A Compact High-Isolation Tri-Band MIMO Antenna Based on Characteristic Mode Analysis
Jinrong Su,
Shiqi Di,
Chunhui Yao and
Xinwei Chen
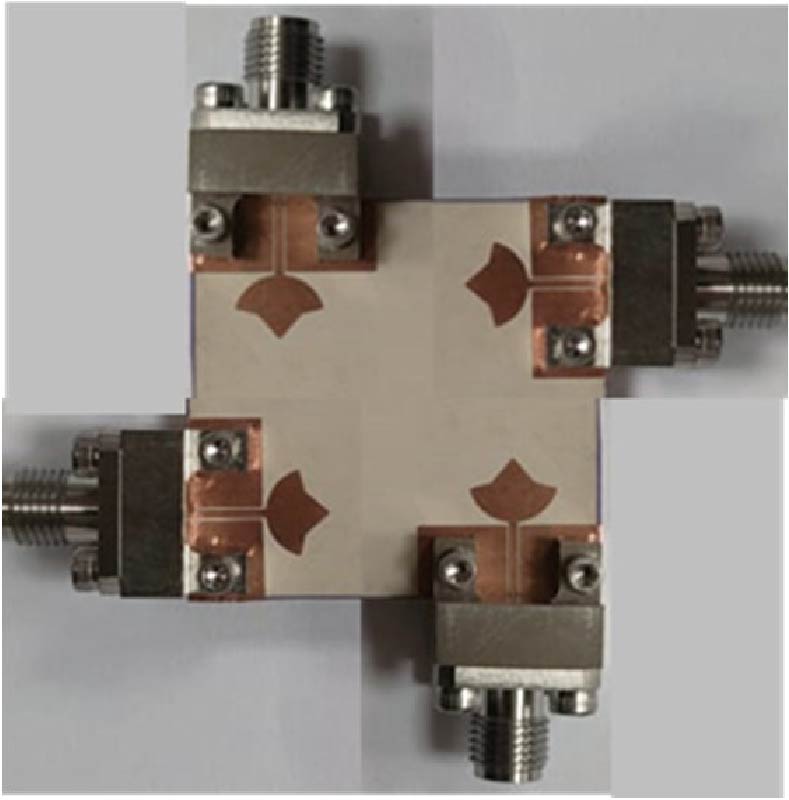
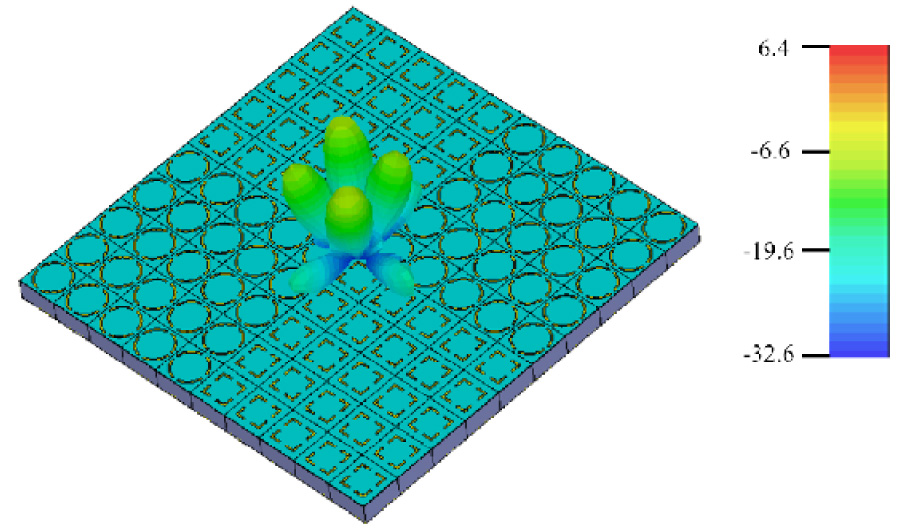
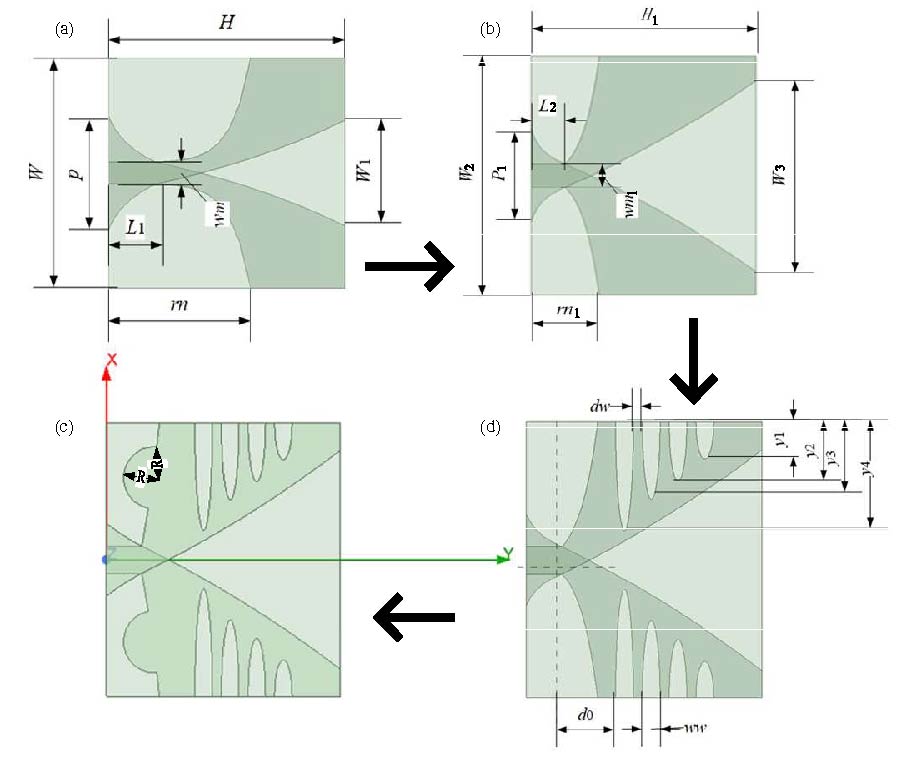
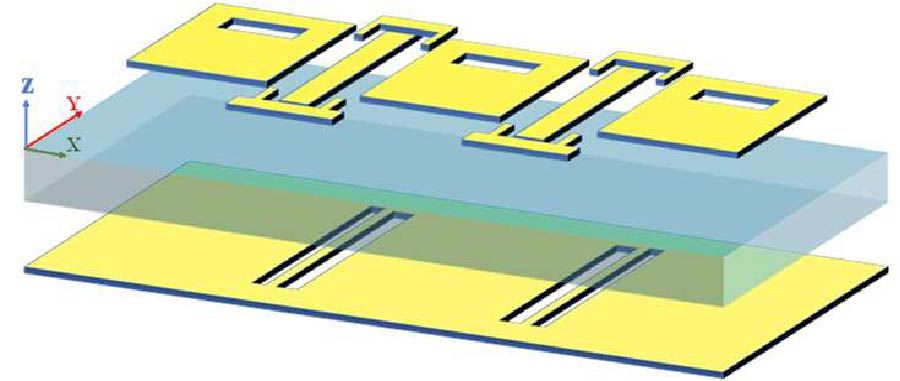
This paper presents a compact 3-port multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) antenna for 5G wireless communication, covering the 2.6 GHz, 3.5 GHz, and 4.8 GHz bands. Three orthogonal modes (TMsub>10, TMsub>01, and TMsub>20 modes) are excited to realize tri-band operation and high isolation simultaneously. Using characteristic mode analysis (CMA), dual-slot structures and I-shaped patches are introduced to block coupling path, and the isolation is improved. Simulated and measured results show that the proposed antenna operates in the frequency bands of 2.57 to 2.64 GHz, 3.4 to 3.5 GHz, and 4.8 to 4.9 GHz with isolation better than 20.6 dB. In addition, it can be calculated that Envelope Correlation Coefficient (ECC) (<0.06), Diversity Gain (DG) (>9.99 dB), Total Active Reflection Coefficient (TARC) (<-10 dB), and Channel Capacity Loss (CCL) (<0.45 bits/Hz/sec) are in acceptable level, implying excellent diversity performance and data transmission quality. It is worth noting that the evolution of the antenna is entirely based on the CMA, which greatly simplifies the design process. The antenna has the advantages of high isolation, compact structure, easy processing, and low cost, positioning it as a compelling candidate for integration into 5G wireless communication systems.