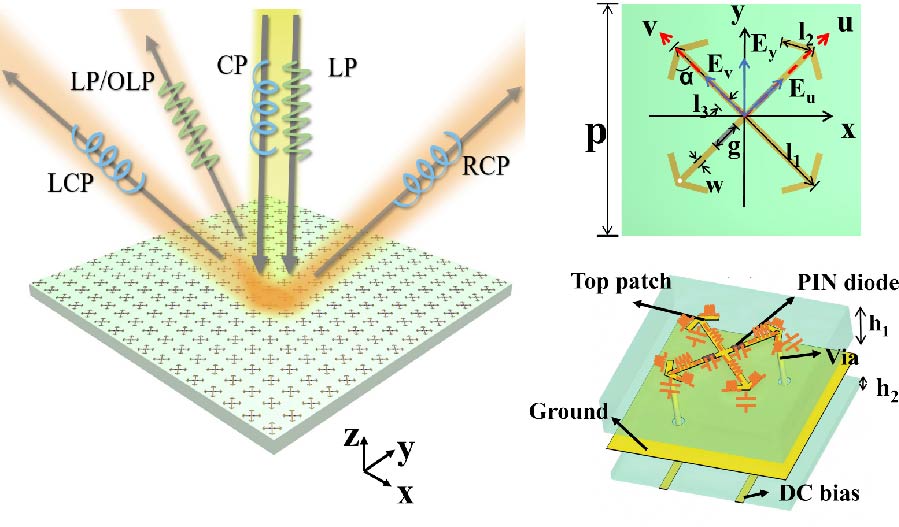
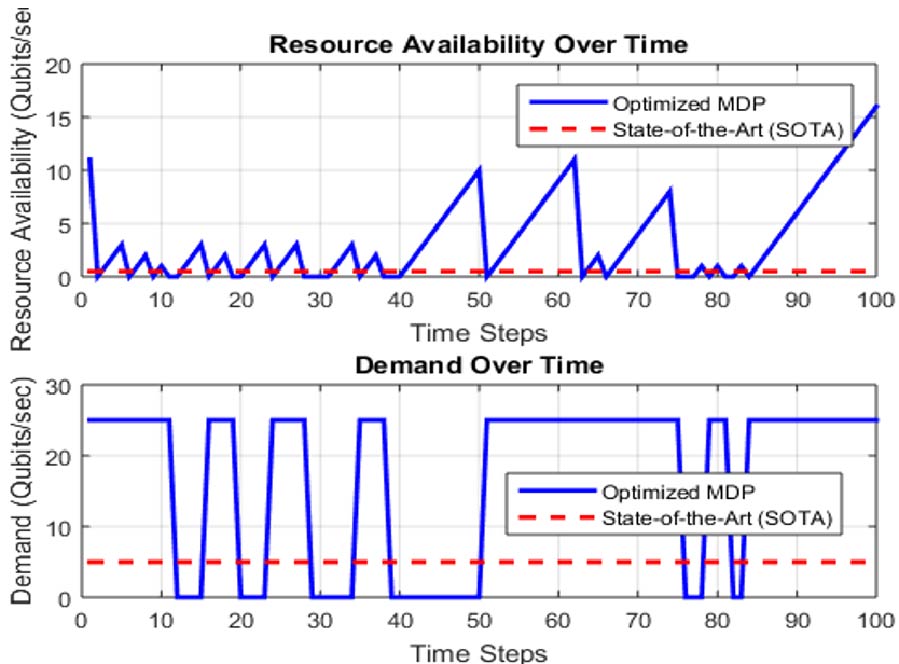
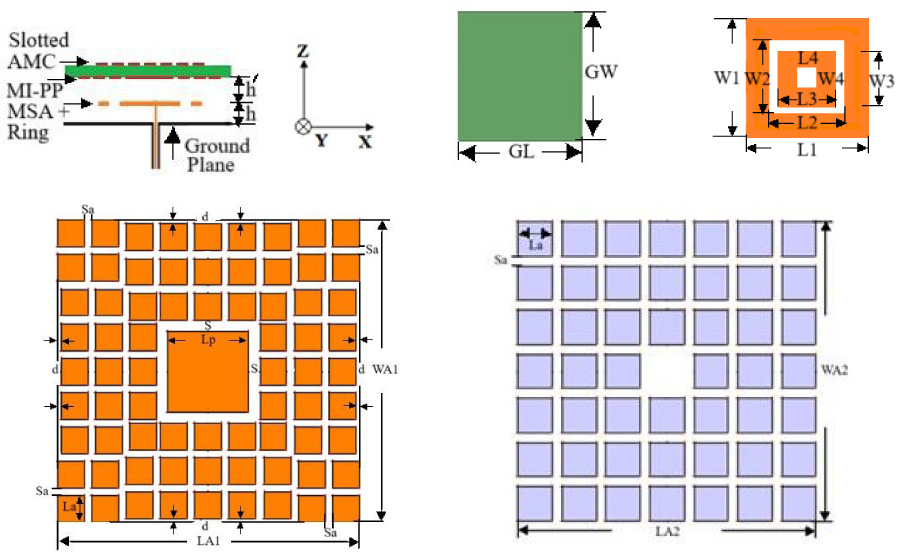
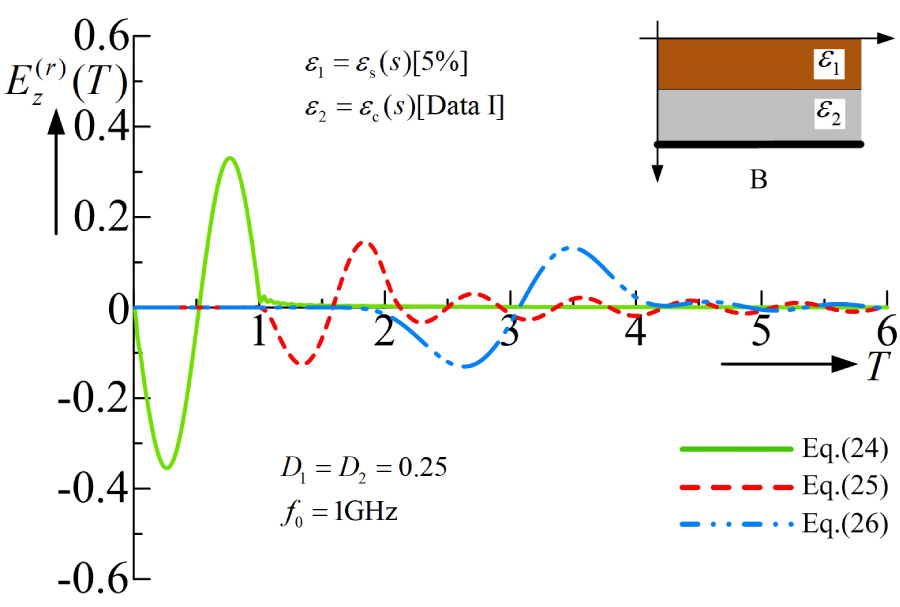
2025-10-28 Latest Published
By Deyu Guo
Yan Zhang
Tengfei Ma
Xinhua Zhu
Sailing He
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 135, 100-111, 2025
Abstract
This study addresses the challenge of detecting Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in children, where clinical diagnostic scales used in practice suffer from subjectivity and high costs. Eye tracking (ET), as a non-contact sensing technology, offers the potential for objective ASD recognition. However, existing studies often use specially crafted visual stimuli, making them less reproducible, or rely on the construction of handcrafted features. Deep learning methods allow us to build more efficient models, but only a few studies simultaneously focused on visual behaviors of ASD in both temporal and spatial dimensions, and many studies compressed the temporal dimension, potentially losing valuable information. To address these limitations, this study employed a relatively lenient visual stimulus selection criterion to collect ET data of ASD in social scenes, enabling analyses to be conducted both temporally and spatially. Findings indicate that the spatial attention distribution of ASD is more dispersed, and gaze trajectories are more unstable in the temporal dimension. We also observed that children with ASD exhibit slower responses in gaze-following scenarios. Additionally, data loss emerges as an effective feature for ASD identification. We proposed an SP-Inception-Transformer network based on CNN and Transformer encoder architecture, which can simultaneously learn temporal and spatial features. It utilized raw eye-tracking data to prevent information loss, and employed Inception and Embedding to enhance the performance. Compared to benchmark methods, our model demonstrated superior results in accuracy (0.886), AUC (0.8972), recall (0.82), precision (0.95), and F1 score (0.8719).