Prediction of Propagation Characteristics in Indoor Radio Communication Environments
Nathalie Yarkony and
Nathan Blaunstein
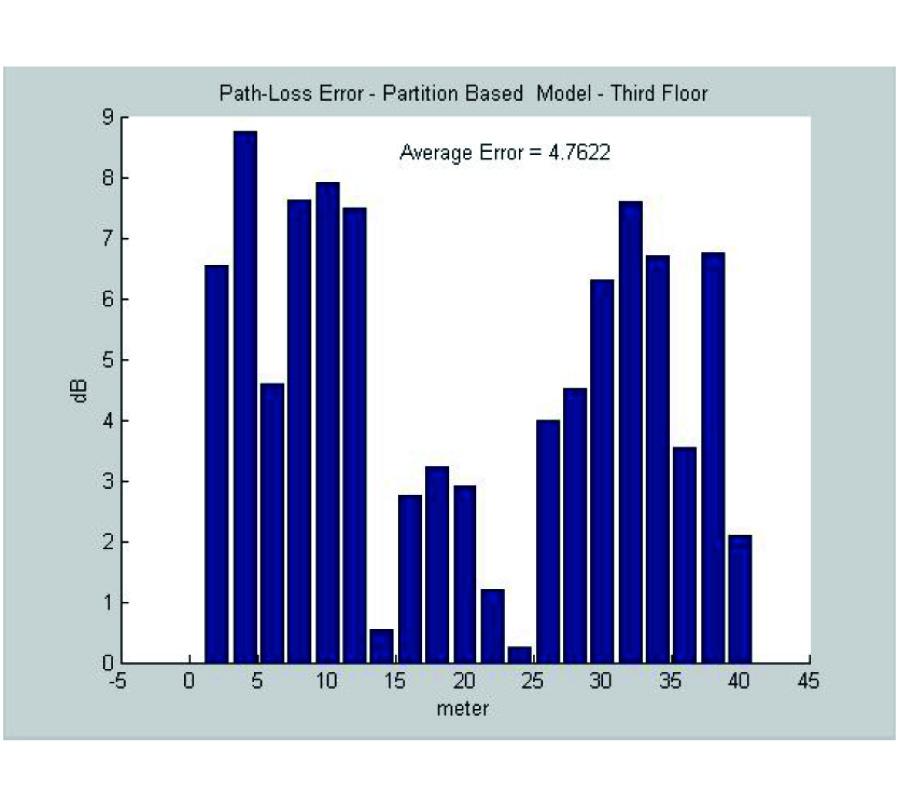
In this work, we present a semi empirical approach and the analytical model on how to predict the total path loss in various indoor communication links, taking into account the new analytical methods of the derivation of the fading phenomenon between floors and along corridors, respectively. We take into account the stochastic method of slow and fast fading estimations, caused by diffraction and multipath phenomena, respectively. The statistical parameters required for statistical description of the diffraction and multipath phenomena, such as the standard deviations of the signal strength due to slow and fast fading are obtained from the corresponding measurements. The path loss characteristics together with evaluated parameters of slow and fast fading give a more precise link budget predictor, and obtain full radio coverage of all subscribers located in the area of service inside each building. Based on strict and completed path loss prediction, an algorithm of link budget performance is presented for different scenarios of radio propagation within indoor communication links. Results of proposed unified approach are compared with the analytical Bertoni's model, which is well-known and usually used in link budget design in various indoor environments. The results are also compared with measurements carried out for different propagation scenarios, along corridor and between floors, occurred in the indoor communication channels. A better agreement with experimental data is obtained compared to the model in consideration.