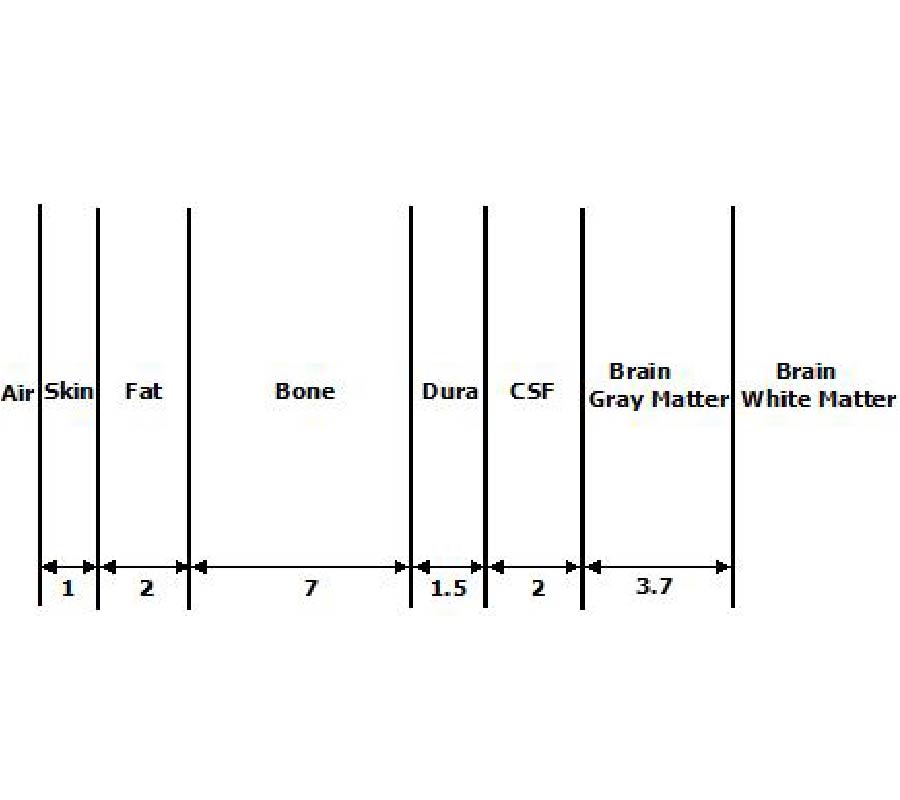
Numerical Computation of SAR in Human Head with Transparent Shields Using Transmission Line Method
Pudipeddi Sai Spandana and
Pappu V. Y. Jayasree
The tremendous proliferation of mobile smartphone handsets and their usage worldwide makes human life comfortable, while the radiation hazards associated with them are alarming, especially among children. There is a necessity to minimize the Electro Magnetic Field (EMF) radiation levels. For the evaluation of Radio Frequency (RF) radiation from the mobile phone, one of the dosimetric parameters used is the Specific Absorption Rate (SAR). The RF radiation can be mitigated by incorporating a barrier or a shield of suitable material in the mobile handset design. In the proposed work, the analysis of SAR evaluation absorbed by the human head is determined with the performance of the shielding material called Shielding Effectiveness (SE) using Transmission Line Method (TLM) mathematically. The proposed shielding materials are composed of flexible and transparent thin films. Flexible and transparent thin shielding materials are advantageous over the other shielding materials in reduced size, less weight, non-corrosiveness, and easy processing. These materials include highly conductive Silver film, Silver Nanowire(AgNW) doped with PDDA (poly(diallyldimethyl-ammonium chloride)) polymer single shields, and a laminated shield comprising AgNW/PDDA with PEDOT:PSS (poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)poly-styrene sulfonate) polymer as lamination. The SARs of planar multi-layered human head models for different ages are estimated at various mobile frequencies with these shields. Under four-layered head models at 6 GHz, adult and child heads absorb 0.0006 W/Kg and 0.000024 W/Kg of RF radiation using pristine Silver film as a single shield. Using a single shield of Ag nanowire and PDDA, the adult and child heads absorb SARs of 0.00058 W/Kg and 0.000023 W/Kg, respectively. With the laminated shield of AgNW/PDDA and PEDOT:PSS as coating material, the same models are exposed to minimal amounts of 0.00054 W/Kg and 0.000012 W/Kg of SAR. At 6 GHz frequency, under seven-layered head models, an adult and a child's head absorb 0.000047 W/Kg and 0.000002 W/Kg of power, respectively, using Ag film. With AgNW/PDDA shield, the adult and child heads absorb a SAR of 0.000046 W/Kg and 0.0000019 W/Kg, respectively. The SARs of 0.000043 W/Kg and a negligible value of 0.0000018 W/Kg are absorbed by adult and child heads individually with the help of AgNW/PDDA/PEDOT:PSS laminated shield. The results exhibit a significant amount of reduction in Specific Absorption Rate with transparent shielding materials compared to SAR absorbed by the head without any shield. This maximum RF exposure rate reduction from mobile phones with the Ag Nanowire/PDDA/PEDOT:PSS laminated shield is achieved for a seven-layered child head model.