2022-06-10 Latest Published
By Suman Sharma
Mukesh Arora
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 110, 235-247, 2022
Abstract
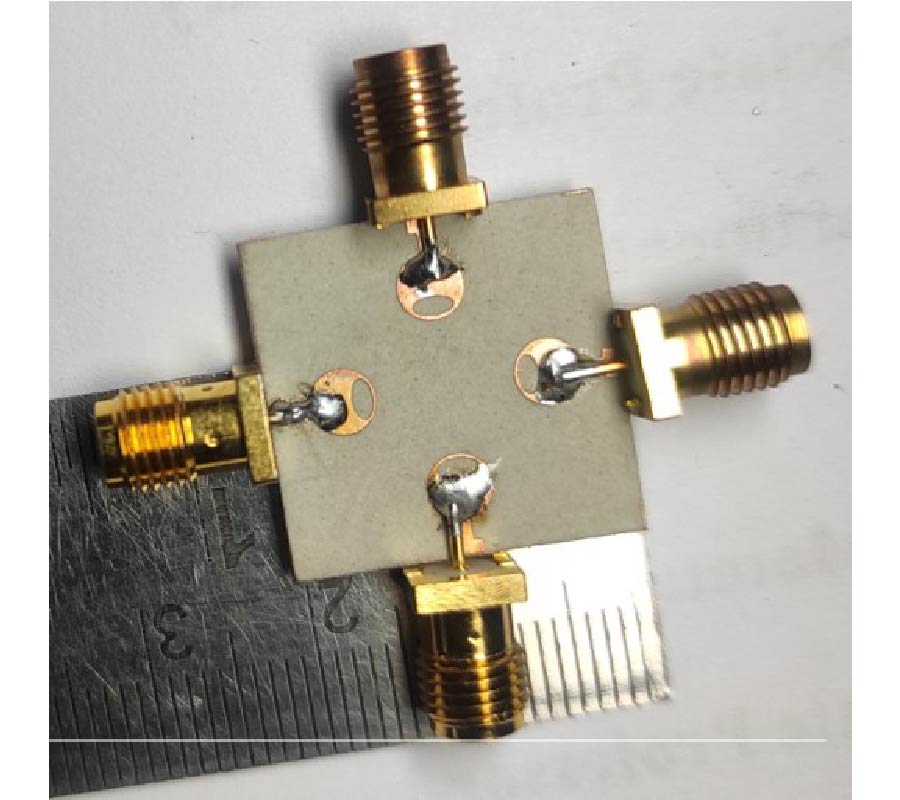
This paper proposes a 4-port MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) antenna operating at 28 GHz in the millimeter wave band for future 5G communications. The first design in this work is a single-element circular shaped microstrip patch antenna with an elliptical slot and a defected ground structure which is intended for 28 GHz band. This antenna is compact with a size of 6 mm × 7 mm. A complete analysis of single patch element antenna is presented with effect of slot and defected ground structure in Section 2. In Section 3, the second design, which is symmetric two-element MIMO slotted circular patch antennas, is analyzed with the dimension L x W as 7 mm x 6 mm. In Section 4, the final fabricated design is presented, which is a 4-port MIMO antenna operating at resonance frequency of 28 GHz along with the improved isolation between the elements due to appropriate spacing. The proposed 4 port MIMO antenna is designed on a Rogers Duroid 5880 substrate having a relative dielectric permittivity of 2.2 and thickness of 0.8 mm. The overall dimension of this designed MIMO antenna is 20×20×0.8 mm3. Simulated results for the S-parameters and radiation pattern are presented for all purposed designs using CST software. Measured results are also presented for the return loss using Rhode & Schwarz ZVA 40 vector network analyzer. Simulated and measured results show a good agreement. The simulation results demonstrate that the return loss at individual port is less than -10 dB in the frequency range of 26.867–28.975 GHz, and it provide a bandwidth of 2.1 GHz. The antenna has a high gain of 9.24 dB with unidirectional radiation pattern, and each element has a mutual coupling less than -20 dB.