SOSANet: Multi-Scale Attention for Robust Rebar Quantity Classification in Complex EMI Scenarios
Jiale Chen,
Ronghua Zhang,
Yuxiang Liu,
Tongyan Liu,
Anan Dai and
Zishu Hu
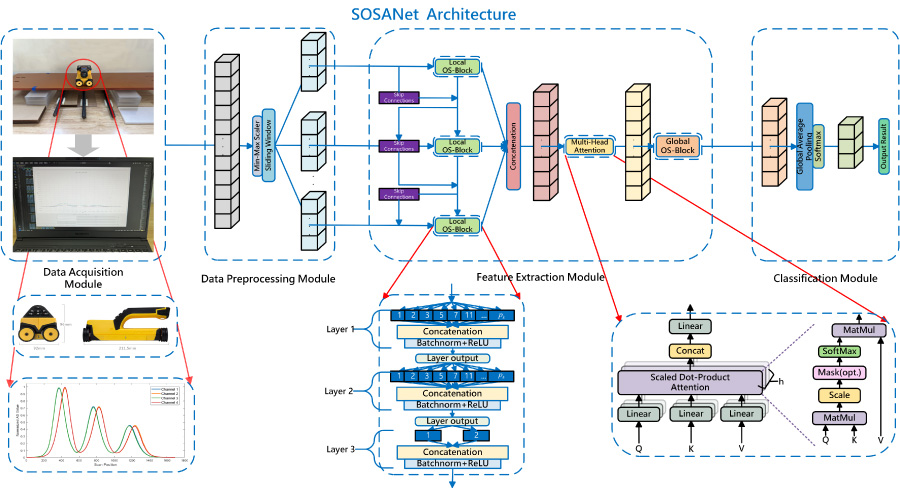
Electromagnetic induction (EMI) is a crucial non-destructive testing (NDT) technique for reinforced concrete structures, particularly for detecting and evaluating rebar distribution. However, the presence of multiple factors - including electromagnetic coupling effects from dense rebar arrangements, nonlinear waveform distortion due to rebar height differences, and environmental interference - renders traditional feature extraction methods inadequate for accurately reconstructing the rebar distribution parameters within the concrete cover. To address these challenges, a Sliding Omni-Scale Attention Network (SOSANet) is proposed in this paper. Initially, adaptive sliding window segmentation processes variable-length signals, preventing information distortion from signal truncation or padding. Subsequently, a dual-scale OS-Block architecture is constructed, wherein local small-scale OS-Blocks perform multi-scale feature extraction on the signals within each window. Furthermore, a multi-head attention mechanism and a global large-scale OS-Block are employed to model cross-window feature correlations, enhancing the discrimination of signal aliasing features induced by electromagnetic coupling among rebars. To address complex working conditions, a dataset of 1,740 samples comprising varying rebar quantities, cover thicknesses, spacings, and height differences was constructed. An interval random truncation strategy was employed to simulate scenarios involving incomplete signals. Five-fold cross-validation demonstrated that SOSANet achieves an F1-score of 99.34% for rebar quantity classification under complex working conditions, significantly outperforming 1D-CNN, Transformer, and other mainstream methods. Moreover, SOSANet maintains a high robustness with an F1-score of 99.03% under signal occlusion conditions.