2011-06-22 Latest Published
By Sanhai Ren
Wenge Chang
Xiangjun Liu
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 18, 259-269, 2011
Abstract
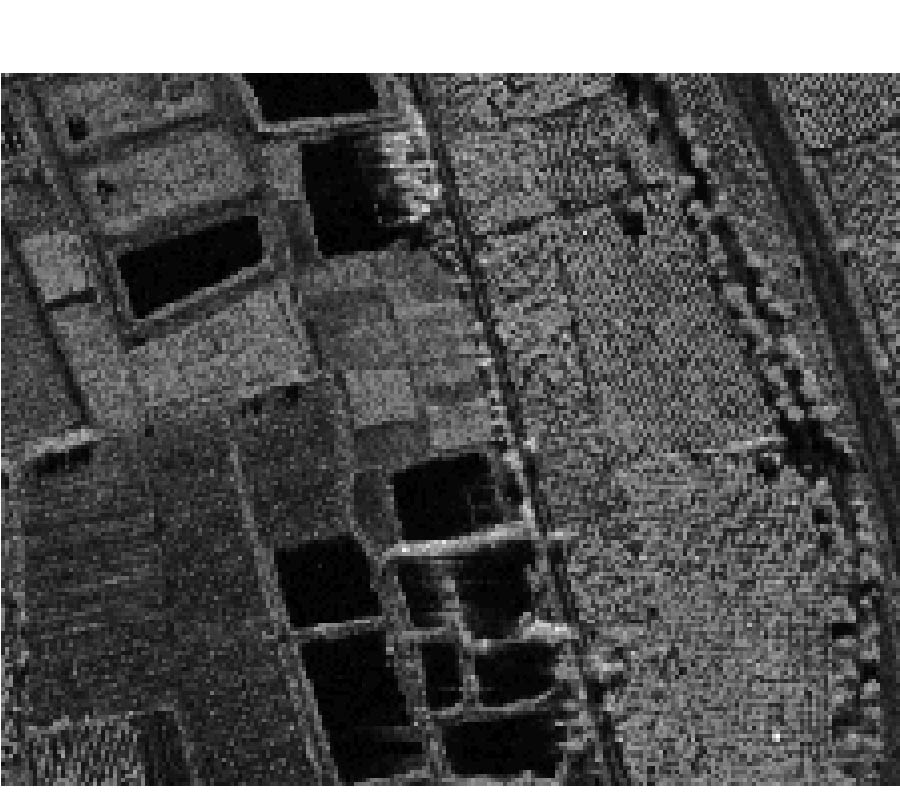
In order to ensure that SAR scene matching aided navigation system can acquire the position errors and yawing errors simultaneously, we propose an image matching algorithm based on Scale Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT). However, the SIFT is proposed for optical image, and its performance degrades when used in SAR image. To enhance the adaptability of SIFT, two ways are employed. One is the application of a preprocessing on image pairs before matching. The other is the establishment of a scale and rotation restriction criteria on tie-points after SIFT matching. Compared with other matching methods, experiment results show that the proposed method is much more suitable for SAR image and successes in matching performance improvement. Furthermore, the method can meet the real-time requirement.