Wearable Dual-Band Frequency Reconfigurable Patch Antenna for WBAN Applications
Umar Musa,
Shaharil Mohd Shah,
Huda Bin Abdul Majid,
Mohamad Kamal Abd Rahim,
Muhammad Sani Yahya,
Zainab Yunusa,
Abubakar Salisu and
Zuhairiah Zainal Abidin
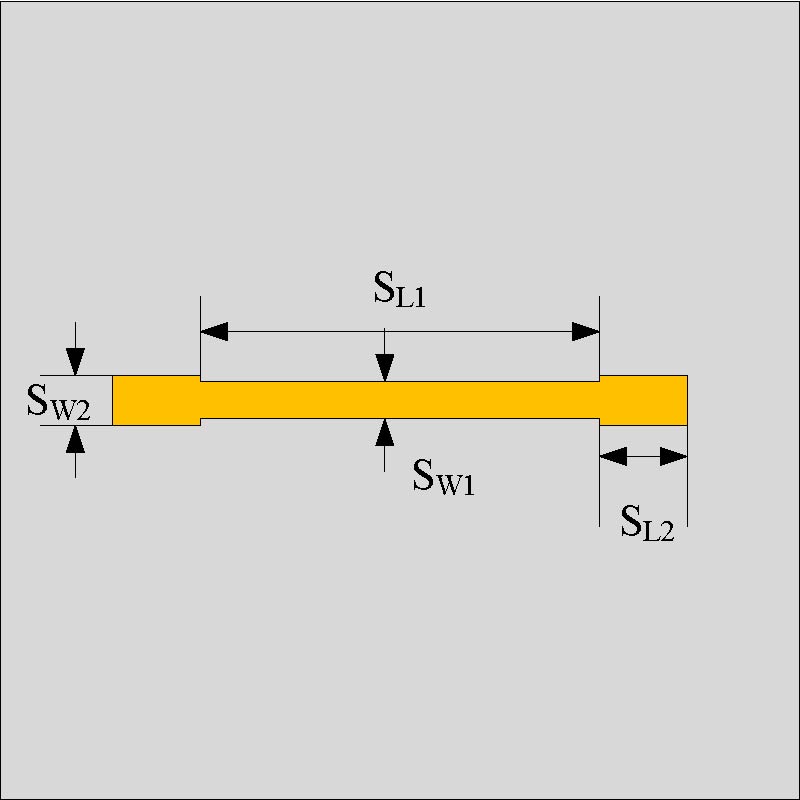
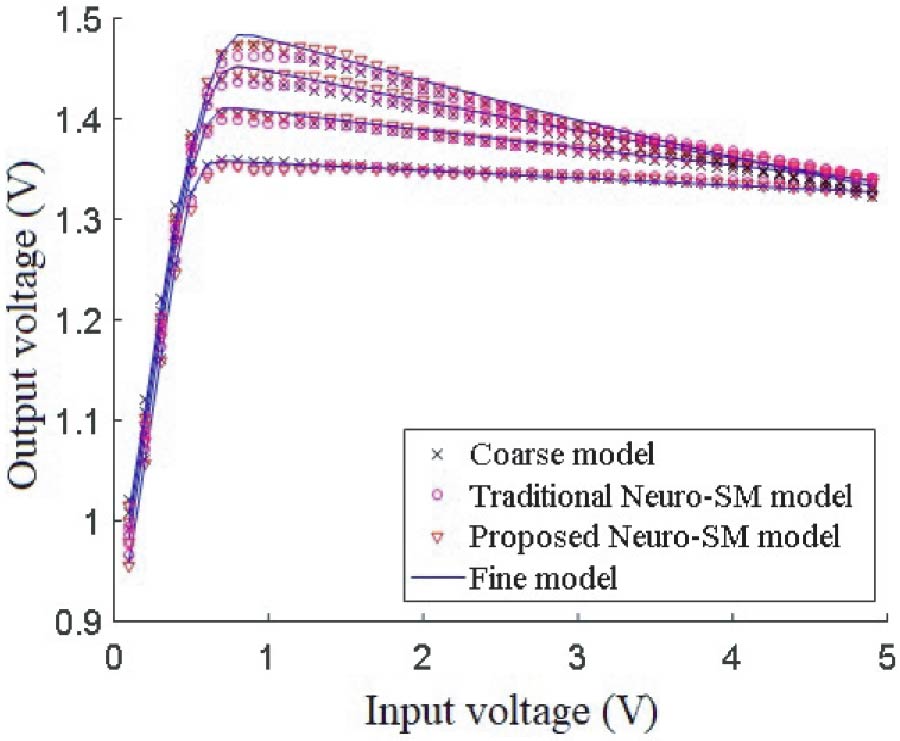
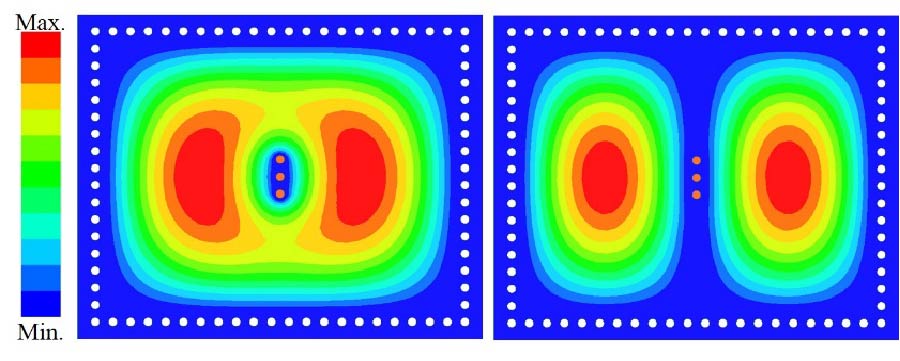
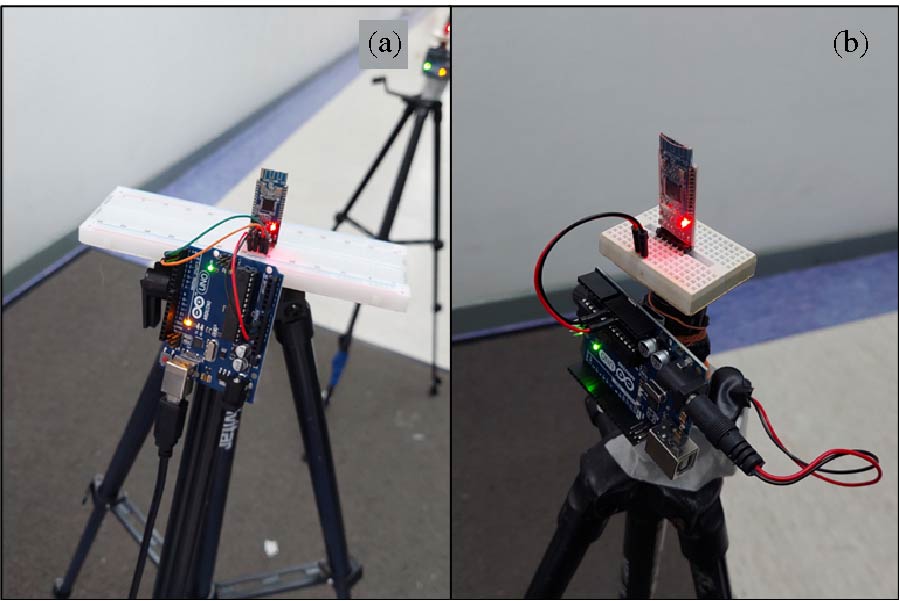
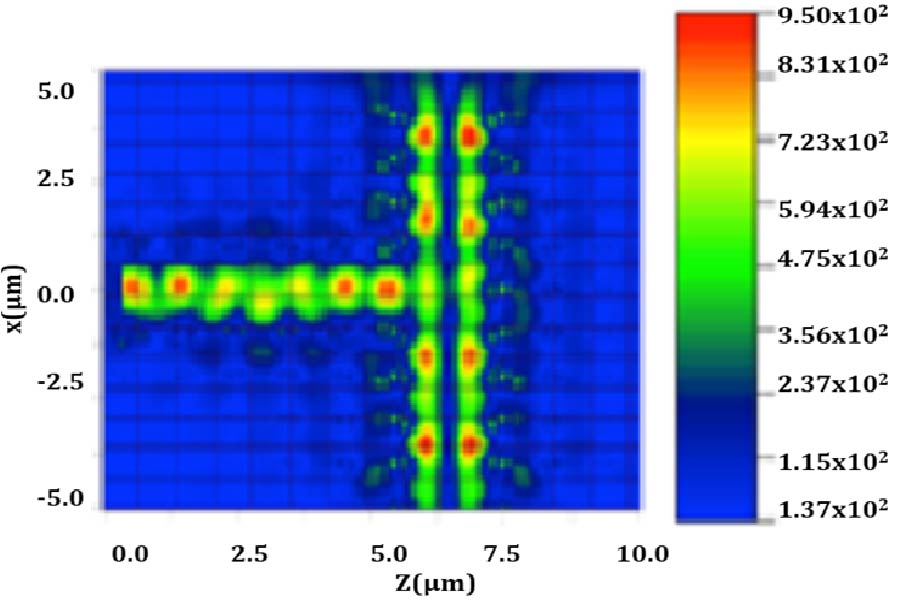
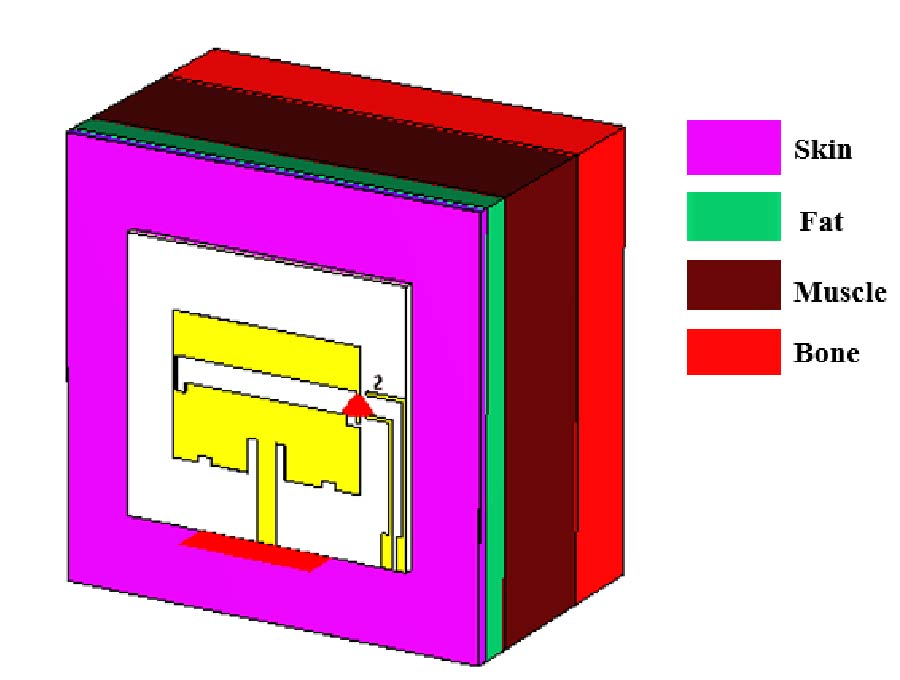
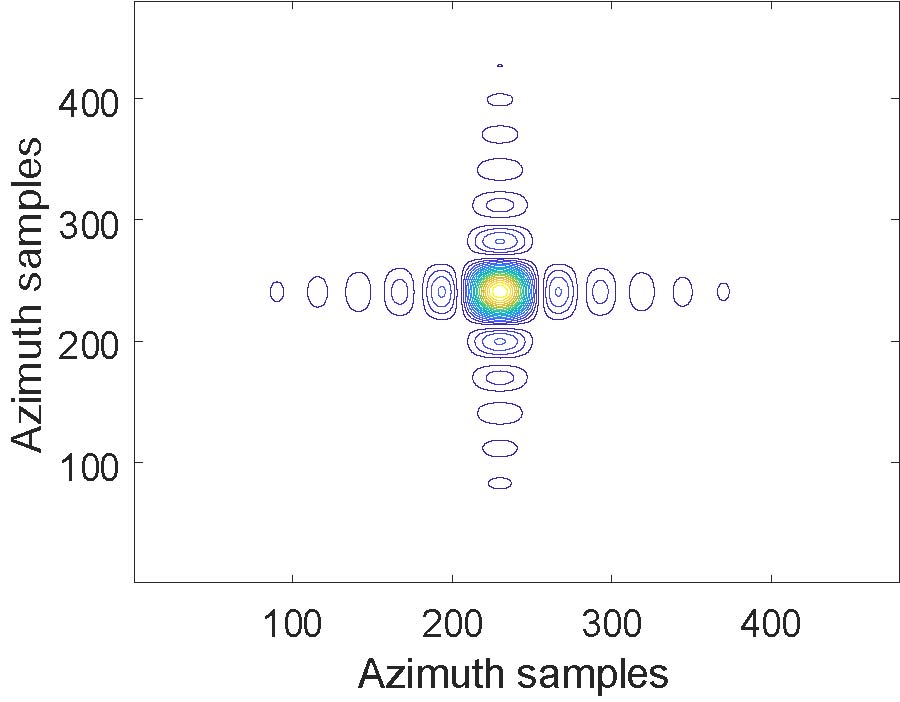
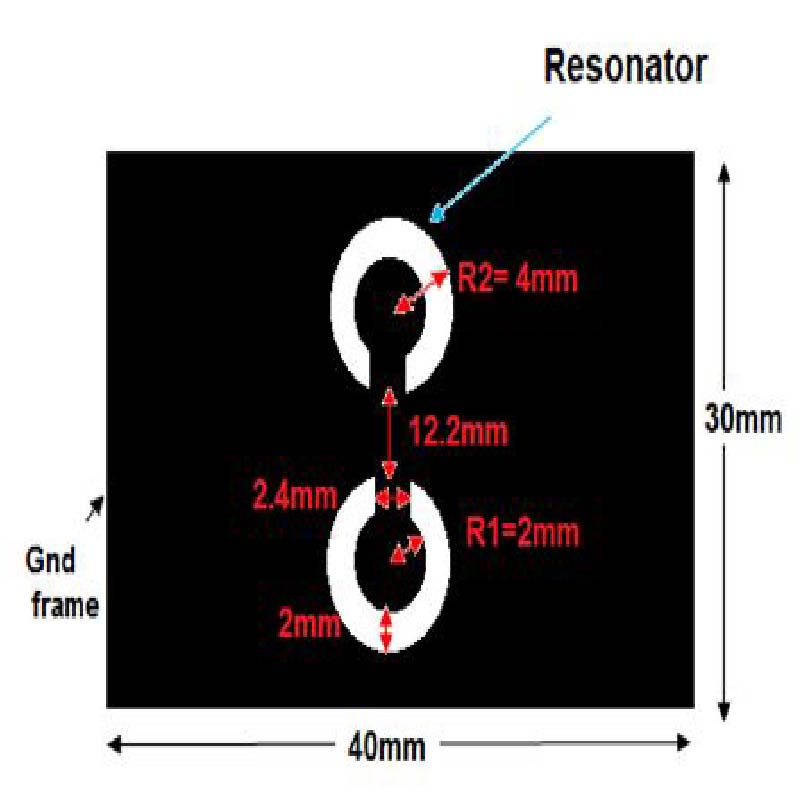
A wearable dual-band patch antenna is presented, which can adjust its frequency for WBAN applications. Frequency reconfiguration is achieved by the antenna through the utilization of the switching properties of a PIN diode. Produced using a Rogers Duroid material with semi-flexible properties, the antenna has a size of 0.33λ0 × 0.35λ0 × 0.012λ0. Initially resonating at 5.8 GHz, a slot in the shape of an inverted letter U is included to introduce a dual-band operation at 2.4 GHz. By controlling the PIN diode's ON and OFF states, the antenna can switch between single-band (ISM 5.8 GHz) and dual-band (ISM 2.4 GHz and 5.8 GHz) operations. The antenna exhibits a bi-directional radiation pattern at 2.4 GHz and a directional pattern at 5.8 GHz. In the ON state, the antenna achieves a peak gain and total efficiency of 4.84 dBi, 5.87 dBi, 92.5%, and 92.7% at 2.4 GHz and 5.8 GHz, respectively. In the OFF state at 5.8 GHz, a peak gain and total efficiency of 6.01 dBi and 91.8% are measured. To evaluate its suitability for WBAN applications, the antenna's performance is assessed by measuring SAR values on a human tissue model. At 2.4 GHz, the SAR values for 1/10 g of human tissue are 0.411/0.177 W/kg respectively. Similarly, at 5.8 GHz, the SAR values are 0.438/0.158 W/kg respectively. The SAR values comply with the established standards of the FCC and ICNIRP for both resonance frequencies for human tissue weighing 1/10 g. Overall, the antenna boasts a compact size, acceptable SAR values, and satisfactory gain and efficiency across all operating bands, surpassing previous works. It also benefits from a simplified design employing a single switch, and the antenna remains a suitable choice for WBAN applications considering its other advantageous characteristics mentioned above.