Design of a W-Band Dual-Circular-Polarization Monopulse Cassegrain Antenna for Polarization Detection of Radar Target
Xin Li,
Kun Gao,
Ying-Chao Zhao,
Jian Yuan,
Jie Cheng and
Yuan-Yuan Wang
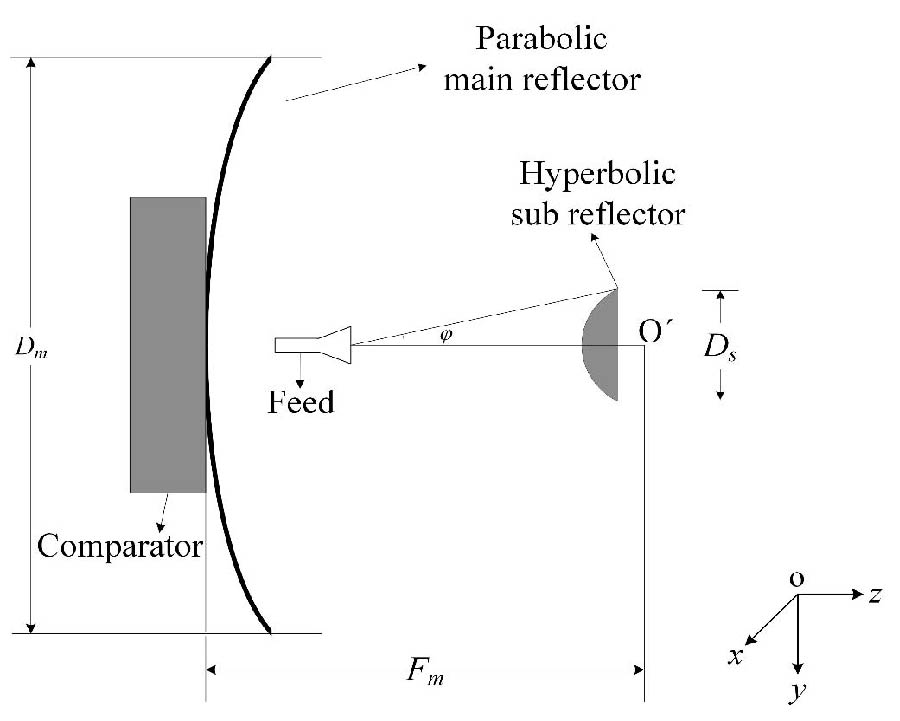
A W-band dual-circular-polarization (dual-CP) monopulse Cassegrain antenna for polarization detection of radar target is presented in this letter. The proposed antenna consists of a main reflector, a sub reflector, a dual-CP feed source based on the septum polarizer, and a comparator. Two orthogonal circular-polarized signals [left-hand circular polarization (LHCP) and right-hand circular polarization (RHCP)] electromagnetic wave can be transmitted and received simultaneously by this antenna. The principle of the antenna is introduced and analyzed, and then a prototype of the antenna is simulated, fabricated, and measured. Measured results are in good agreement with the simulated ones. At 94 GHz, the gains of the LHCP and the RHCP sum beam (SUM beam) are 38.6 dBi and 38.8 dBi counting the insertion loss of the comparator, which indicates that the radiation efficiency is better than 44.2%. The 3-dB beamwidth is about 1.5° with a sidelobe level (SLL) of -16.6 dB, and the axial ratio is lower than 1.43. A null depth of -26 dB for the difference beam (DIFF beam) is observed, and the gain ratio between the LHCP monopulse beams is 5.9 dB. Measured results demonstrate that the proposed antenna is very applicable in the polarization detection of radar target at W-band.