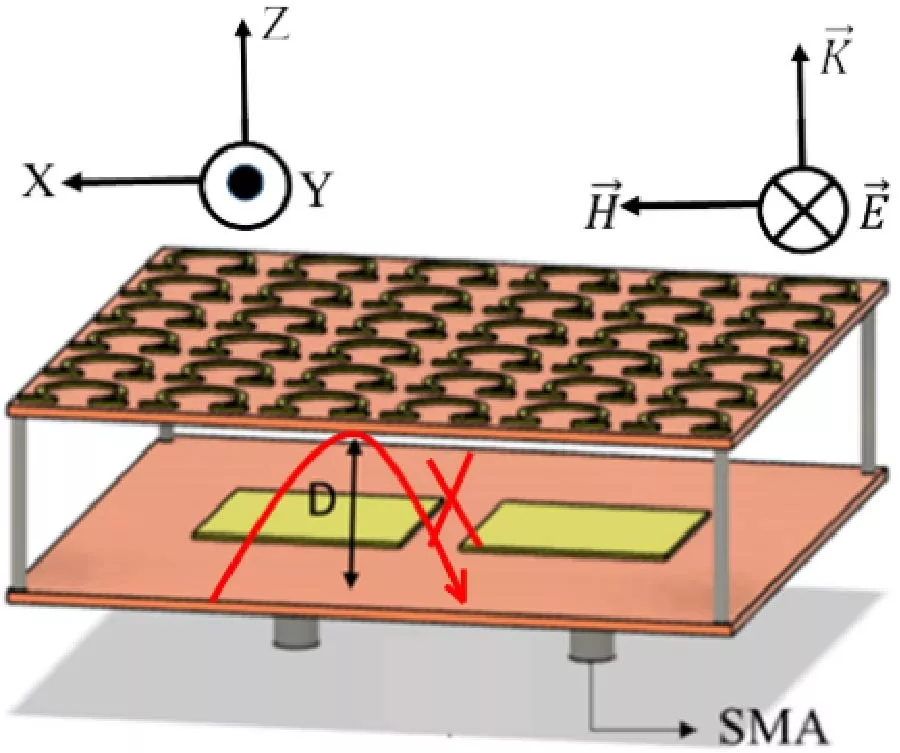
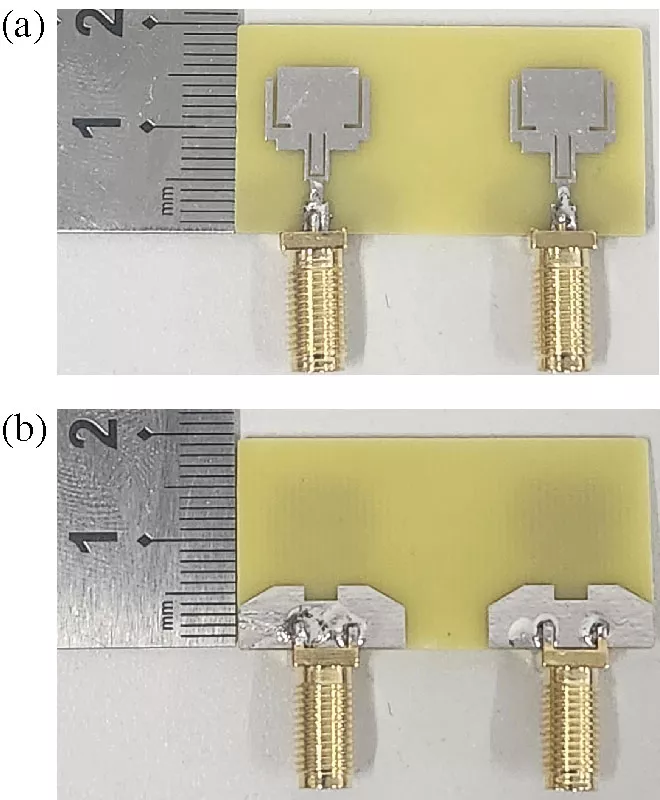
Multilayer Waveguide Bandpass Filters Based on Subwavelength CSRR and Omega Type Inclusions
Ivan Eduardo Diaz Pardo,
Juan Domingo Baena Doello,
Carlos Arturo Suarez Fajardo and
Hector Guarnizo
This paper presents the design, modeling, and experimental validation of multilayer waveguide bandpass filters employing two subwavelength resonator topologies: complementary split-ring resonators (CSRRs) and Ω-type cells. A hybrid methodology is adopted, combining equivalent circuit models, polarizability extraction from scattering parameters, and full-wave simulations. Mirrorsymmetric configurations are introduced to suppress frequency splitting and improve band uniformity. For both CSRR and Ω arrays, equivalent LC parameters are derived and incorporated into a transmission-matrix framework, enabling accurate prediction of resonant behavior in cascaded layers. Numerical simulations in WR340 waveguides demonstrate that CSRR arrays achieve narrowband responses with high selectivity, while Ω-cells provide wider passbands and improved tolerance to interlayer spacing. Prototypes fabricated on high-purity aluminum sheets were measured using a vector network analyzer, confirming the theoretical and simulation results. The experimental data show close agreement with the proposed model, validating the scalability of the approach to multilayer designs. Quantitatively, the mirror-symmetric CSRR filter exhibits a center frequency of 2.49 GHz, a fractional bandwidth of 1.8%, and an insertion loss of 1.26 dB, whereas the proposed Ω-based configuration achieves a 2.41 GHz center frequency, 5.6% fractional bandwidth, and only 0.27 dB insertion loss. These results show that the Ω topology attains a wider fractional bandwidth and the consequently lower insertion loss predicted by fractional-bandwidth theory, rather than a reduction of intrinsic resonator loss. The proposed framework thus provides a systematic and efficient route for metamaterial filter synthesis, bridging analytical models, numerical simulations, and experimental validation.