A Symmetrical Circuit Model Describing All Kinds of Circuit Metamaterials
Tie-Jun Cui,
Hui-Feng Ma,
Ruo Liu,
Bo Zhao,
Qiang Cheng and
Jessie Chin
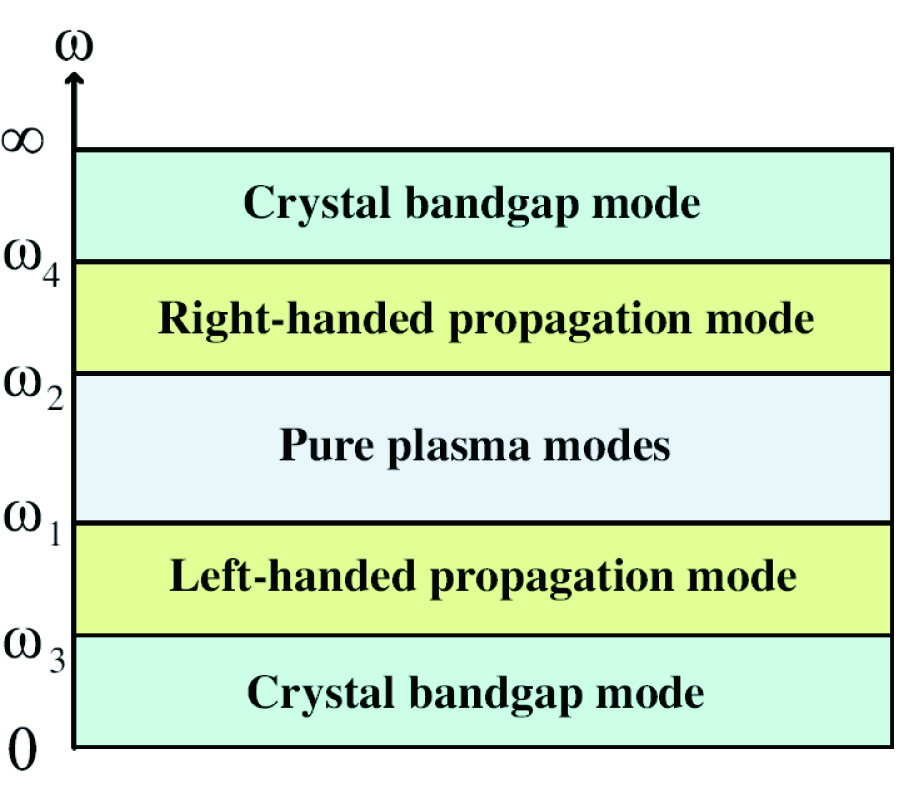
We present a generally symmetrical circuit model to describe all kinds of metamaterials with effective permittivity and permeability. The model is composed of periodic structures whose unit cell is a general T-type circuit. Using the effective medium theory, we derive analytical formulations for the effective permittivity and effective permeability of the circuit model, which are quite different from the published formulas [1, 2]. Rigorous study shows that such a generally symmetrical model can represent right-handed materials, left-handed materials, pure electric plasmas, pure magnetic plasmas, electric-type and magnetic-type crystal bandgap materials at different frequency regimes, with corresponding effective medium parameters. Circuit simulations of real periodic structures and theoretical results of effective medium models in this paper and in [1] and [2] are presented. The comparison of such results shows that the proposed medium model is much more accurate than the published medium model [1, 2] in the whole frequency band.