2026-03-06 Latest Published
By Guibao Wang
Keyi Yu
Xianghui Wang
Shuzhen Wang
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 167, 21-31, 2026
Abstract
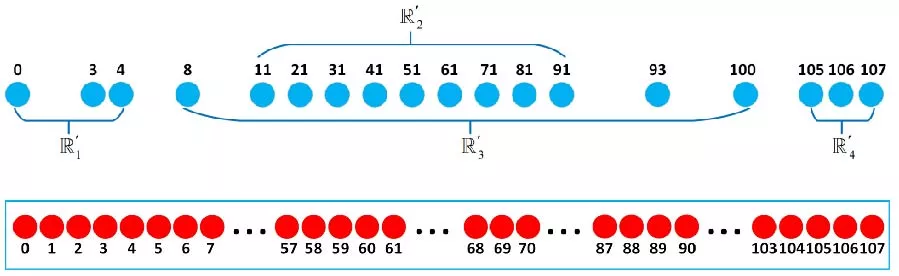
Sparse arrays have been extensively investigated for their capability to enhance degrees of freedom (DOFs). However, conventional nested array configuration is susceptible to strong mutual coupling (MC), while its achievable uniform DOFs (uDOFs) remains limited. To address these challenges, this paper proposes two optimized hierarchical nested arrays, designated as OHNA-I and OHNA-II. OHNA-I reconstructs the spatial arrangement of subarrays through a hierarchical shifting operation, effectively extending the continuous segment of the difference co-array (DCA). Building on this, OHNA-II further optimizes the subarray geometry via sensor displacement, achieving a better balance between uDOF enhancement and MC suppression, thereby maintaining higher uDOFs while reducing inter-sensor coupling interference. Numerical simulation results demonstrate that, under the same number of physical sensors, the proposed structures - particularly OHNA-II - achieve a greater number of uDOFs than existing classical sparse arrays. Furthermore, in scenarios with strong MC, the proposed structure exhibits superior robustness and lower root mean square error (RMSE) in DOA estimation.