2025-12-19 Latest Published
By Víctor Daniel Vazquez Pereira
Marcelo E. Chávez
Sebastián Murcia
Jordi Verdú Tirado
Pedro de Paco
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 136, 86-94, 2025
Abstract
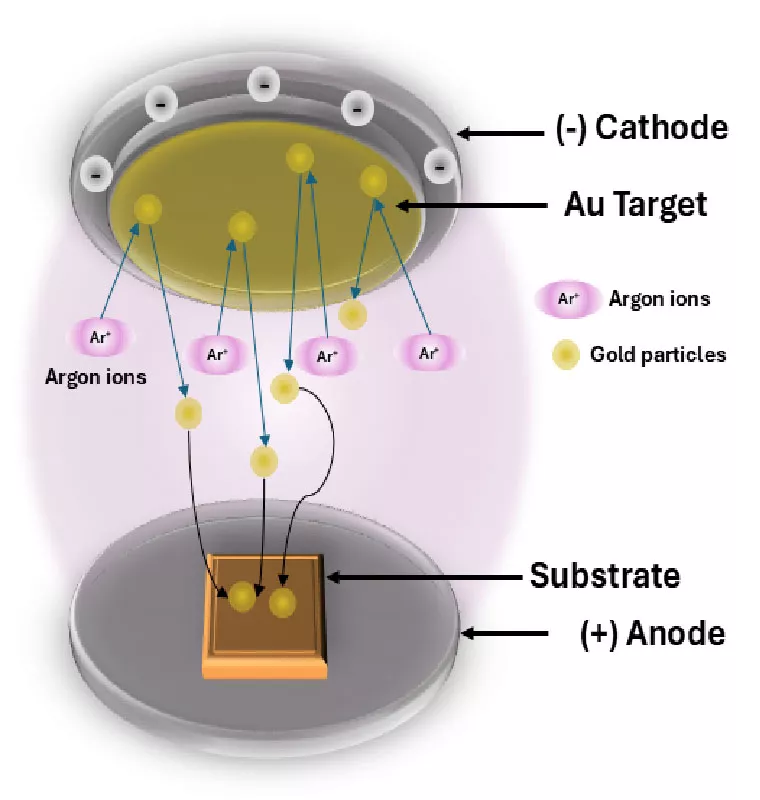
In the design and fabrication of ceramic filters, the quality of metallization is crucial to minimize resistive losses and ensure optimal resonator performance. This work presents the design and fabrication of a monoblock dual-mode filter with two distinct types of couplings, based on barium titanate (BaTiO3) ceramics, operating at S-band frequencies. Sputtering deposition was used to create a 5 nm gold seed layer, on which a 30 μm copper metallization was grown through electroplating. This method guarantees high conductivity in the resonator coating, and test results demonstrated that the fabricated device offers very good filtering performance with a minimal insertion loss of 0.57 dB.