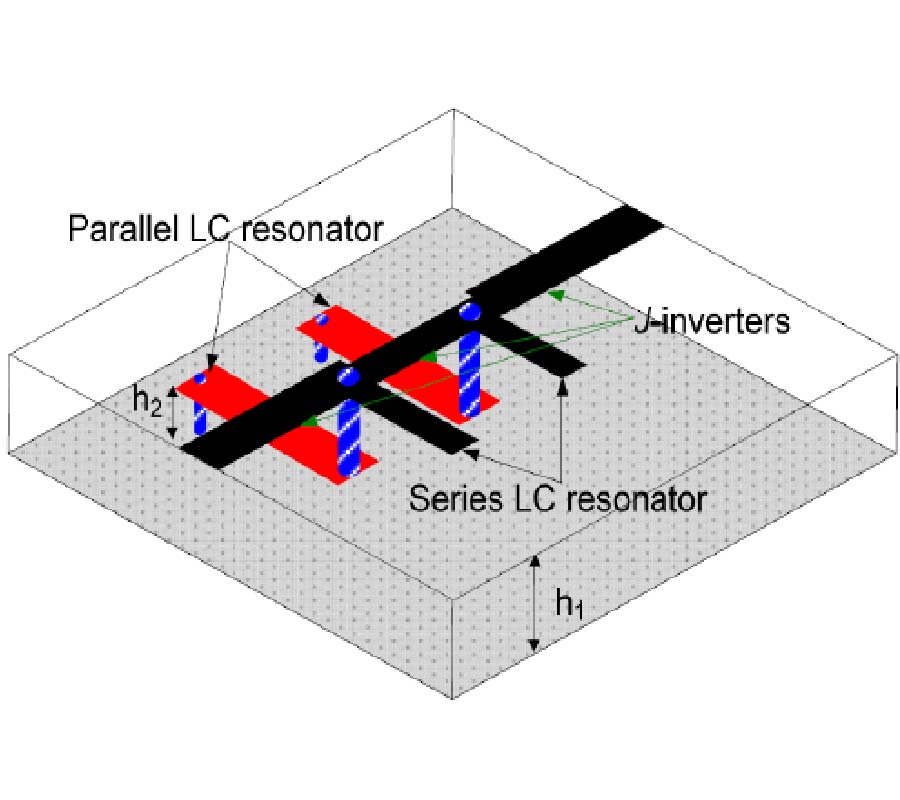
Improved CRLH-TL with Arbitrary Characteristic Impedance and Its Application in Hybrid Ring Design
Xianqi Lin,
Peng Su,
Yong Fan and
Zhong Bo Zhu
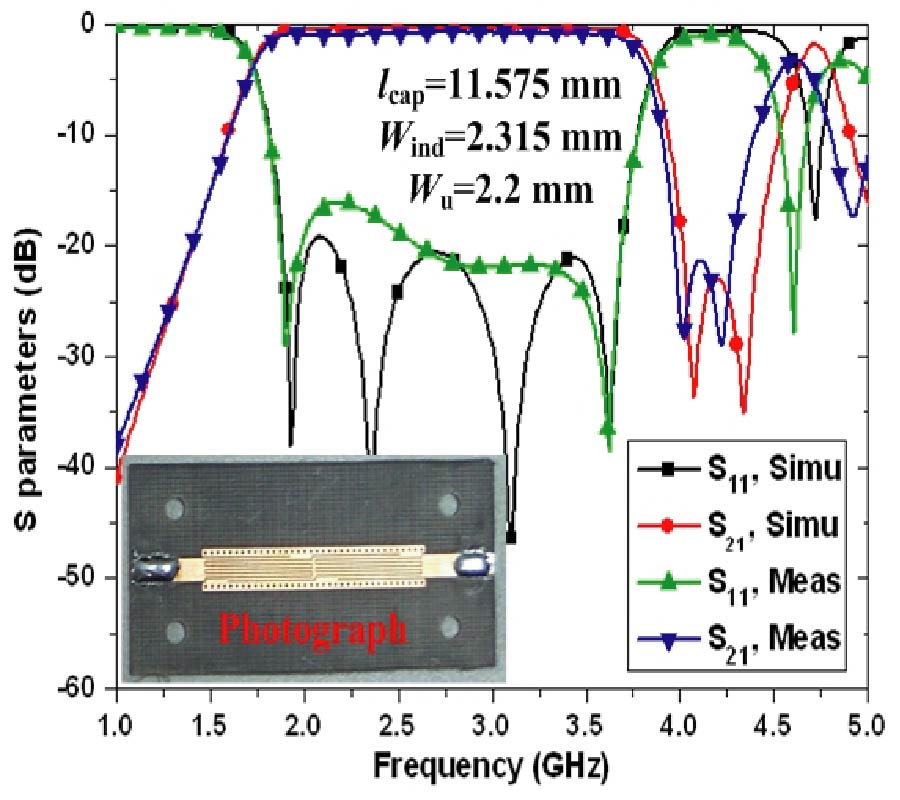
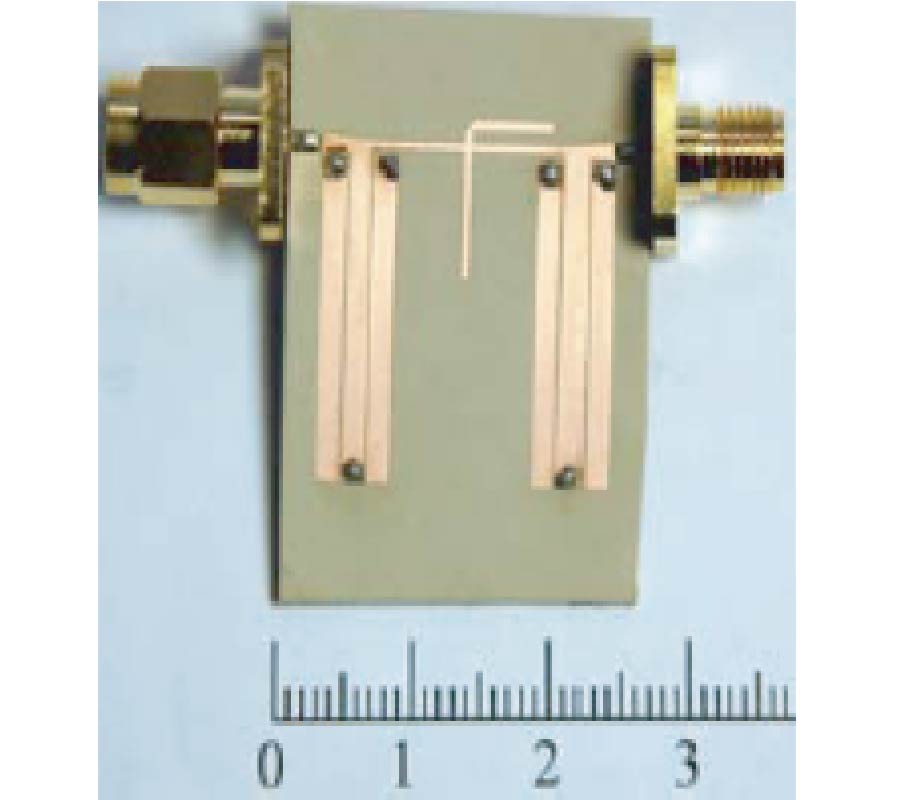
An improved designable composite right/left-handed transmission line (CRLH-TL) is presented in this paper, whose operating frequency-band and transmission characteristics can be tuned, respectively, by three structure variables. The equivalent characteristic impedance is studied carefully, and CRLH-TLs with arbitrary characteristic impedances are obtained. Some useful empirical formulae are derived for engineering application. Then, a sample of 50-Ω CRLH-TL, which can be used directly as a wide-band filter, is fabricated with the center frequency of 2.8 GHz. The measured results show that a relative 3-dB bandwidth of 74.6% is achieved, in good agreement with the simulated results. Moreover, the phase-frequency responses of our proposed CRLH-TLs are discussed in detail. A novel hybrid ring is then proposed, where 70-Ω CRLH-TL is used. At the center frequency of 5.8 GHz, equal power dividing is achieved with return loss and isolation more than 20 dB and 30 dB, respectively. The sample is finally fabricated and good agreements among theoretical analysis, simulated results, and measured results are obtained.