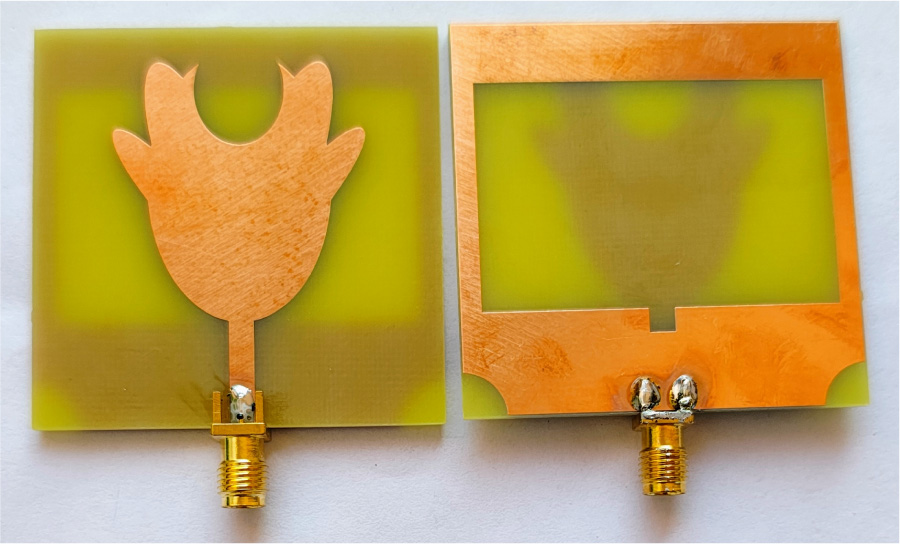
Highly Isolated Compact Dual-Band MIMO Antenna Using Stubs, Slots and Neutralization Line for 5G Wi-MAX and WLAN Applications
Amit A. Deshmukh,
Shankar D. Nawale,
Vijay Ramesh Kapure,
Shubhangi A. Deshmukh,
Mahadu Trimukhe and
Rajiv Kumar Gupta
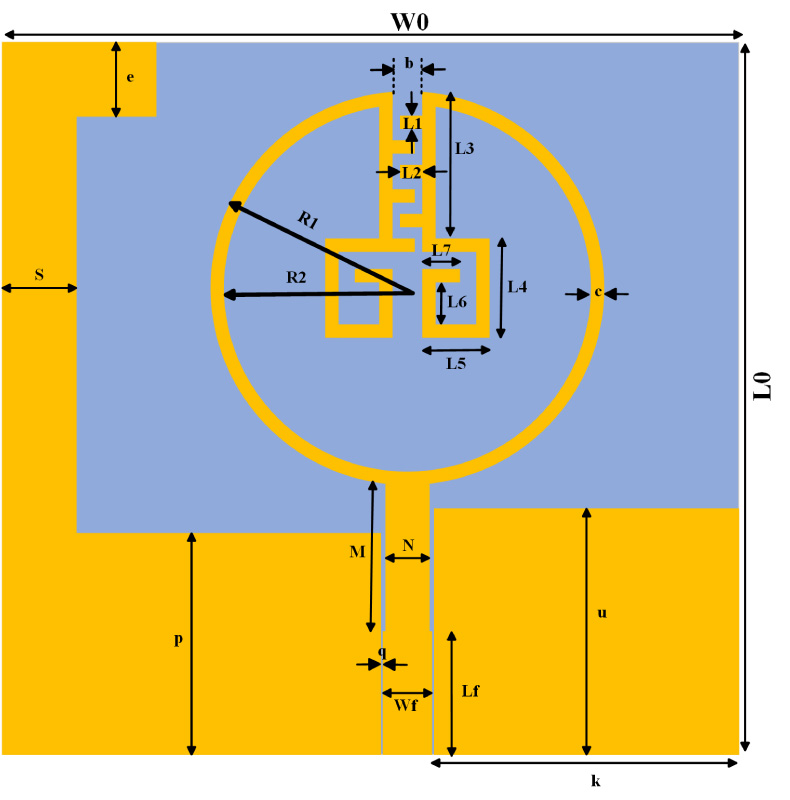
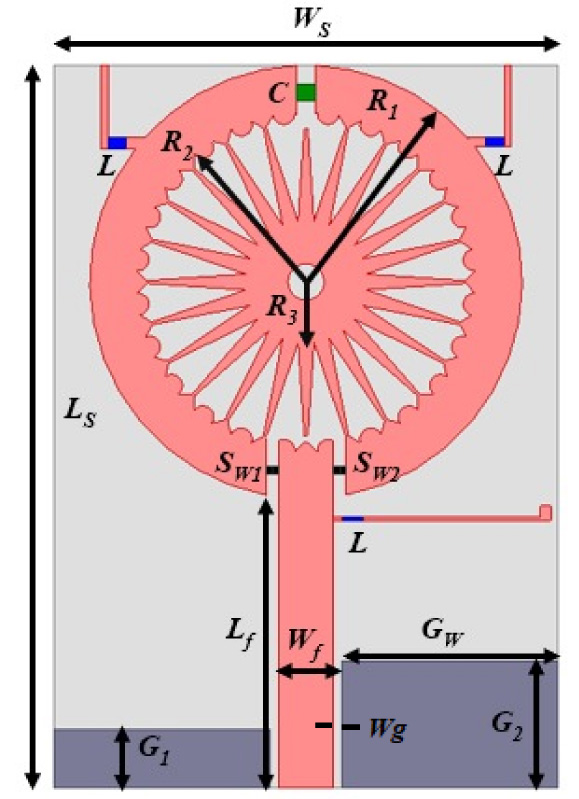
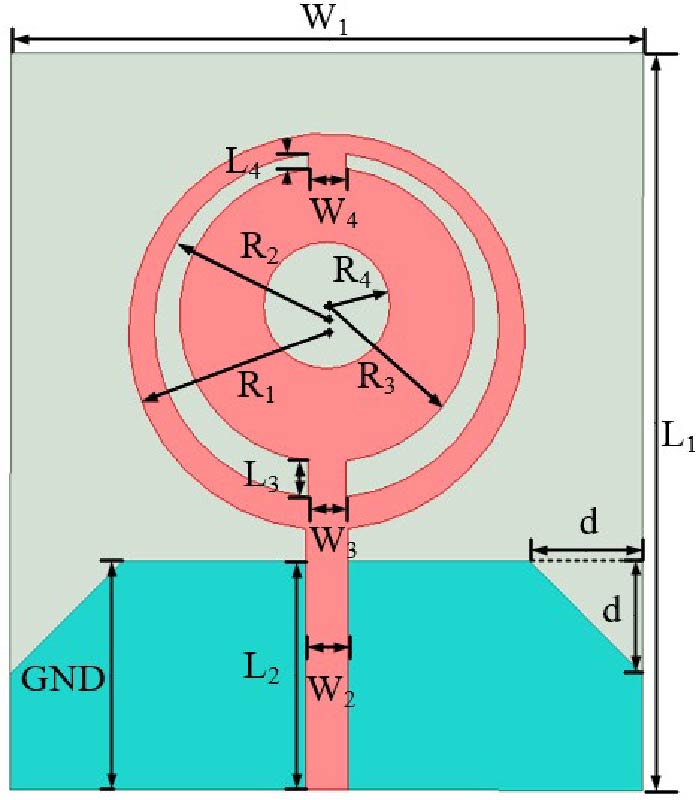
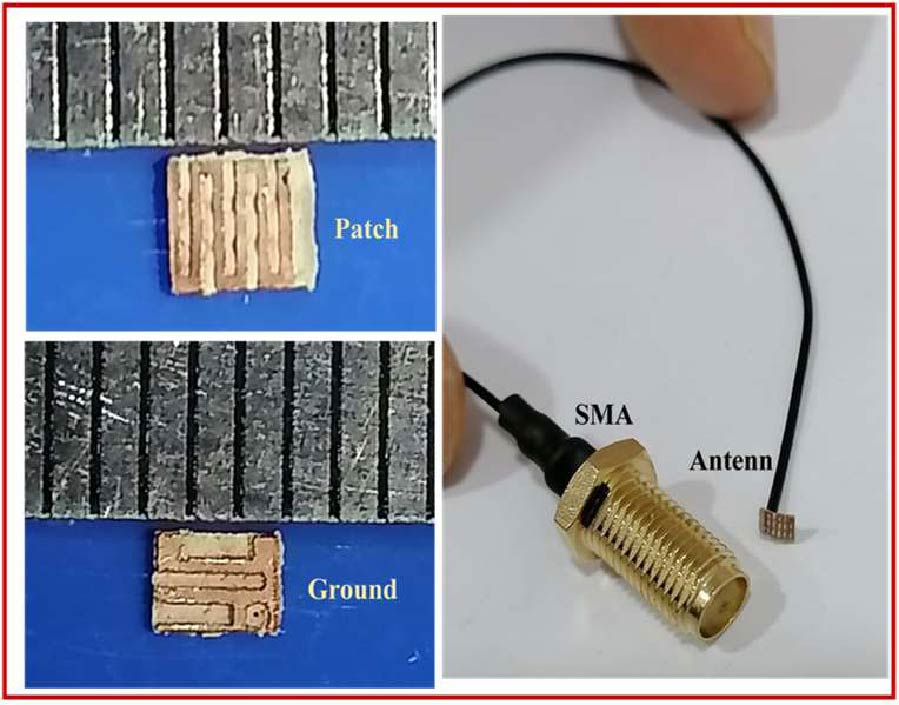
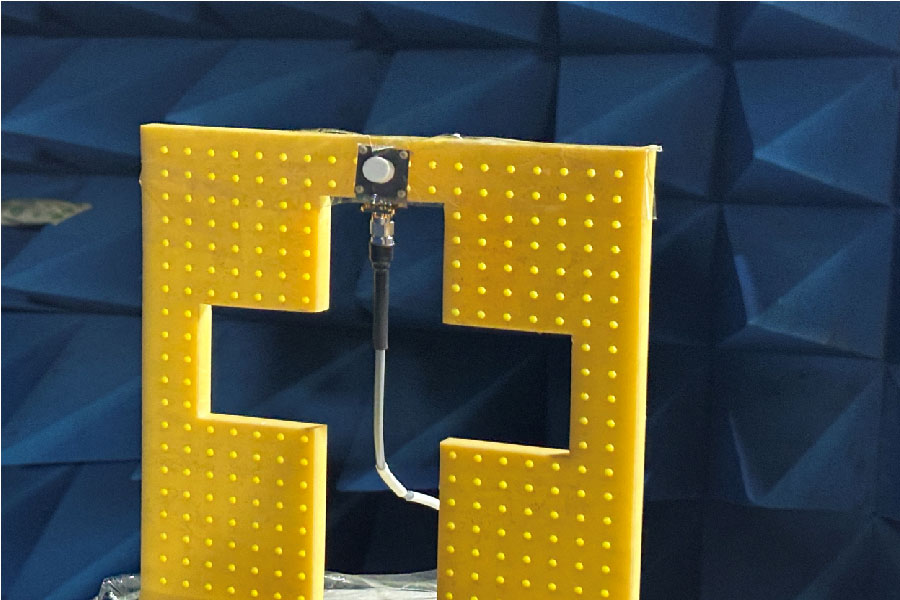
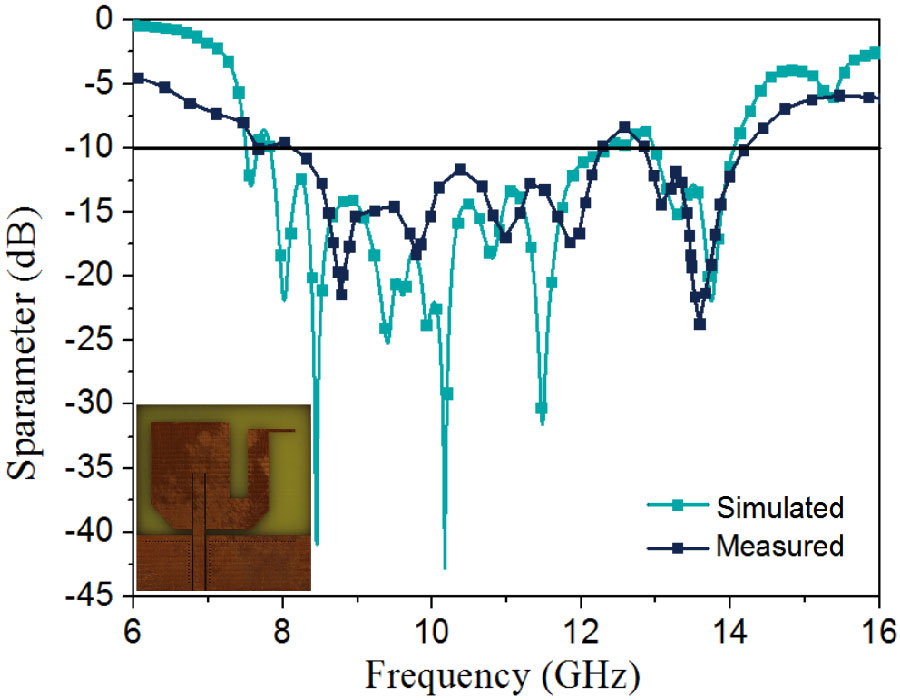
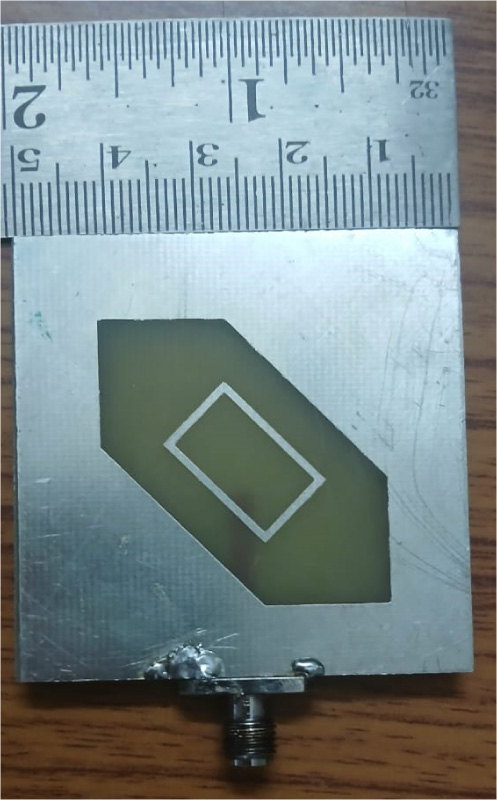
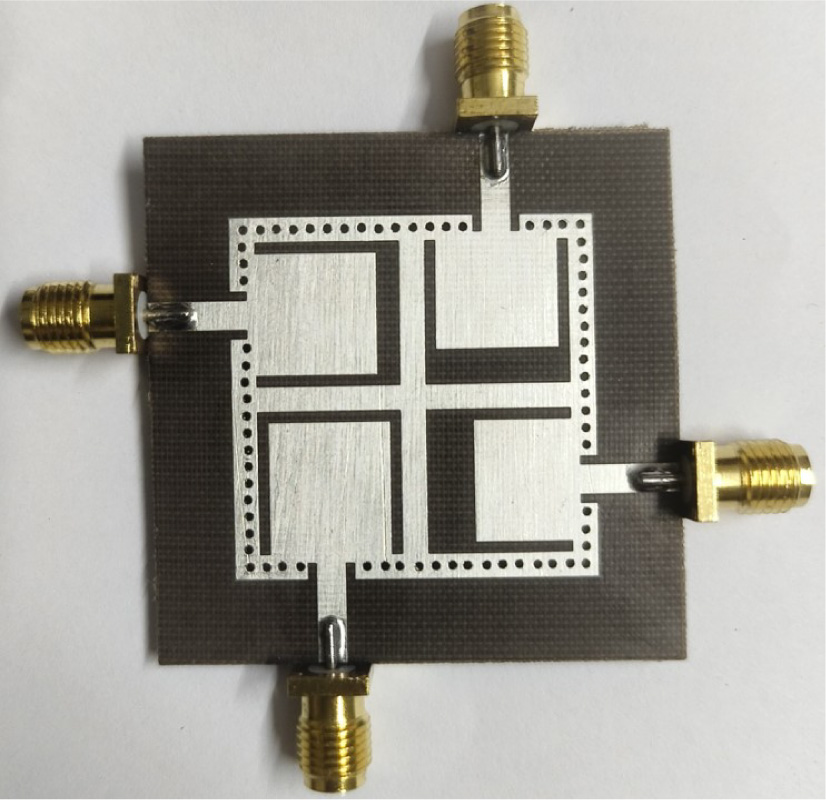
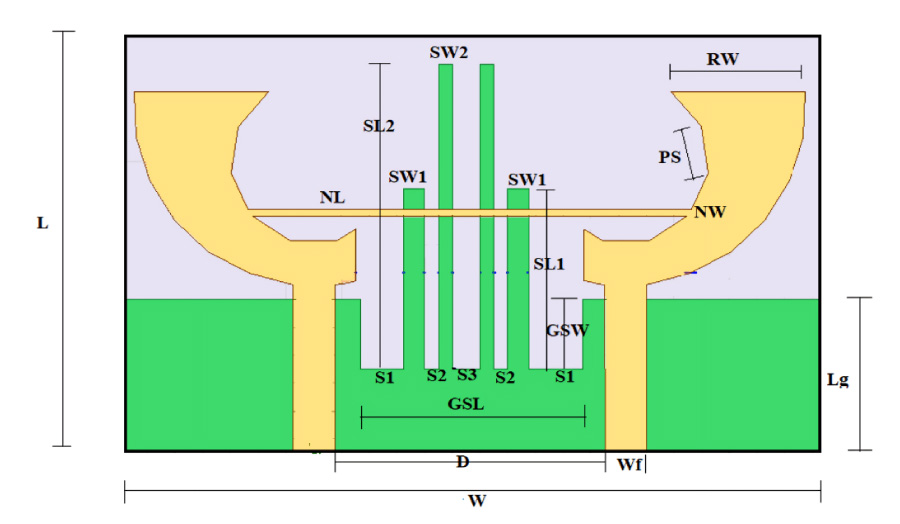
A highly isolated MIMO antenna is designed using a neutralization line (NL), stubs, and slots for 5G, Wi-MAX, and WLAN operations. A quarter circular ring monopole is modified to have a circular outer shape and a polygon inner shape. Thickness of the monopole is reduced to decrease the electromagnetic (EM) coupling between the higher order modes and to obtain dual band characteristics. A two-element MIMO antenna is designed. High isolation is achieved by combining isolation techniques of neutralization line with stubs and slots. Isolation >20 dB is achieved with stubs and slots in ground plane. Without altering the overall dimensions, isolation is improved from 20 dB to 30 dB by using an NL in the MIMO structure that uses slots and stubs in the ground plane as isolation techniques. S11 < -10 dB over 2.9-3.9 GHz and 5.6-6.2 GHz and S12 < -30 dB over 3.3-3.9 GHz, and S12 < -40 dB over 5.6-6.2 GHz covering 5G, Wi-MAX, V2X, and WLAN bands are obtained. The antenna has stable radiation patterns. ECC (Envelope Correlation Coefficient) < 0.002, DG (Diversity Gain) close to 10 dB, and MEG (Mean Effective Gain) about 0 dB satisfy MIMO specifications. The compact, low-cost antenna on a 30 × 50 mm FR4 substrate is simple to design and fabricate. These features make it a suitable candidate for 5G, Wi-MAX, and WLAN applications.