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Mean Squared Error (MSE), R-squared (R2), Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE), and Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) across different training and testing set configurations (30%, 50%, and 70%). The Extra Trees model achieves the best performance for predicting gain, with an R2 of 0.9990, MAE of 0.0069, MSE of 0.0002, RMSE of 0.0145, and MAPE of 0.3106. Feature importance analysis reveals that specific features, such as pr and p0 for gain and Ya and Xa for bandwidth, are critical in the predictive models. These findings highlight the potential of ML methods to improve the efficiency and accuracy of metamaterial antenna design.