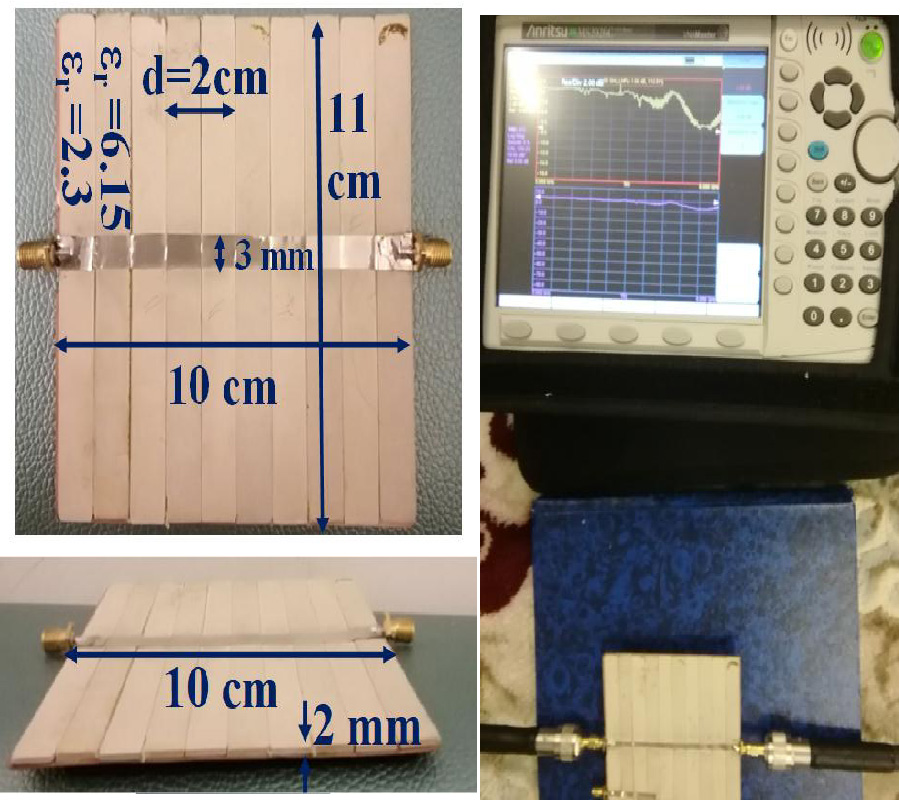
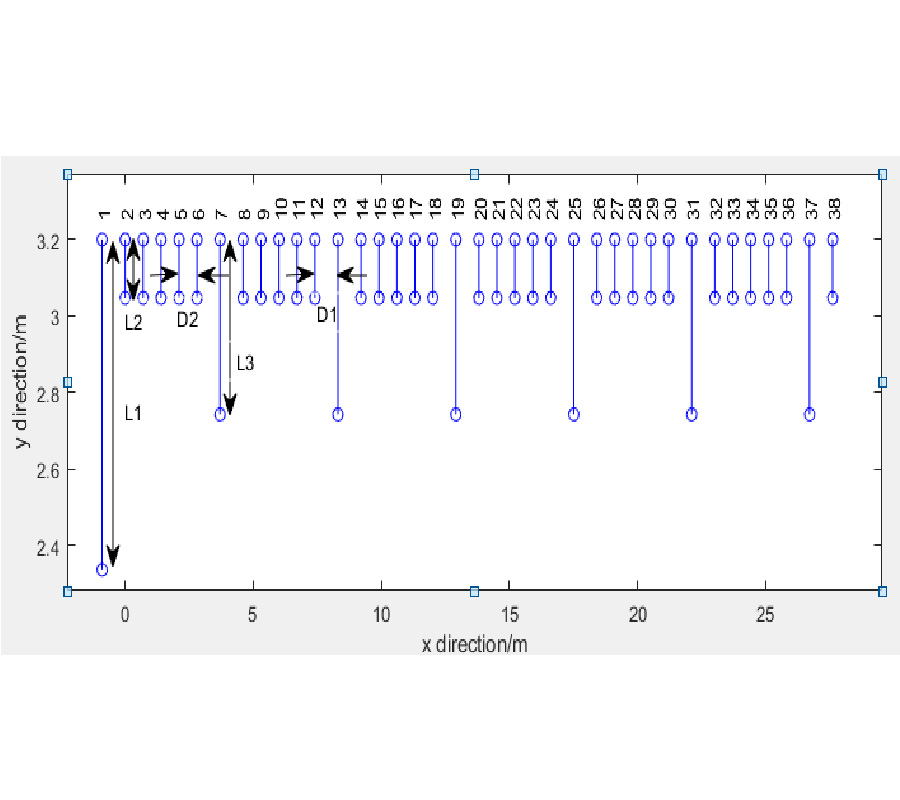
Microwave Imaging Solutions for Medical Imaging Using Re-Weighted Basic Pursuit Algorithm
Thathamkulam Anjit,
Ria Benny,
Philip Cherian and
Mythili Palayyan
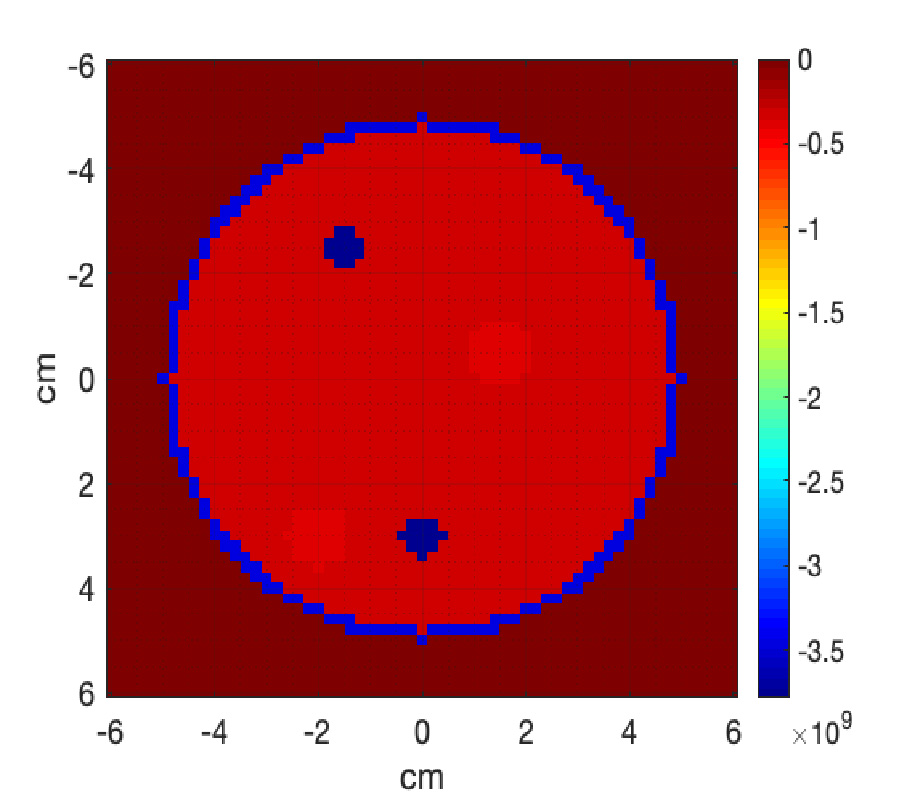
This paper describes an innovative technique for the quantitative reconstruction of the dielectric and conductivity distribution of objects in a microwave tomography framework using sparse data. The proposed method tries to extract information about the size, shape, localisation and dielectric distribution of various inclusions within the object under study using an iterative reconstruction methodology in the sparse domain. The proposed algorithm combines the Distorted Born Iteration method (DBIM) and a convex optimization technique for solving the inverse ill-posed problem. The Re-weighted Basis Pursuit (RwBP) algorithm is chosen as the convex optimization technique in this work. The performance of the proposed algorithm has been compared with the TV-norm method, and the results obtained are highly encouraging. The proposed method produces a significant reduction in the reconstruction error as compared to the TV norm method with an error value of 0.083 as against 0.32 in the case of TV norm in the presence of 25 dB noise. By accurately preserving the edges of the inclusions the proposed technique is found to provide an overall improvement in the reconstruction in terms of tissue differentiation (permittivity and conductivity), dimensions of inclusions, resolution, shape, size and coordinate localisation of inclusions. The proposed algorithm converges within 10-12 iterations as compared to other complex imaging algorithms available in the literature. Further, this proposed technique is validated using experimental data from an actual breast imaging setup. The three inclusions of 10 mm, 6 mm, and 3 mm have been localised with errors of 0.052, 0.04, and 0.09, respectively The results obtained from the real-time data show the applicability and feasibility of the proposed algorithm in breast tumor imaging application