Performance Enhancement of High-Gain STDA Antennas with Reflector for 4G LTE and Sub-6 GHz 5G Applications: Design, Measurement, and Analysis
Mohd Wasim,
Shelej Khera,
Tanvir Islam,
Praveen Kumar Malik,
Sivaji Asha and
Sudipta Das
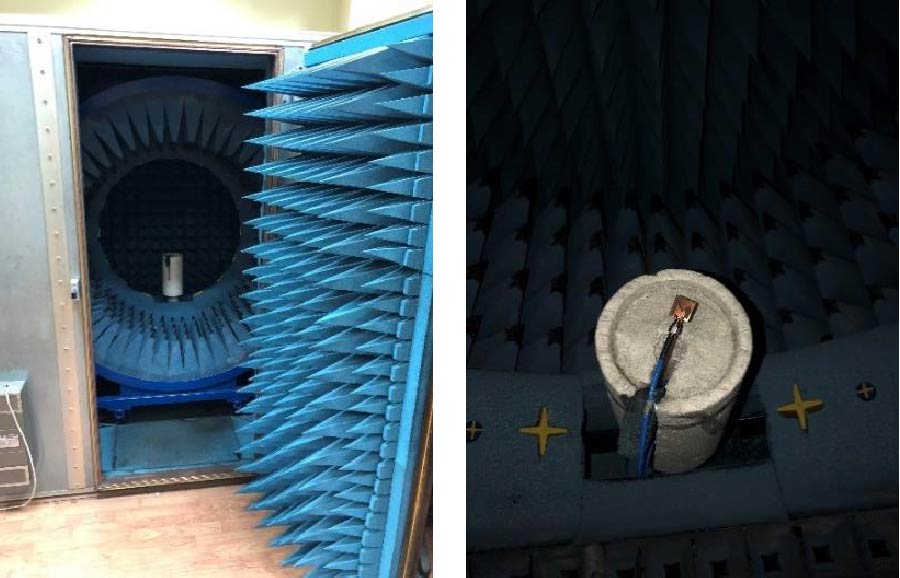
The paper focuses on the design, measurement, and performance analysis of a high-gain cross-orthogonal series fed two dipole antenna (STDA) arrays with side-wall reflectors. The antenna is specifically designed for 4G Long Term Evolution (LTE) and sub-6 GHz 5G band applications. The designed antenna is capable of operating at multiple frequencies aiming to support 4G LTE and the sub-6 GHz 5G application bands. To improve the radiation characteristics and prevent coupling effects in the presence of side-wall reflectors, parasitic strip pair directors are included in the antenna design. Furthermore, the performance of the designed STDA is evaluated by forming different array configurations, such as 2×1, 2×2, and 2×3 arrays. The various array configurations are proposed to investigate the effect of the projected array arrangements on the radiation pattern, impedance bandwidth, and gain characteristics. The results of the measurements show that the radiation characteristics of the antenna has improved significantly. The proposed antenna operates at six distinct frequencies for S11≤-10 dB. The operating frequencies at 1.8, 2.35, and 2.6 GHz can be utilized for LTE and 3.2, 4.2, and 5.2 GHz can support sub-6 GHz 5G bands. The antenna is characterized by its compact size, measuring around 89 mm × 71 mm, while still achieving high gain of 12.3 dB for single STDA element with parasites and with reflector. These results emphasize the importance of the proposed design, which incorporates parasitic strip pair directors and side-wall reflectors. This design methodology plays a crucial role in enhancing the performance of the prescribed STDA array for both 4G LTE and sub-6 GHz 5G applications.