2022-09-29 Latest Published
By Shilong Yan
Xueyi Zhang
Zhidong Gao
Mingjun Xu
Lei Wang
Yufeng Zhang
Wenchao Zhang
Kai Geng
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 124, 253-267, 2022
Abstract
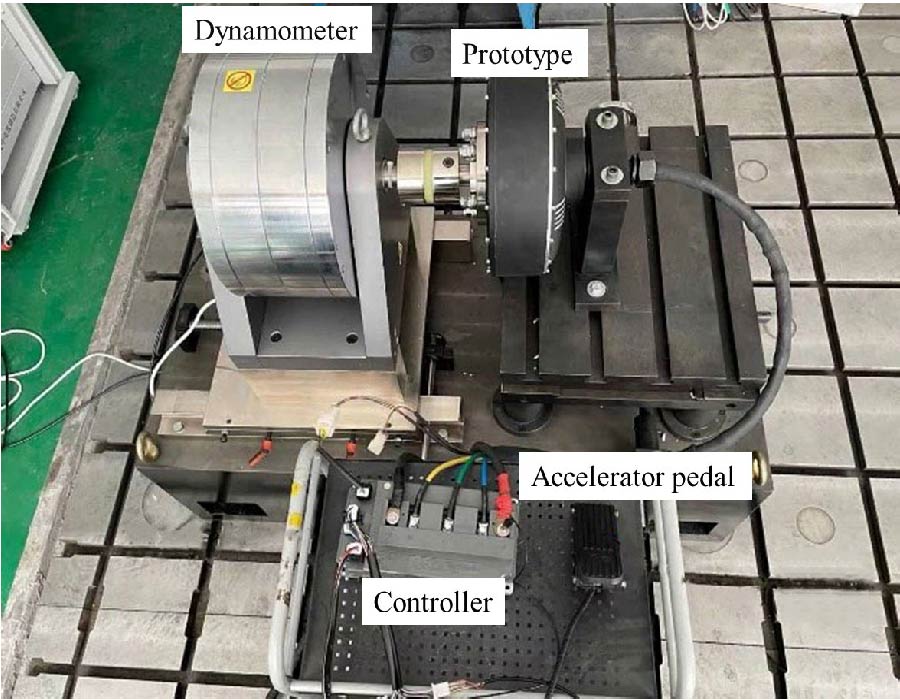
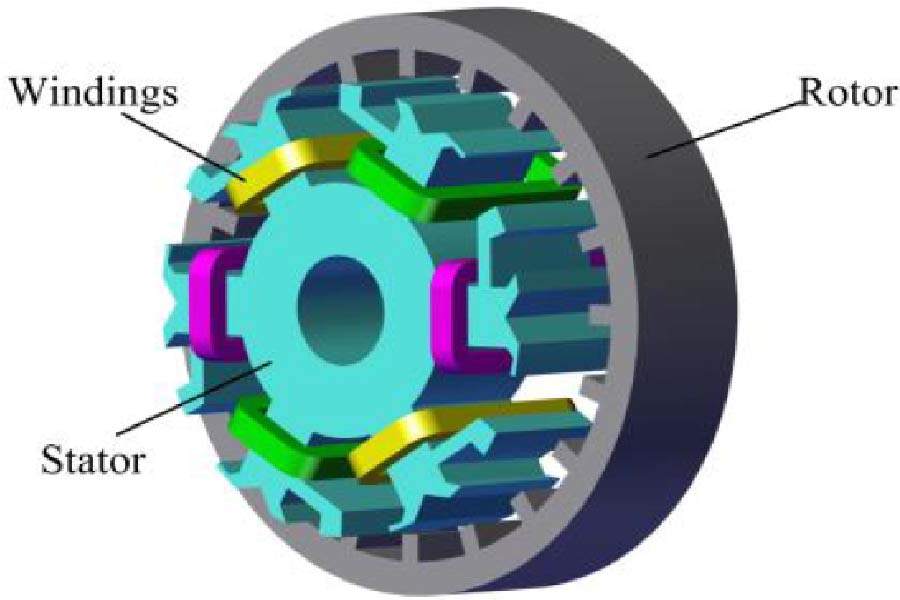
In order to solve the problems of high THD (total harmonic distortion) of air-gap magnetic density, large cogging torque and low power density of permanent magnet (PM) hub motor, a built-in tangential and radial PM combined-pole hub motor is proposed in this paper. The magnetic field provided by tangential PM is the main magnetic field, and the magnetic field provided by radial PM plays an auxiliary role in regulation, which can effectively improve the air-gap magnetic density of the motor, reduce the THD of back electromotive force (EMF), and weaken the peak value of cogging torque. Based on the equivalent magnetic circuit method, this paper analyzes the magnetic circuit of the motor, deduces the leakage magnetic flux coefficient, and reduces the leakage magnetic flux by optimizing the structure of the motor. Finally, the prototype is manufactured and tested to verify the effectiveness of finite element analysis. The results show that the designed PM hub drive motor has low THD of back EMF and good sinusoidality of waveform under no-load condition, and good output performance.