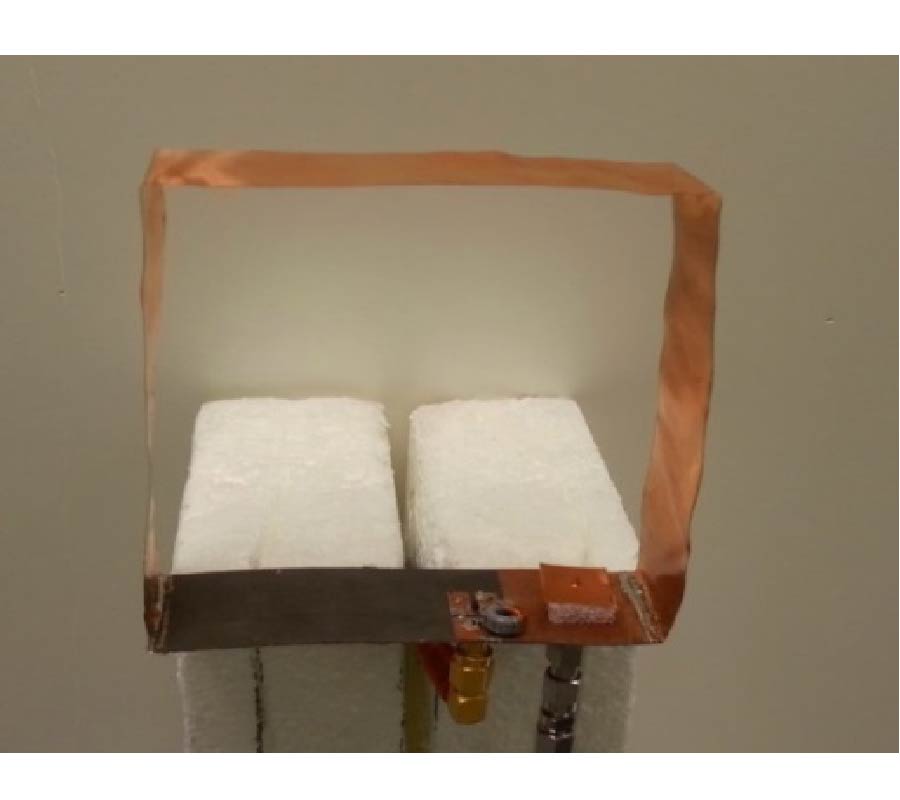
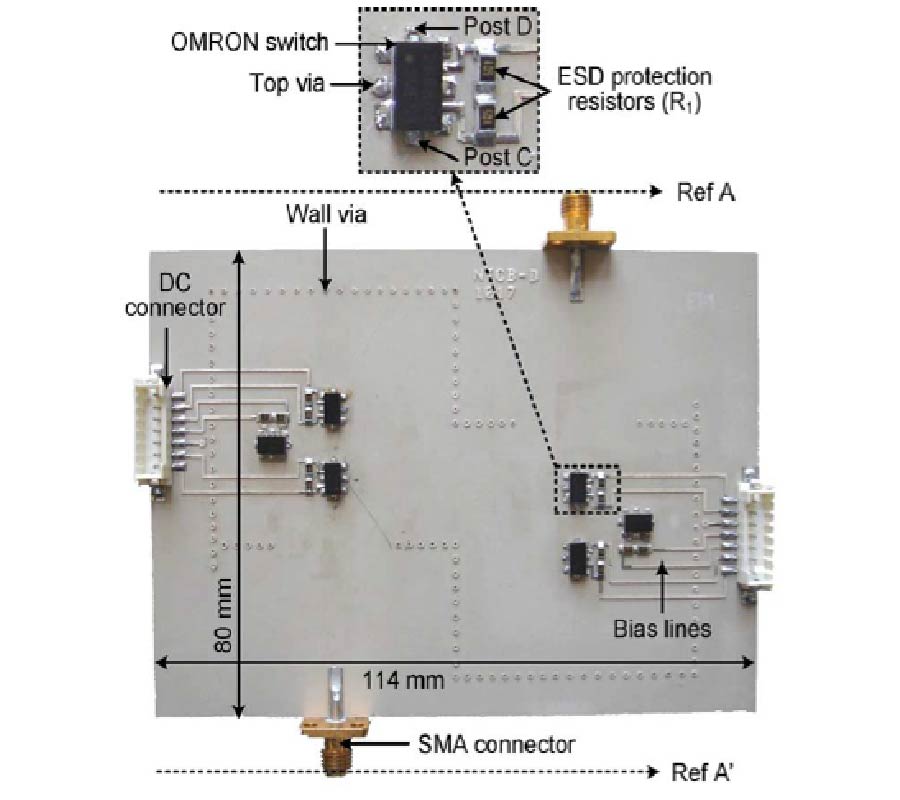
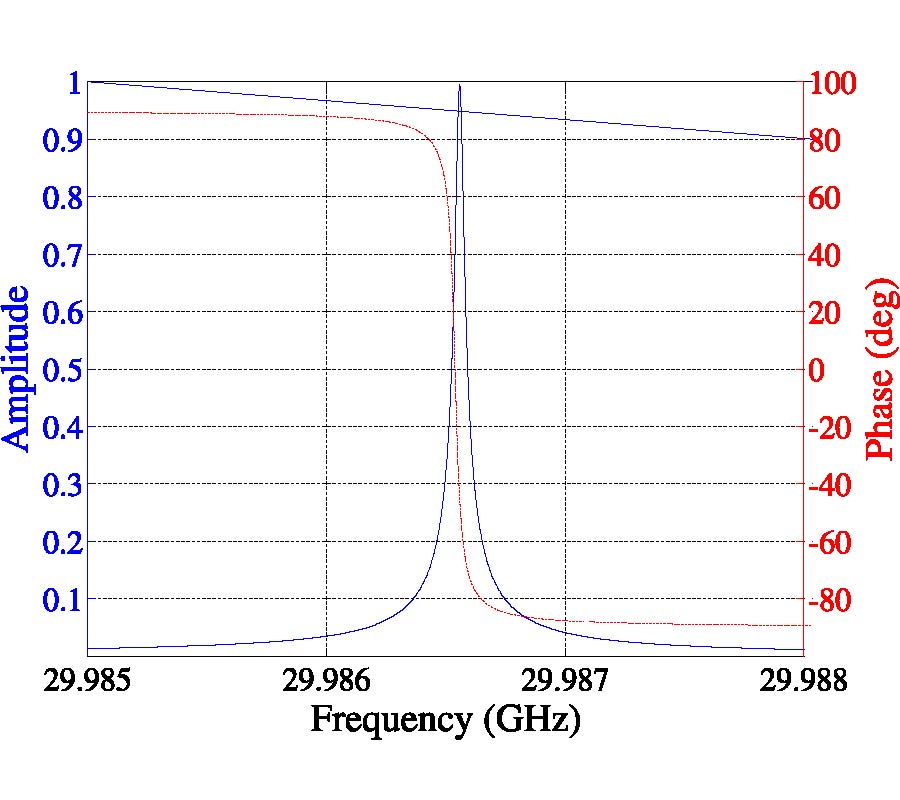
A Wideband Frequency-Shift Keying Modulation Technique Using Transient State of a Small Antenna (Invited Paper)
Mohsen Salehi,
Majid Manteghi,
Seong-Youp Suh,
Soji Sajuyigbe and
Harry G. Skinner
The rate of wireless data transmission is limited by the antenna bandwidth. We present an efficient technique to realize a high-rate direct binary FSK modulation by using the transient properties of high-Q antennas. We show that if the natural resonance of a narrowband resonant-type antenna is switched at a high rate, the radiating signal follows the variation of resonant frequency and provides a high-rate data-transmission regardless of the narrowband characteristics of the antenna. The bit-rate in this method is dictated by the switching speed rather than the impedance bandwidth. Since the proposed technique employs the antenna in a time-varying arrangement, carrier frequencies are not required to be simultaneously within the antenna bandwidth. When demanded, the antenna is tuned to required carrier frequency according to a sequence of digital data. Moreover, if the switching frequency is properly chosen such that the stored energy in the near-zone is not dramatically disturbed, any variation in the antenna resonance will instantaneously appear in the far-field radiation due to the previously accumulated energy in the near field. Therefore, depending on the Q factor and switching speed, radiation bandwidth of the antenna can be improved independently from the impedance bandwidth. Furthermore, we show that a single RF source is sufficient to excite both carrier frequencies and the need for a VCO is obviated. Experimental results are presented to validate the feasibility of the proposed technique.