2007-04-26 Latest Published
By Zhi-Hui Chen
Qing-Xin Chu
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 73, 327-341, 2007
Abstract
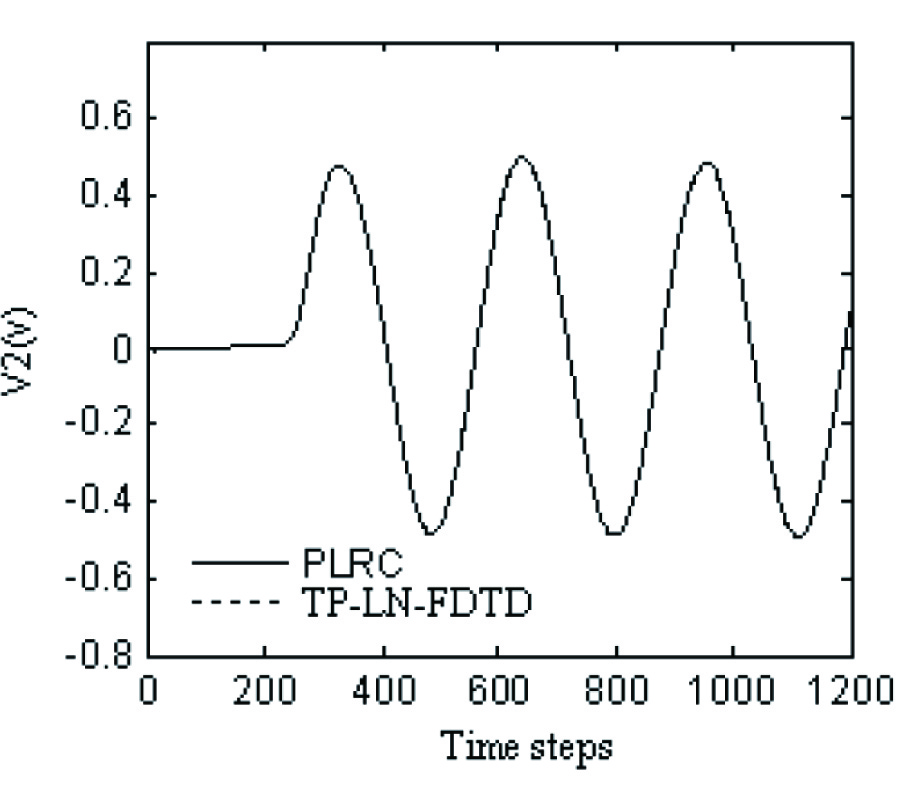
Based on the piecewise linear recursive convolution (PLRC) technique, FDTD modeling of Arbitrary linear lumped networks is studied in this paper, including one-port networks and two-port networks. Their general FDTD iterative formulations are obtained. Firstly, the admittance parameters in Laplace domain of lumped network are written as a summation form of several rational fractions; then the time domain admittance parameters can be obtained by means of inverse Fourier transform technique. Finally the time domain results are directly incorporated into the Maxwell- Ampere's difference equation using the PLRC technique. It is worth pointing out that this approach preserves the second-order accuracy and the explicit nature of the conventional FDTD method. The proposed technique can be extended to model arbitrary linear multiport lumped networks. To show the validity of the proposed algorithm, we analyze two microstrip circuits including lumped networks. The results are compared with those obtained from the Z-transform technique and the good agreement is achieved.