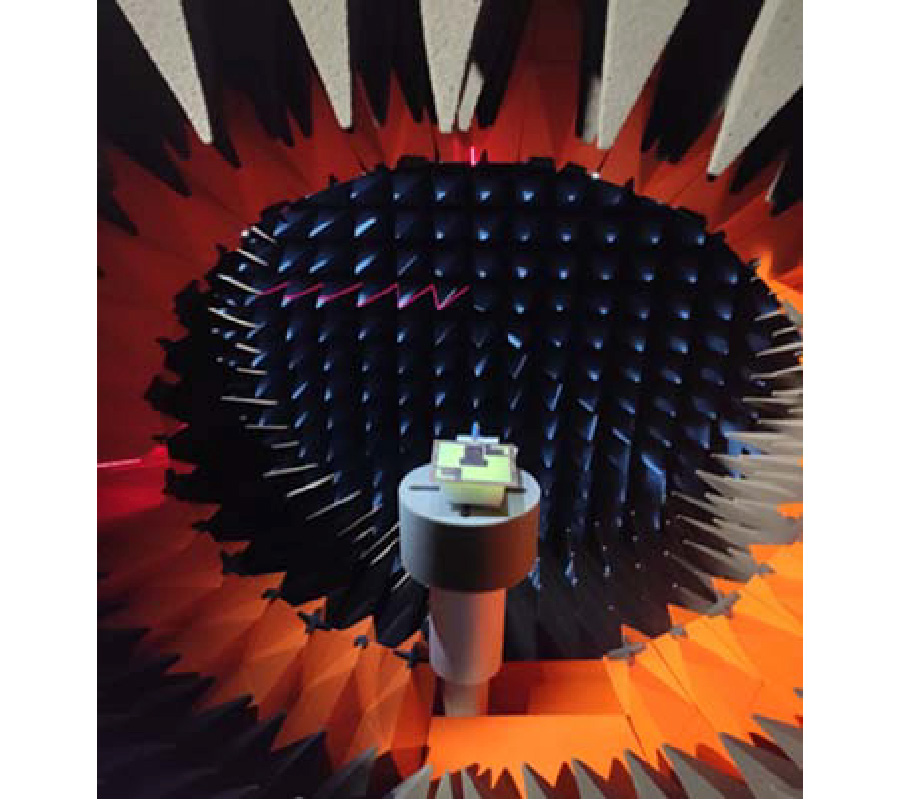
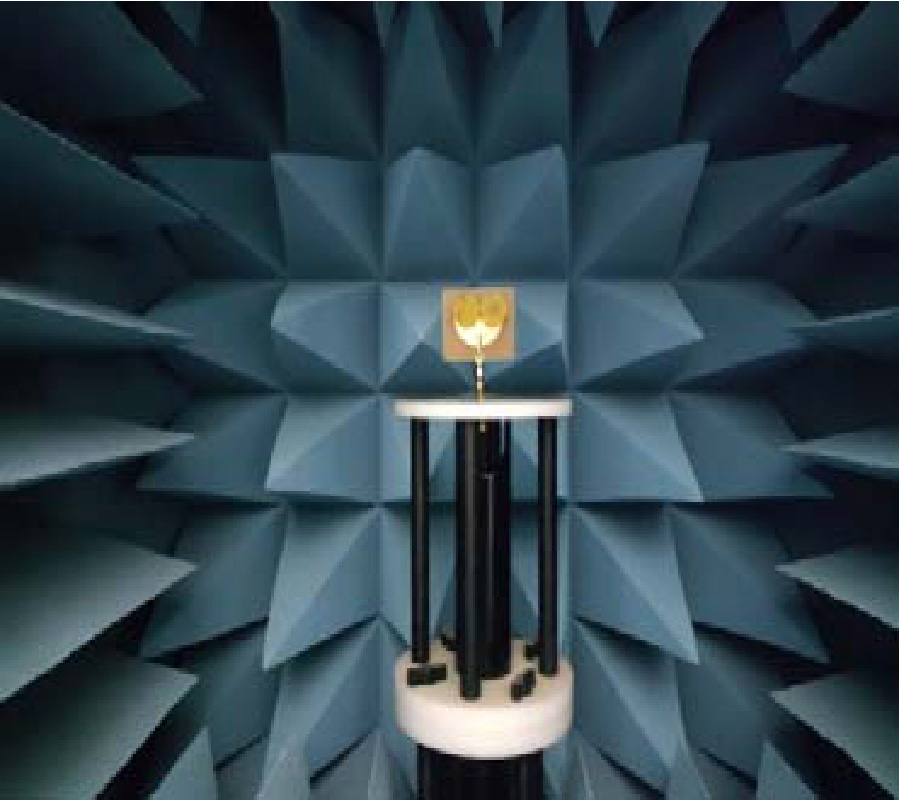
Design of a 3-Port Compact MIMO Antenna Based on Characteristics Mode Analysis Approach
Asutosh Mohanty and
Bikash Ranjan Behera
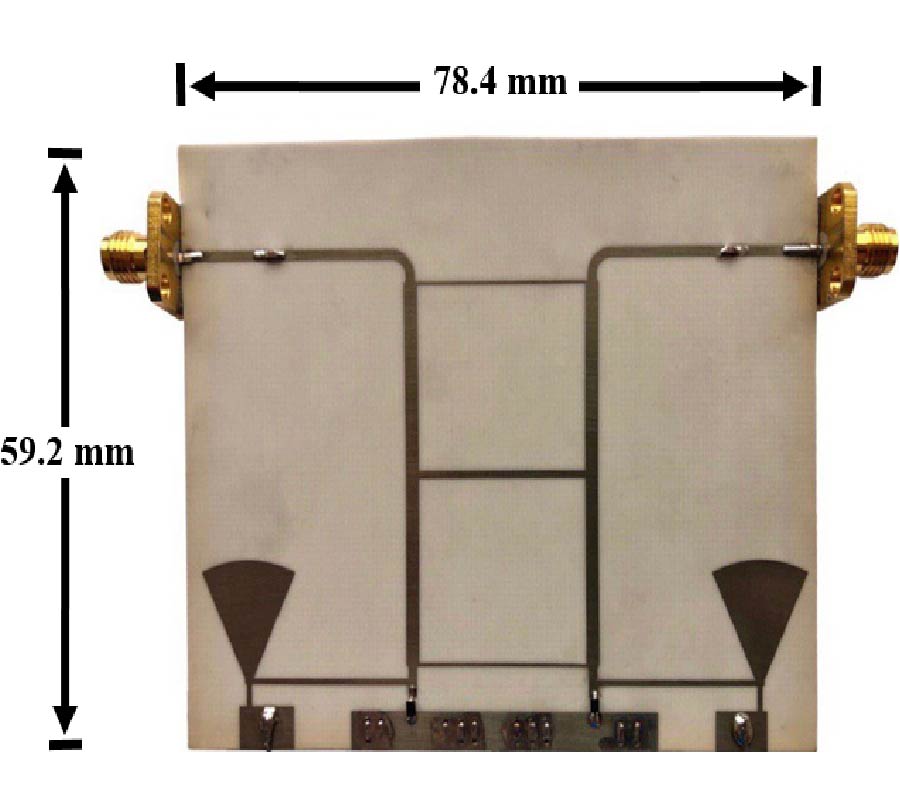
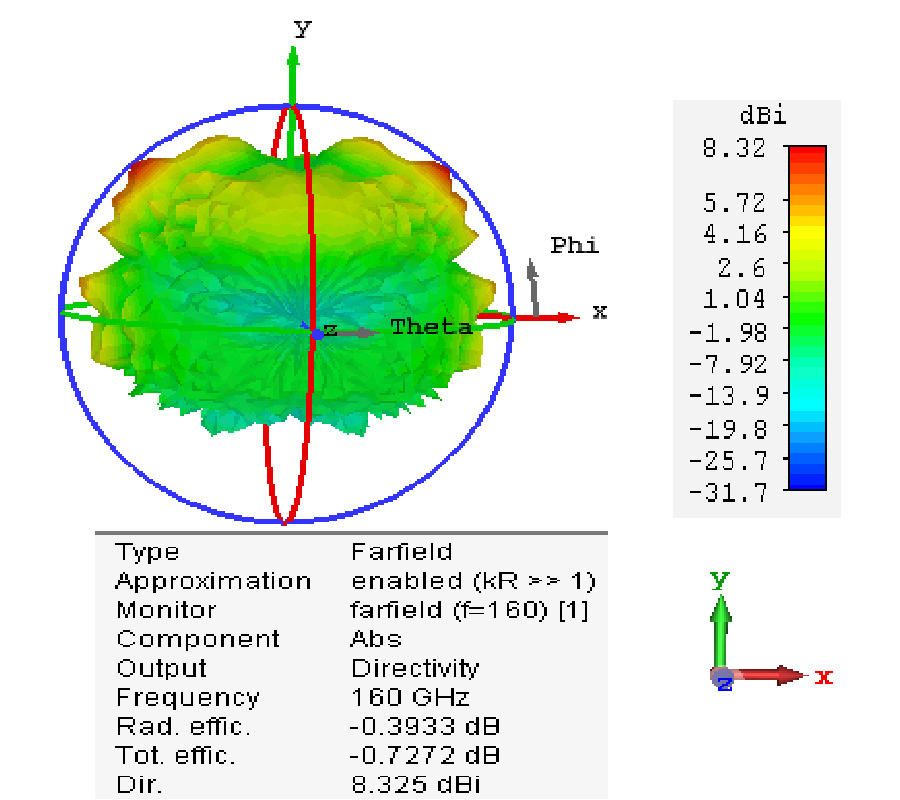
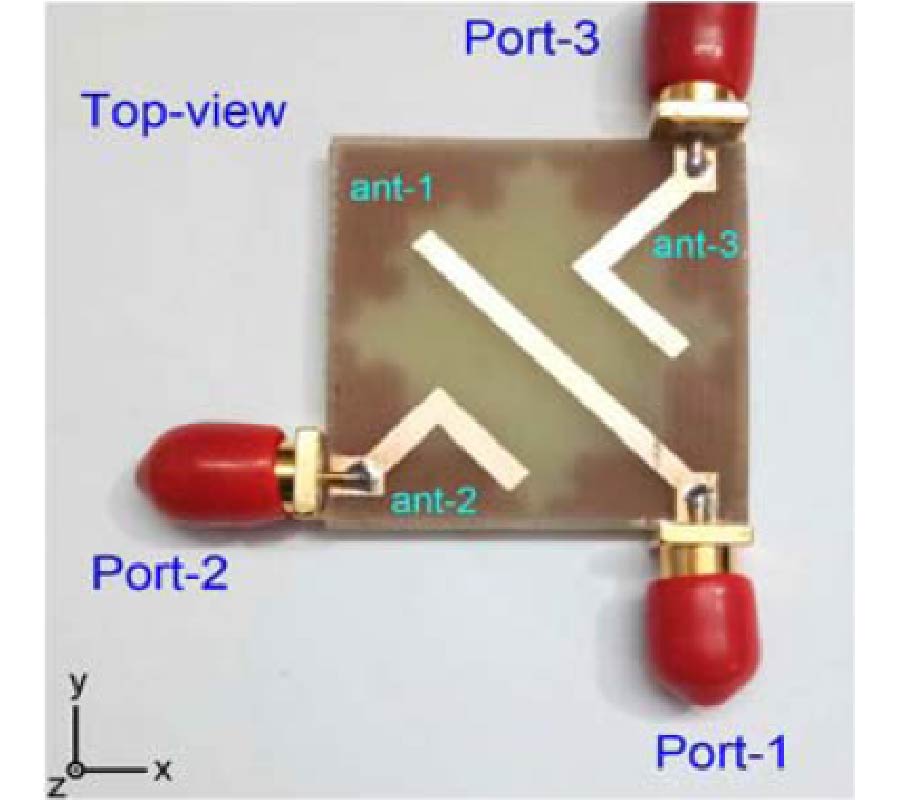
In this paper, a 3-port compact MIMO antenna is designed using Characteristics Mode Analysis (CMA). It consists of three antenna elements. Ant-1 is 45˚ tilted, and Ant-2 and Ant-3 has L-bend transitions. Ant-2 is 1/4th, and Ant-3 is 1/2 in size w.r.t. Ant-1. To improve 10-dB impedance bandwidth and isolation > 17 dB, fractal slot is etched at bottom, and deformity in antenna structures has three distinct modes. Ant-1 operates in UWB mode from (4.8-10.6) GHz with 75.32% IBW, and Ant-2 and Ant-3 operate in wide-band mode from (8.1-10.8) GHz with 28.57% IBW and from (7.2-9.8) GHz with 30.58% IBW. CMA is utilized to investigate the anonymous behaviour of antenna, predicts modal significance (MS), characteristics angle (CA) and eigen values (EV). From these parameters bandwidth potential, radiation energy source and Q-factor are estimated. For investigations first six modes are swept in modal navigator, where dominant modes are traced as ideal antenna resonant modes, and unwanted modes are neglected. The antenna gain is (3-7) dBi with ECC < 0.08. The proposed antenna is fabricated and measured for validation. From the outcomes, it is found suitable for UWB, air traffic and defense tracking, meteorological, amateur satellite, maritime vessel traffic controlling, and X-band satellite applications.