Study on Conformal FDTD for Electromagnetic Scattering by Targets with Thin Coating
Xiao-Juan Hu and
De-Biao Ge
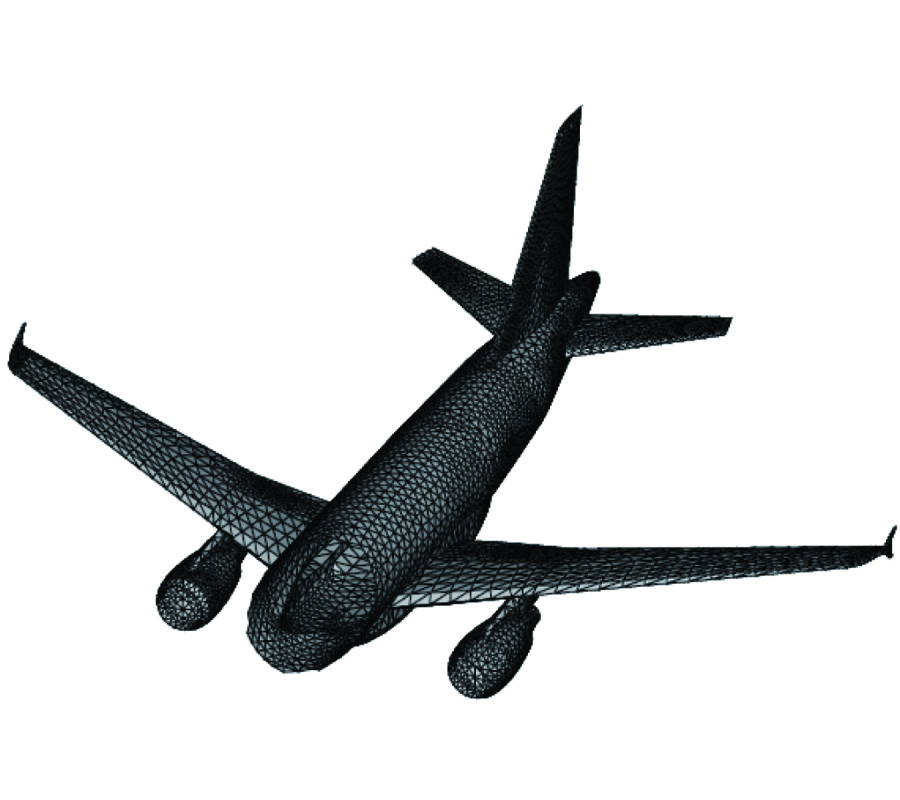
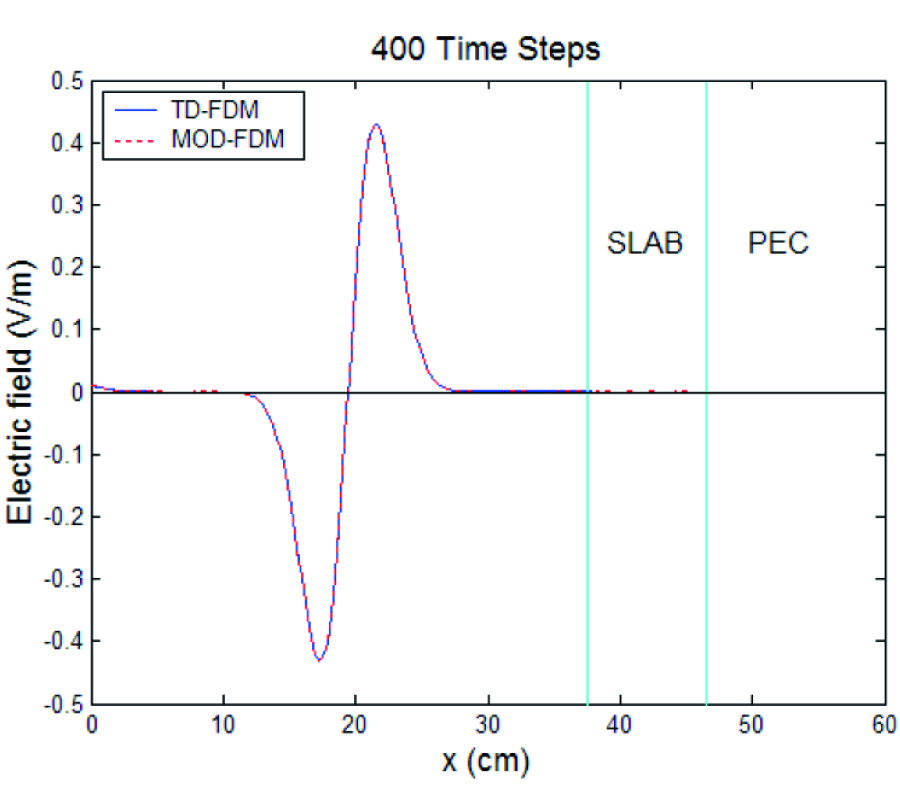
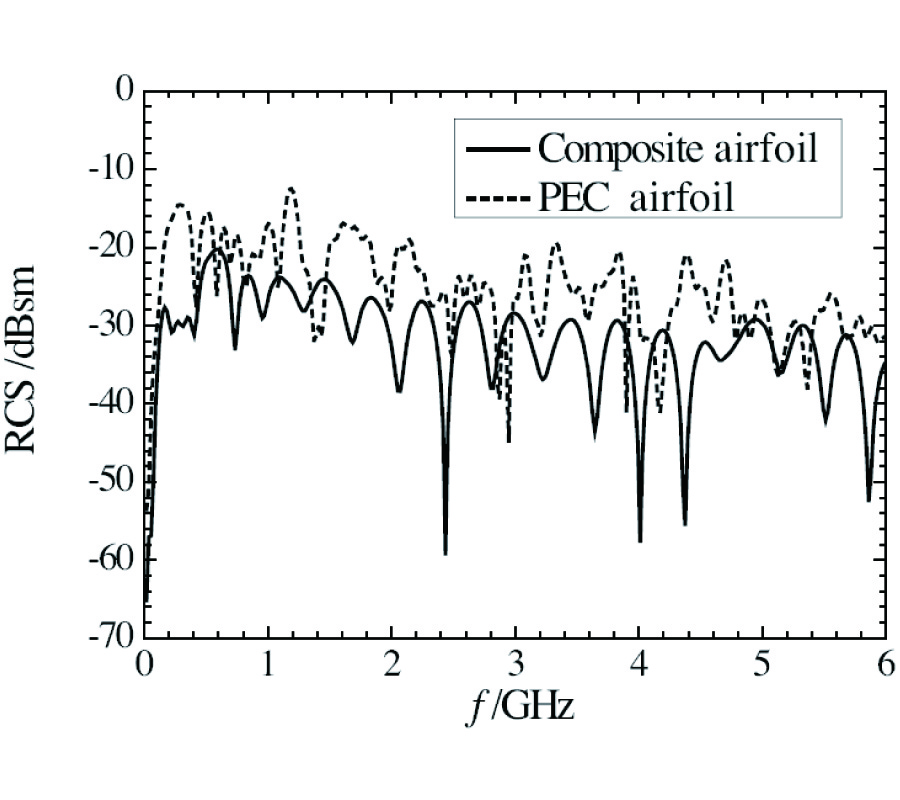
In order to simulate the electromagnetic scattering of targets with thin-coating accurately, a conformal finite-difference timedomain (CFDTD) method based on effective constitutive parameters is presented in this paper. Two kinds of coating problems are considered. For a coated target with medium backing material, the CFDTD formulations on conformal cells are the same as those of the conventional FDTD, but the parameters in FDTD formulations are replaced by effective constitutive parameters to include the curved coating message of target. For a coated target with perfectly conducting (PEC) backing material, the contour-path integral is used to exclude the curved PEC part, and effective constitutive parameters are then introduced to include the coating message. The bistatic radar cross section (RCS) of coated spheres with medium backing material and with PEC backing material are computed, respectively, to validate the presented CFDTD scheme. The backscattering of a composite airfoil, which is made of radar absorbing material (RAM) and metal framework, and coated by fiberglass-reinforced plastics, is also analyzed to demonstrate the feasibility of presented scheme.