Computational Aspects of the Cell Method in Electrodynamics
M. Marrone
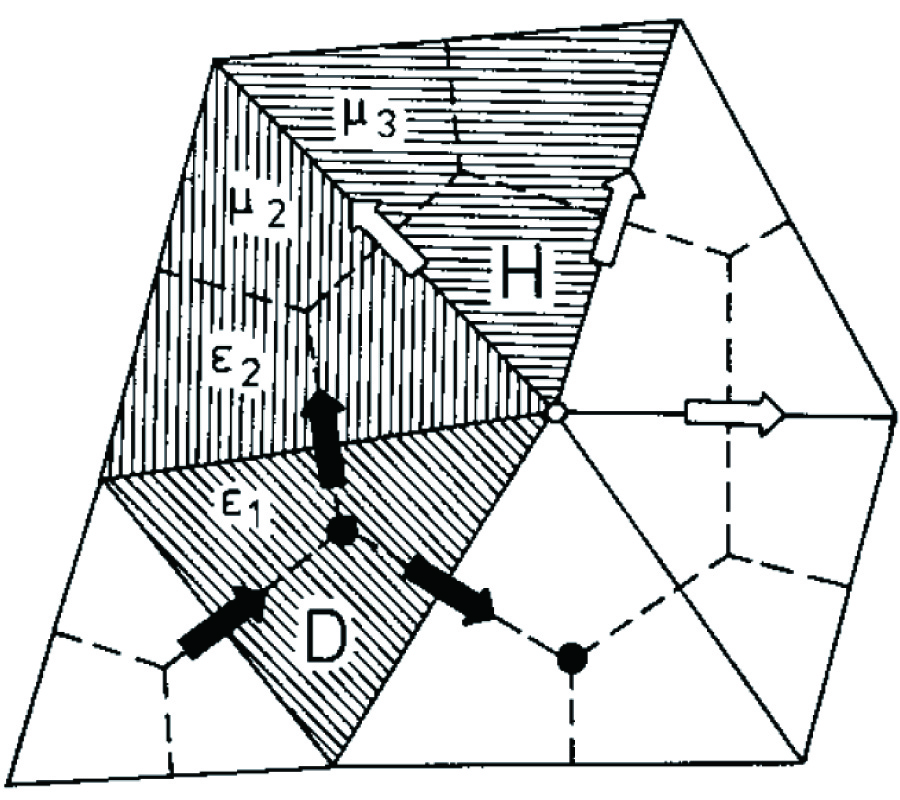
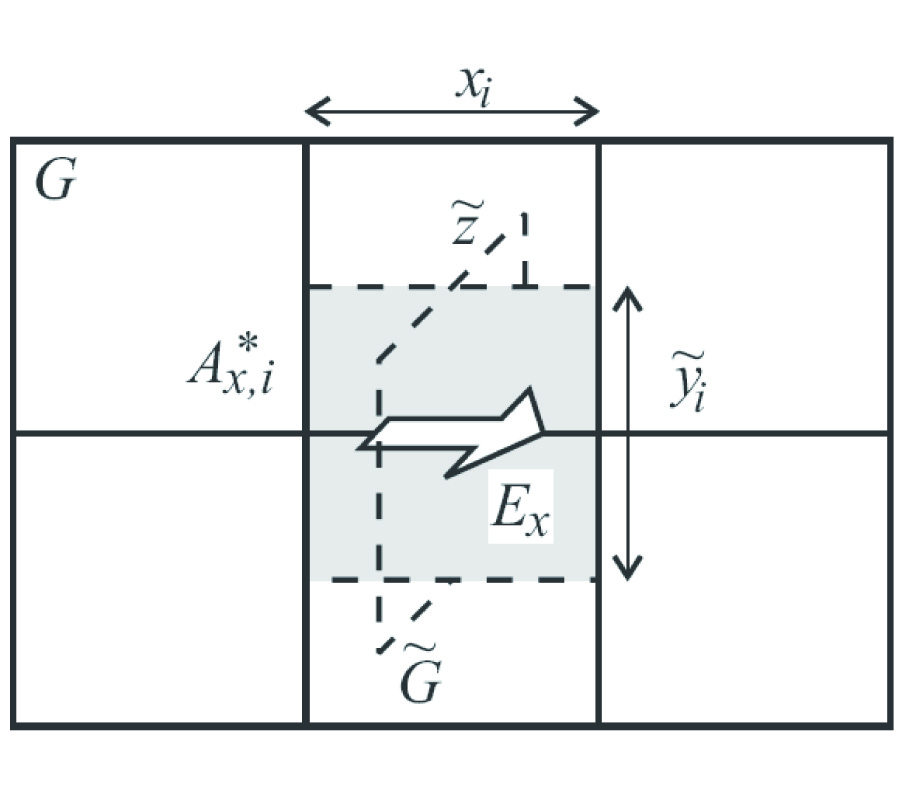
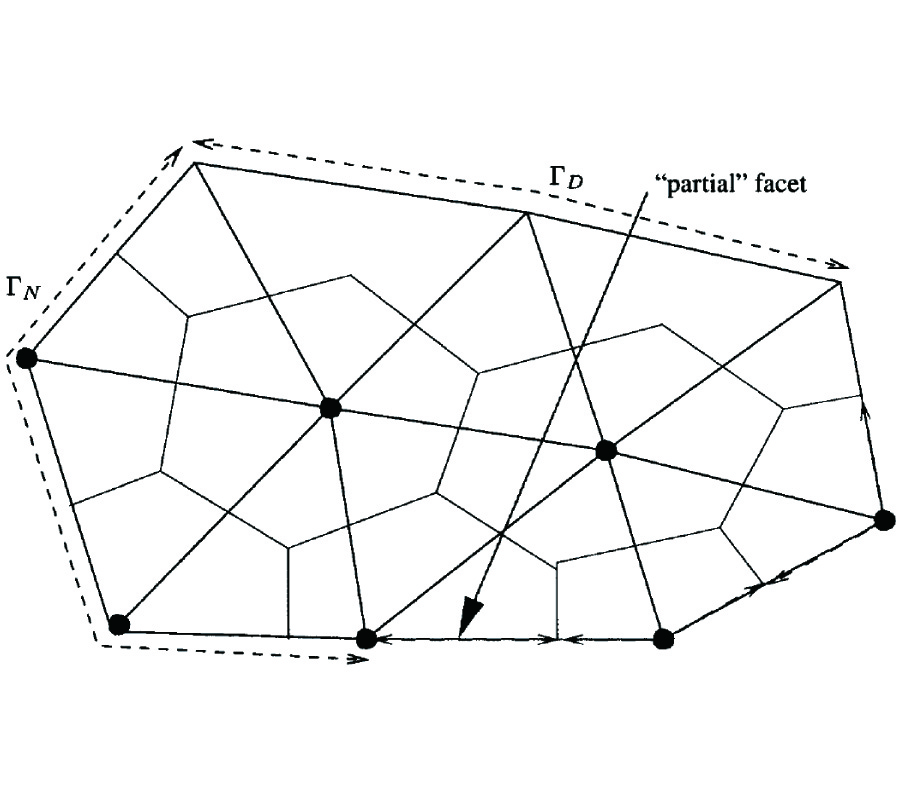
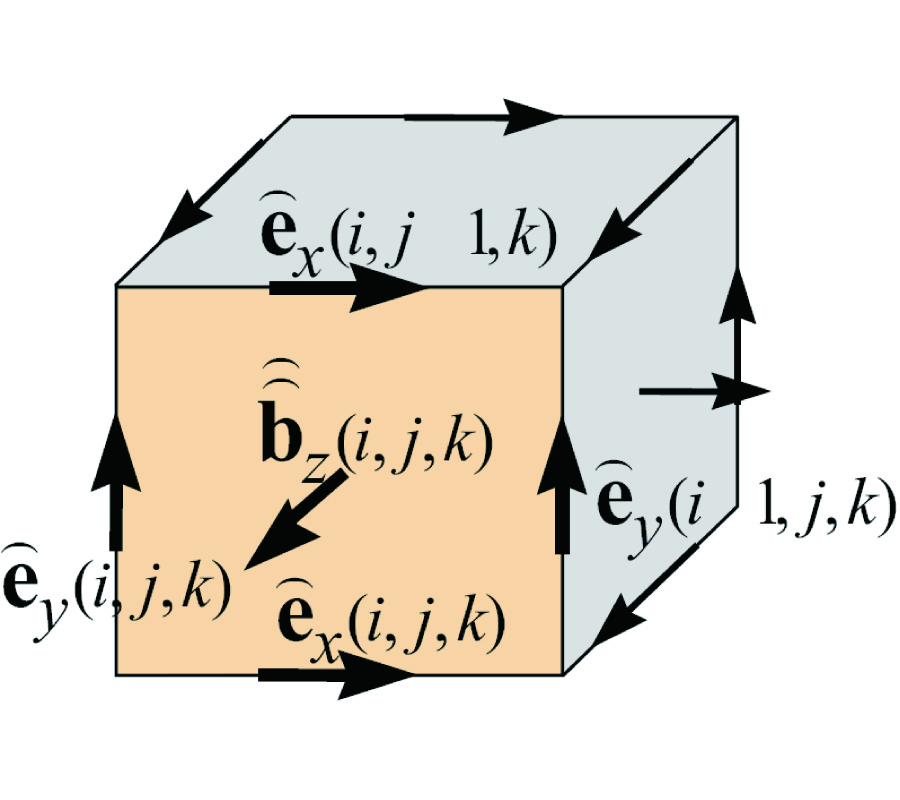
A desire to unify the mathematical description of many physical theories, such as electrodynamics, mechanics, thermal conduction, has led us to understand that global (=integral) physical variables of eachth eory can be associated to spatial geometrical elements suchas points, lines, surfaces, volumes and temporal geometrical elements suchas instants and intervals. This association has led us to build a space-time classification diagram of variables and equations for each theory. Moreover, the possibility to express physical laws directly in a finite rather than differential form has led to the development of a computational methodology called Cell Method [12]. This paper discusses some practical aspects of this method and how it may overcome some of the main limitations of FDTD method in electrodynamics. Moreover, we will provide some numerical examples to compare the two methodologies.