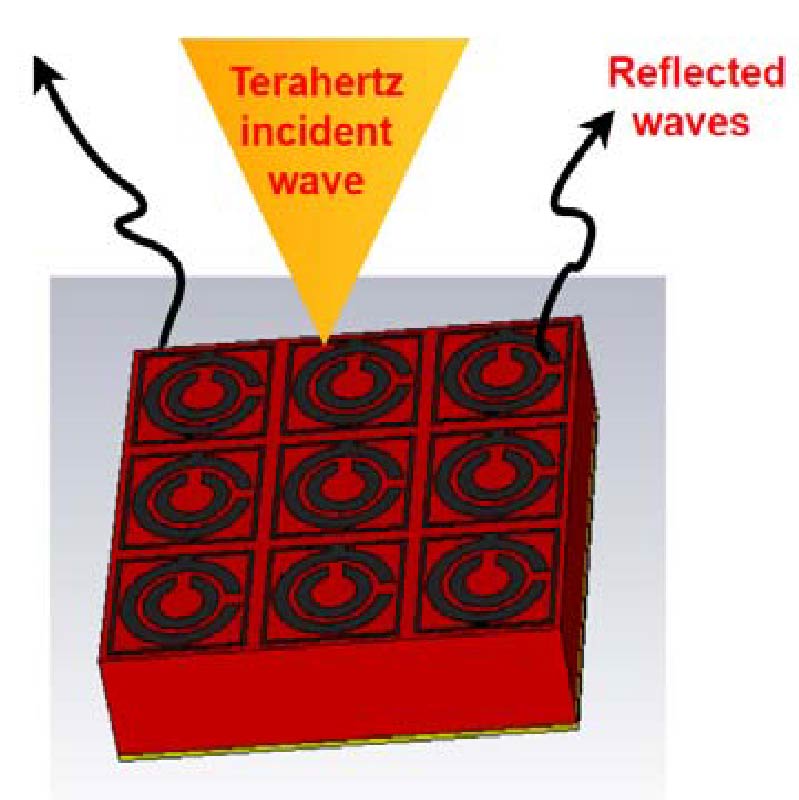
A Circular Split Ring Resonator Absorber with Graphene Material for Terahertz Communication Applications
Nagandla Prasad,
Pokkunuri Pardhasaradhi,
Boddapati Taraka Phani Madhav,
Yarlagadda Ramakrishna and
Yepuri Aarthi Hasitha
In this research article, we propose a split ring resonator (SRR) based metasurface absorber based on graphene material. The performance of the graphene-based absorber at terahertz frequencies can be altered by varying the chemical potential of graphene material. Because of its excellent tunability and optical responsiveness at terahertz frequency, graphene-based metamaterials have been widely used in optoelectronic devices, sensors, filters, and many more. The proposed structure contains three layers namely graphene-based patch as a conductive layer, lossy silicon as a dielectric layer, and finally gold as a bottom conductive layer. The proposed unit cell resonates at three different absorption peak frequencies of 2.91 THz, 8.1 THz, and 9.61 THz with operating frequency bands at (2.66 THz to 3.12 THz), (7.71 THz-8.47 THz), and (9.57 THz-9.63 THz), respectively. The purpose of this research is to present a thorough investigation of graphene-based THz metamaterial absorbers, including modeling and verification of the structure through an equivalent circuit approach. It is very much beneficial to understand the conductive phenomenon of graphene material by tuning the Fermi chemical potential and achieve a high percent level of absorption for the corresponding absorption frequency bands.