A Novel Approach to Design of Microstrip UWB Bandpass Filter Using Modified Genetic Algorithm
Huaxia Peng,
Junding Zhao,
Hao Zhang,
Minxian Du,
Yufeng Luo,
Xin Wang and
Wenhai Wang
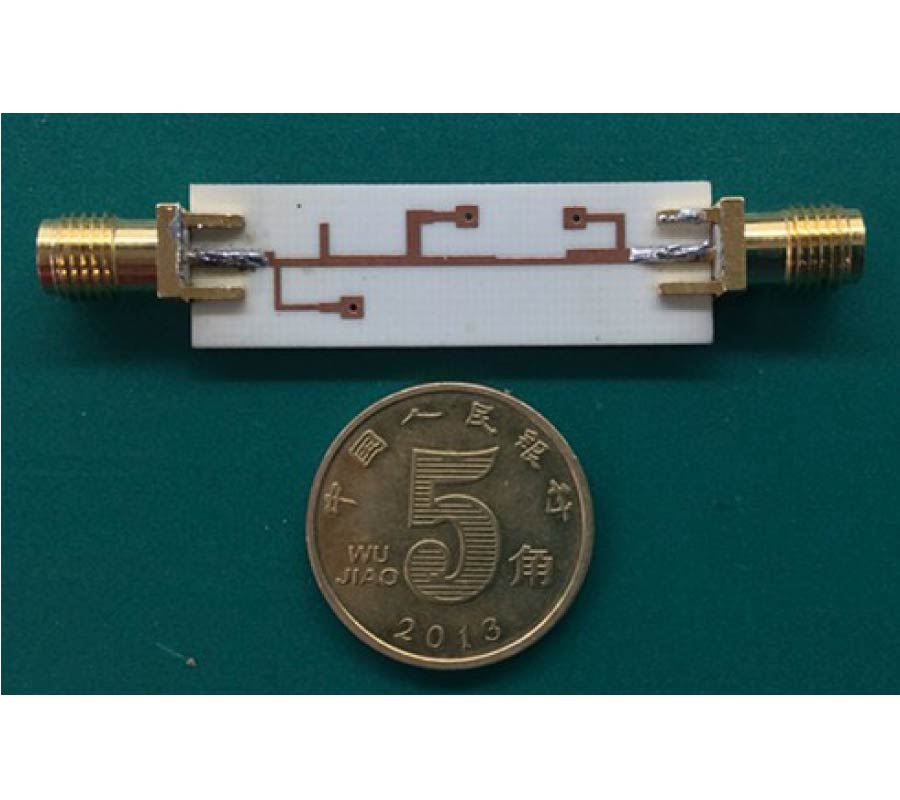
A novel approach to design microstrip ultra-wideband (UWB) bandpass filter (BPF) using modified genetic algorithm (MGA) is proposed in this paper. To achieve high efficiency and accuracy, conventional GA is modified. By improving the fitness evaluation, selection, crossover, and mutation, the two possible drawbacks of conventional GA, i.e., slow rate of convergence and local-best solution, are overcome. The modified genetic algorithm is then applied to simultaneously search for the appropriate circuit topology and the corresponding electrical parameters with UWB characteristic. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the novel approach, a new microstrip UWB BPF is designed and fabricated. Measurement results agree well with the design index and full-wave EM simulated results.