Optically Transparent Broadband Microwave Absorber with Tunable Absorptivity Based on Graphene-ITO Structure
Shuomin Zhong,
Enbang Yu,
Yu Zhang,
Xianjia Chen,
Zi-Wei Zheng,
Qiping Lin and
Sailing He
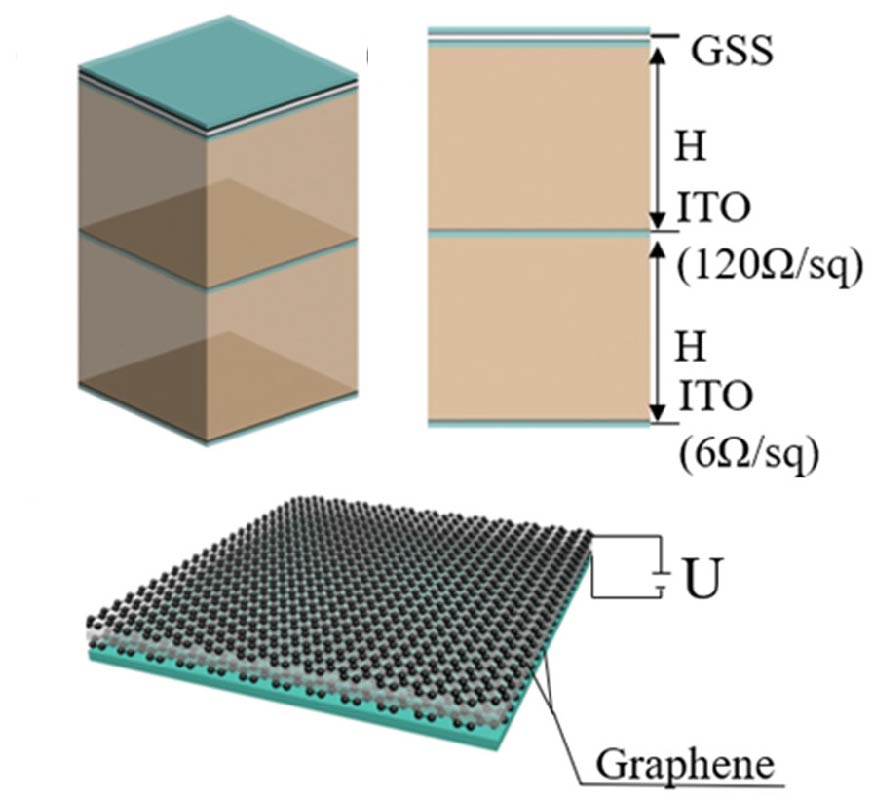
In this study, we present a novel broadband microwave absorber that is both optically transparent and capable of dynamically adjusting its absorptivity. The absorber is composed of a graphene sandwich structure (GSS), a polyvinyl chloride (PVC) layer, an indium tin oxide (ITO) layer, another PVC layer, and an ITO ground plane, arranged in a top-to-bottom configuration. This unique design allows for a working bandwidth of 6.8 GHz to 14.0 GHz, with absorption levels ranging from 95% to 60%, achieved by varying the impedance of the GSS from 1000 Ω/sq to 200 Ω/sq through tuning the bias voltage. By utilizing materials with high optical transmittance, this nonpatterned device maintains exceptional optical transparency. Furthermore, by incorporating additional ITO layers with different impedances at equal intervals, this multilayer design can be extended to create an ultra-broadband absorber covering a range of 5.28-39.52 GHz. This is made possible due to the dispersionless resistance of nonpatterned graphene and ITO sheets in the microwave spectrum. This transparent wideband microwave absorber, with tunable absorptivity, holds great potential for a wide range of applications in broadband and intelligent stealth technology.