A Low-Profile UWB Monopole Antenna and High-Isolated UWB-MIMO Antenna for Wireless Communications Networks
Ibrahime Hassan Nejdi,
Mohamed Marzouk,
Mustapha Ait Lafkih,
Seddik Bri,
Jamal Abdul Nasir,
Zahriladha Zakaria and
Ahmed Jamal Abdullah Al-Gburi
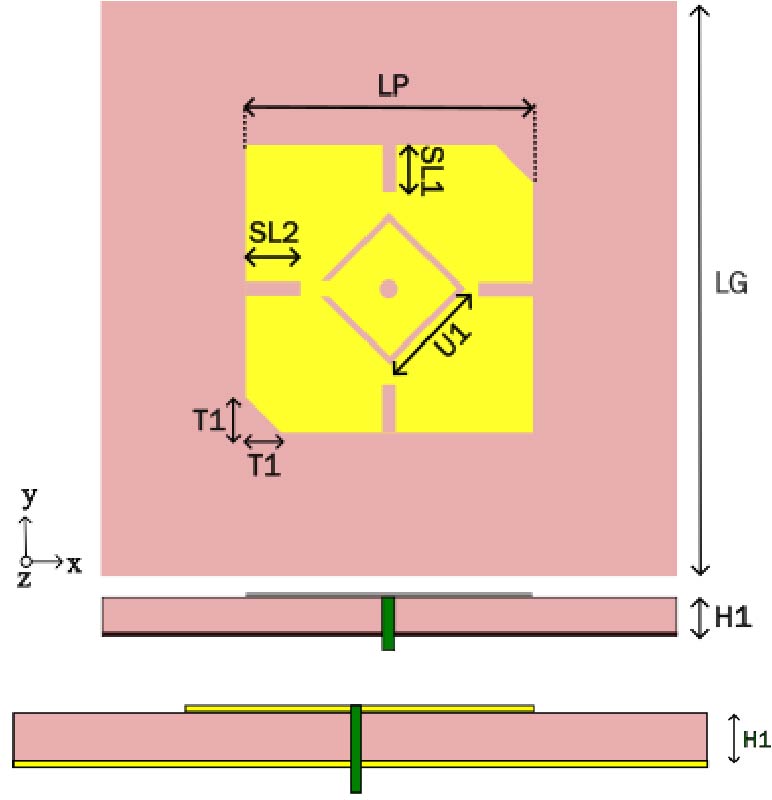
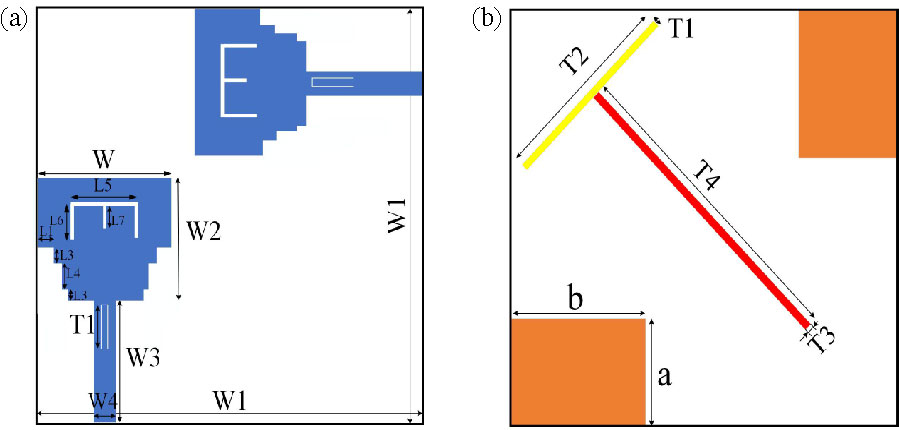
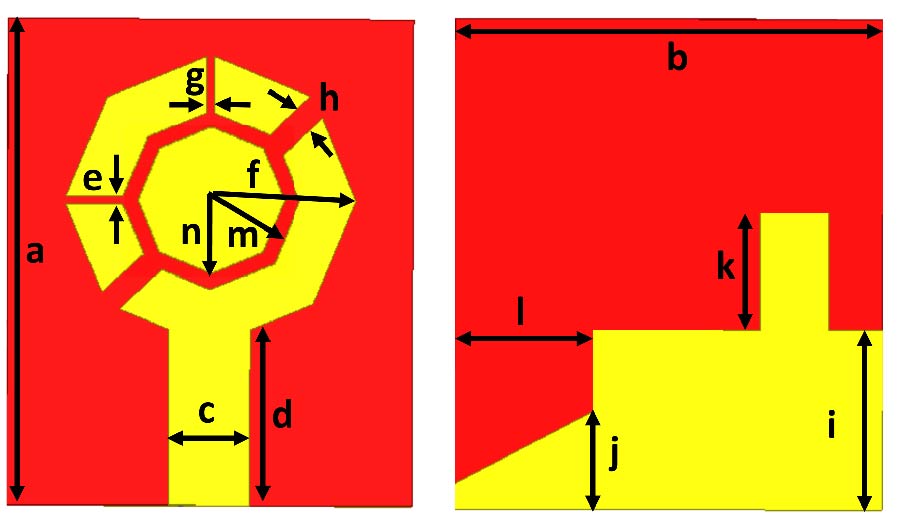
This study proposes a space-efficient ultra-wideband (UWB) monopole antenna engineered for superior gain and performance. The innovative design, modeled and analyzed using HFSS software, involves etching the resonator onto one side of an affordable FR4 substrate. The manufactured antenna features an extended impedance bandwidth, achieved by incorporating ``E'' and ``inverted E'' shaped slots on the patch, an irregular hexagonal substrate structure, and a slotted partial ground plane. Covering a frequency range from 2.5 to 11.1 GHz, the patch achieves a maximum gain exceeding 7.9 dB and an efficiency of 98%. Parametric analyses based on numerical simulations evaluate the impact of design elements, such as slots on the resonator and ground plane, and cuts in the substrate. The excellent match between simulated and measured data verifies the antenna's performance across multi-band environments. The article concludes by introducing a second antenna, designed through the symmetrical integration of four prototypes of the suggested antenna. Mutual coupling between elements is reduced through the use of an orthogonal, four-directional staircase structure, and a defective ground is intentionally left unconnected. This new antenna covers an impedance spectrum from 2.42 to 12 GHz, with a gain of 12.77 dB, an efficiency of up to 98%, and a voltage standing wave ratio (VSWR) ranging between 1 and 2. Overall, the article emphasizes the design, optimization, and application of UWB antennas, highlighting their performance and suitability for various wireless communication scenarios.