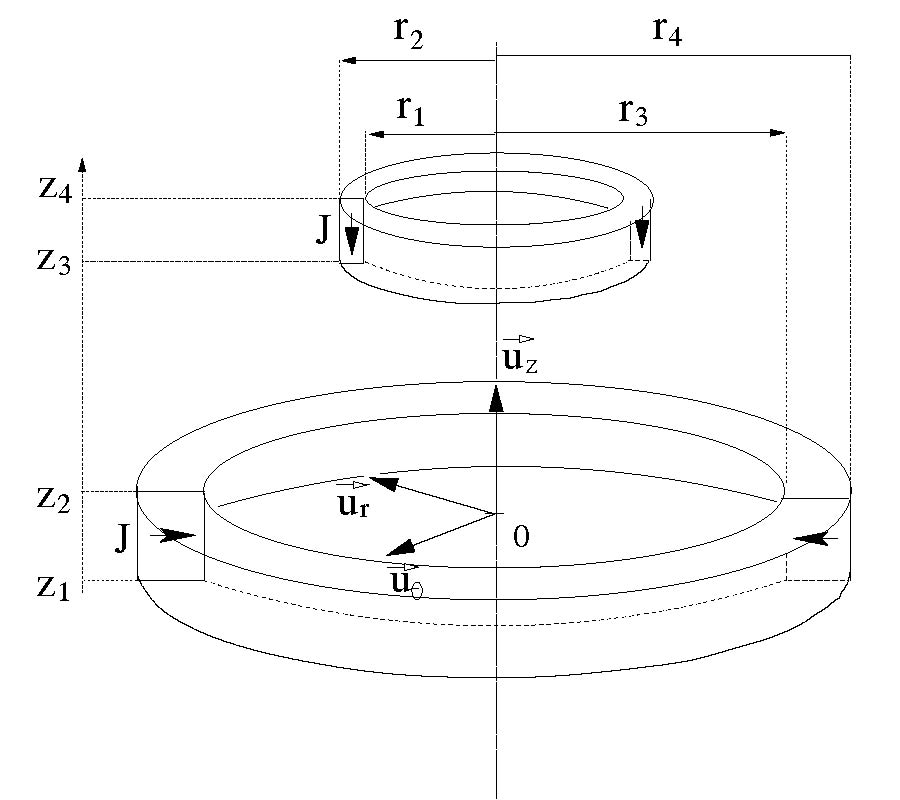
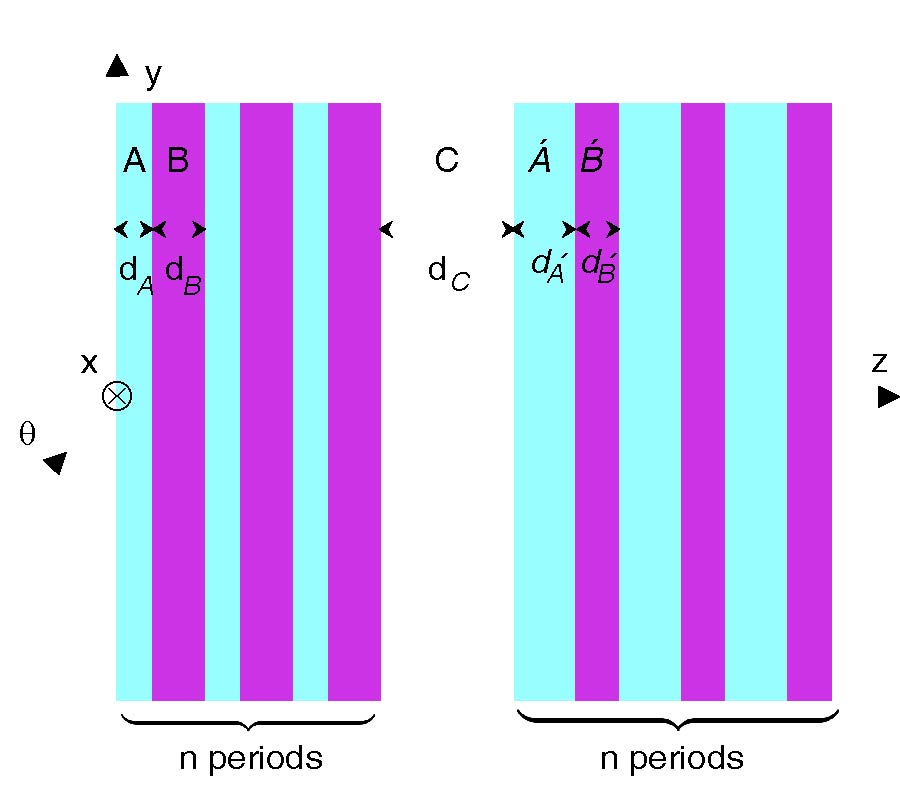
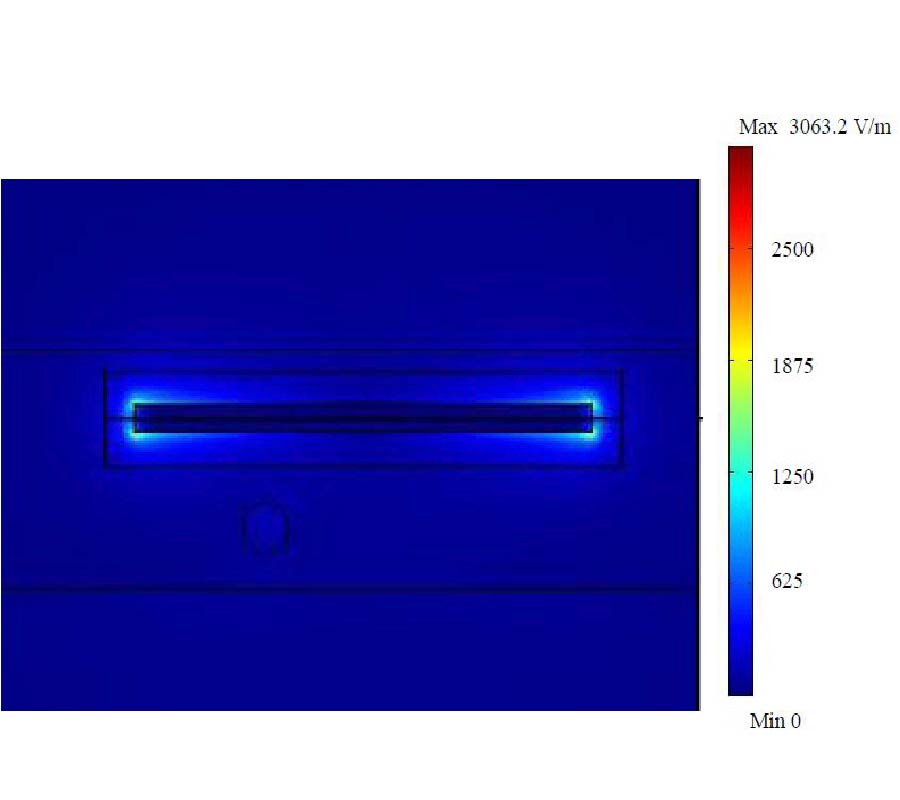
EC Modelling and Enhancement Signals in CFRP Inspection
Giuseppe Megali,
Diego Pellicano,
Matteo Cacciola,
Salvatore Calcagno,
Mario Versaci and
Francesco Carlo Morabito
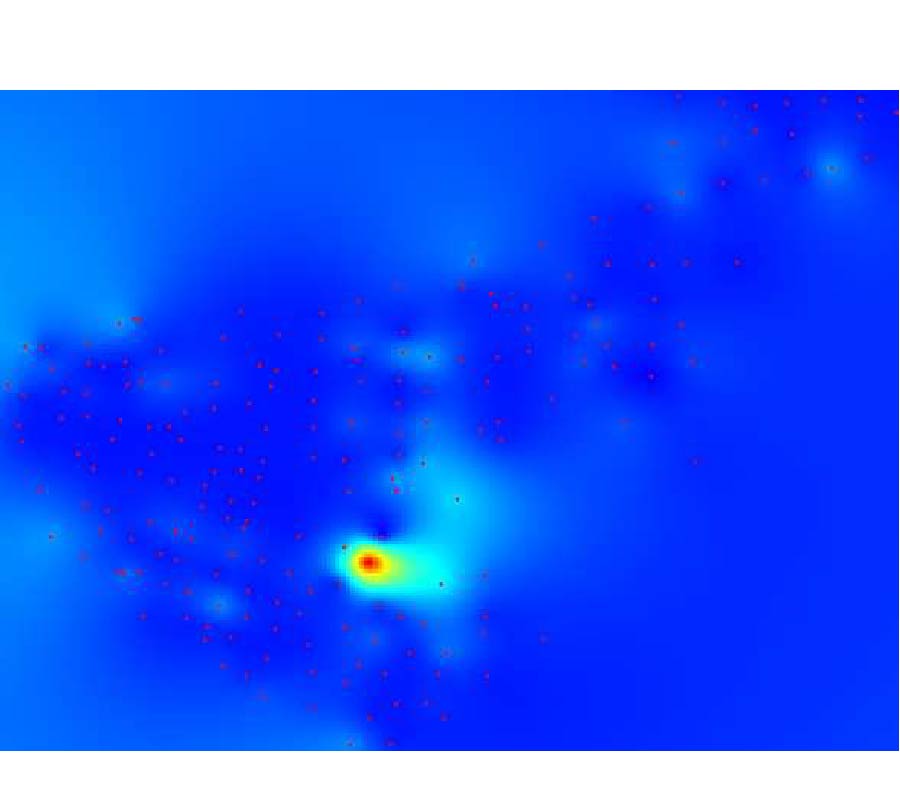
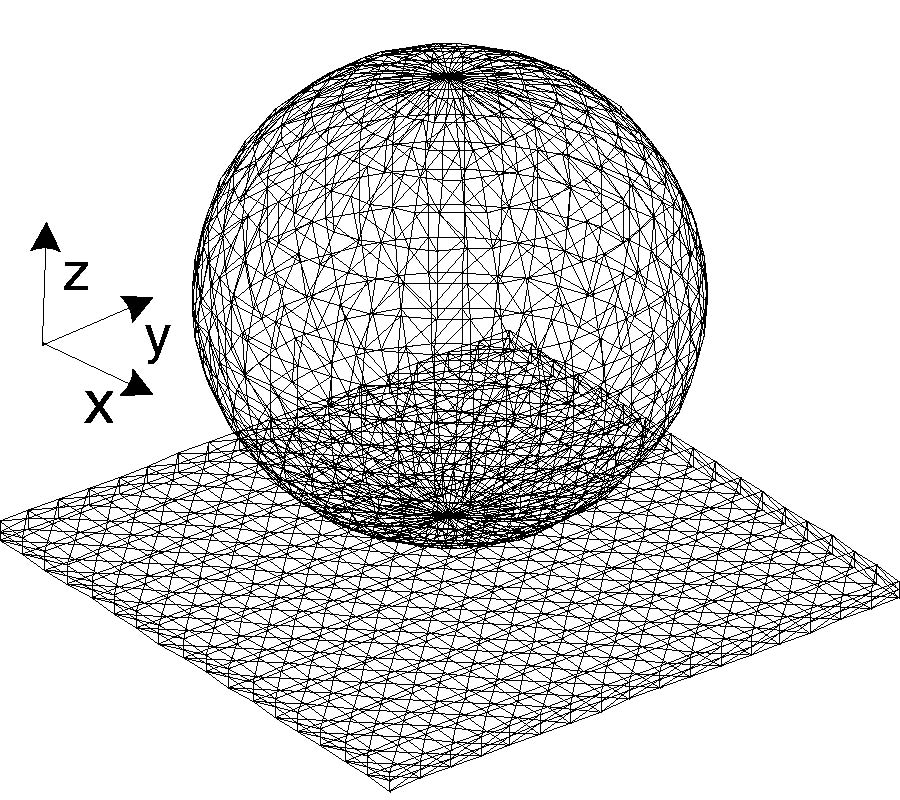
Non Destructive Testing techniques are more and more exploited in order to quickly and cheaply recognize flaws into the inspected materials, specially for carbon fiber reinforced polymers in recent years. Their production which are widely used both in civil and military applications, is an elaborate process un-free from faults and problems. Problems during the manufacturing, such as plies' overlapping, can cause flaws in the resulting material, this way compromising its integrity. Within this framework, this work aims to propose a design of ferrite core probe for eddy current non destructive evaluation, in order to investigate the presence of defects in carbon fiber epoxy composite materials. In this context, modelling is a powerful tool for inspection improvements. It helps probe-coil designers to optimize sensors for each examination requirement, providing better understanding of the involved physics, supporting operator training and increasing defect analysis reliability. Particularly, Finite Element based analyzes will be carried out into this path. After this step, in order to improve the quality of simulated measurement, a filtering technique has been exploited in order to improve the accuracy and performance of the flaw detection.