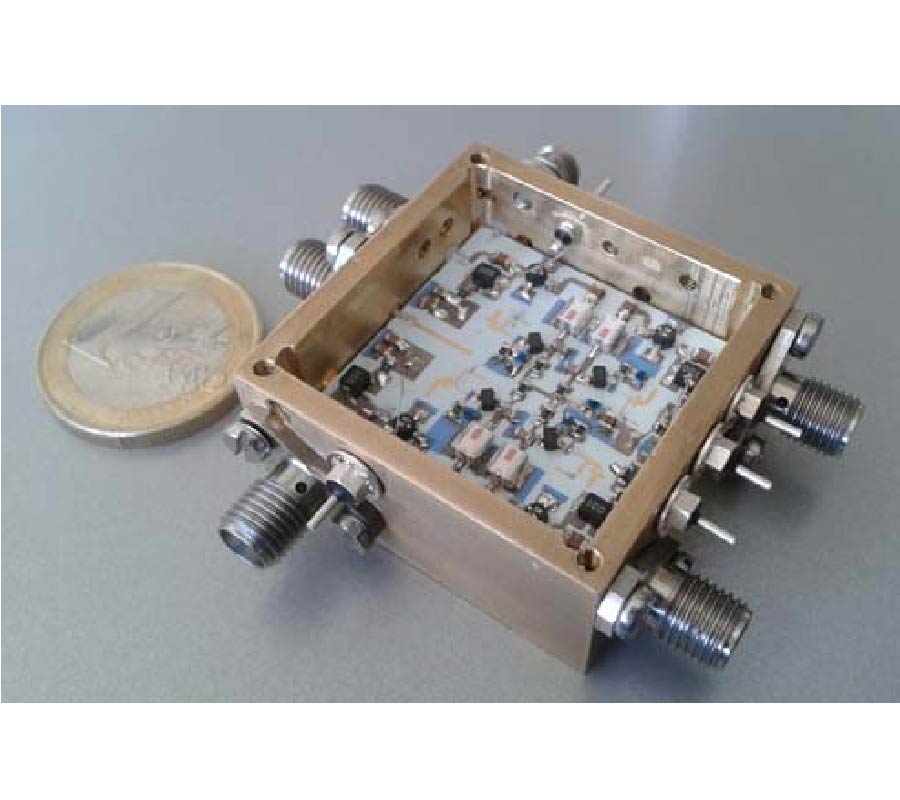
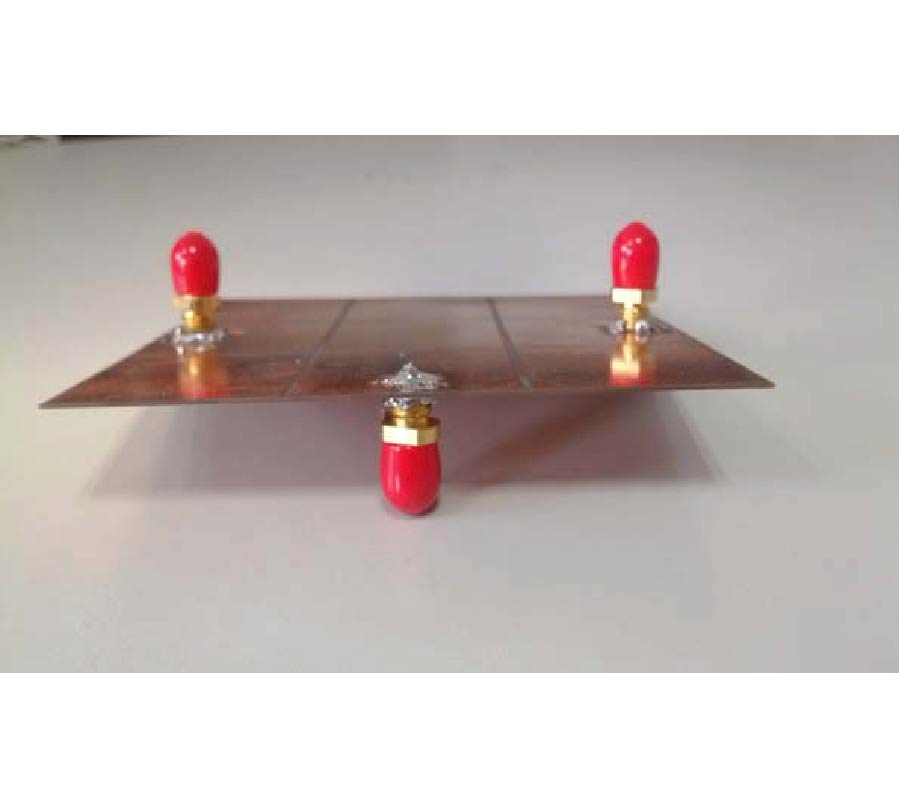
NMR Detection at 8.9 mT with a GMR Based Sensor Coupled to a Superconducting Nb Flux Transformer
Raffaele Sinibaldi,
Cinzia De Luca,
Jaakko O. Nieminen,
Angelo Galante,
Vittorio Pizzella,
Piero Sebastiani,
Myriam Pannetier-Lecoeur,
Antonietta Manna,
Piero Chiacchiaretta,
Gabriella Tamburro,
Antonello Sotgiu,
Claude Fermon,
Gian Luca Romani and
Stefania Della Penna
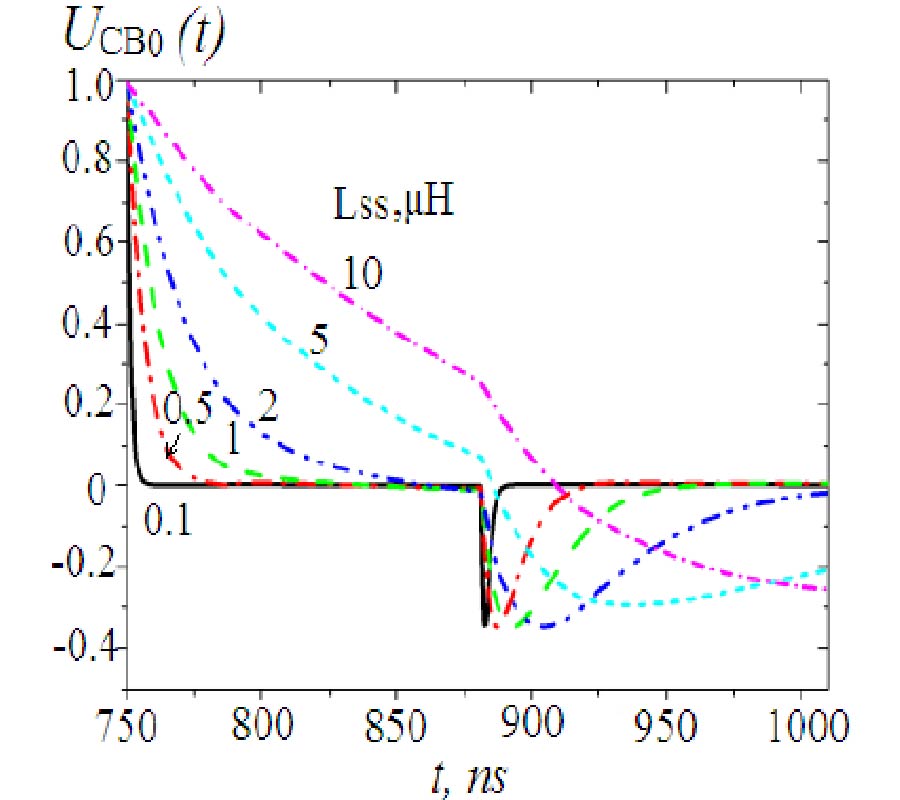
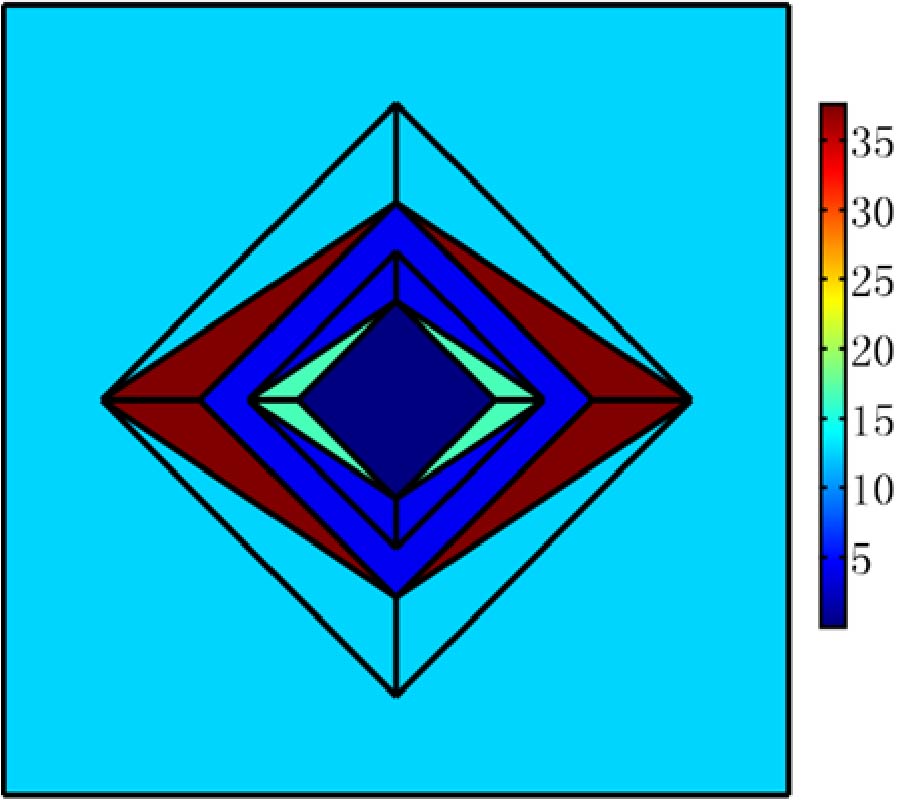
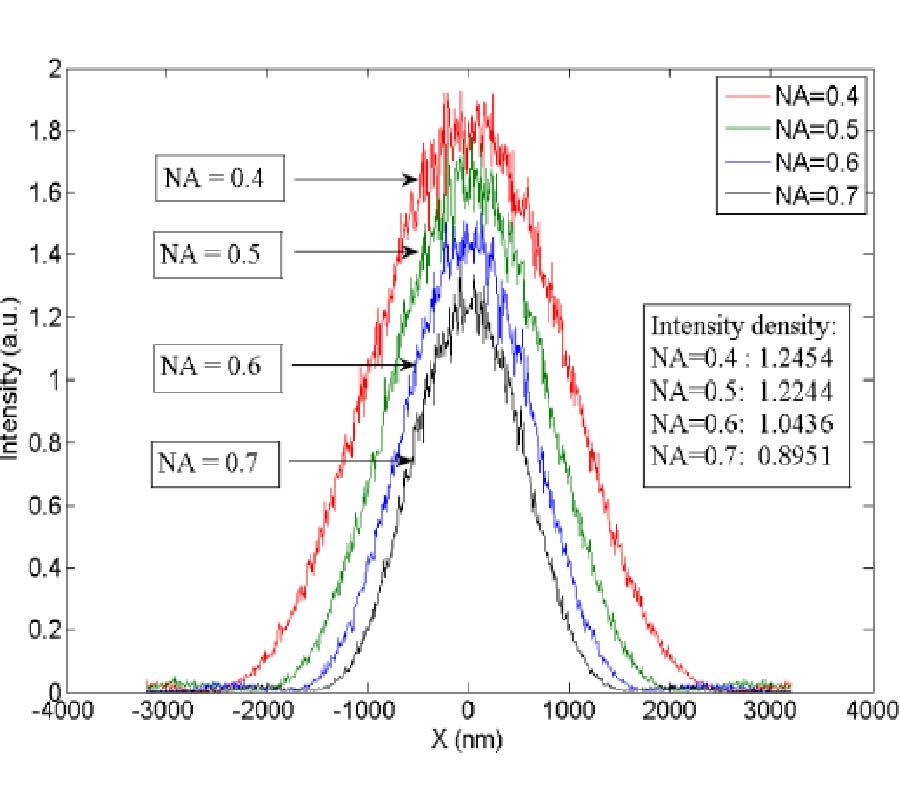
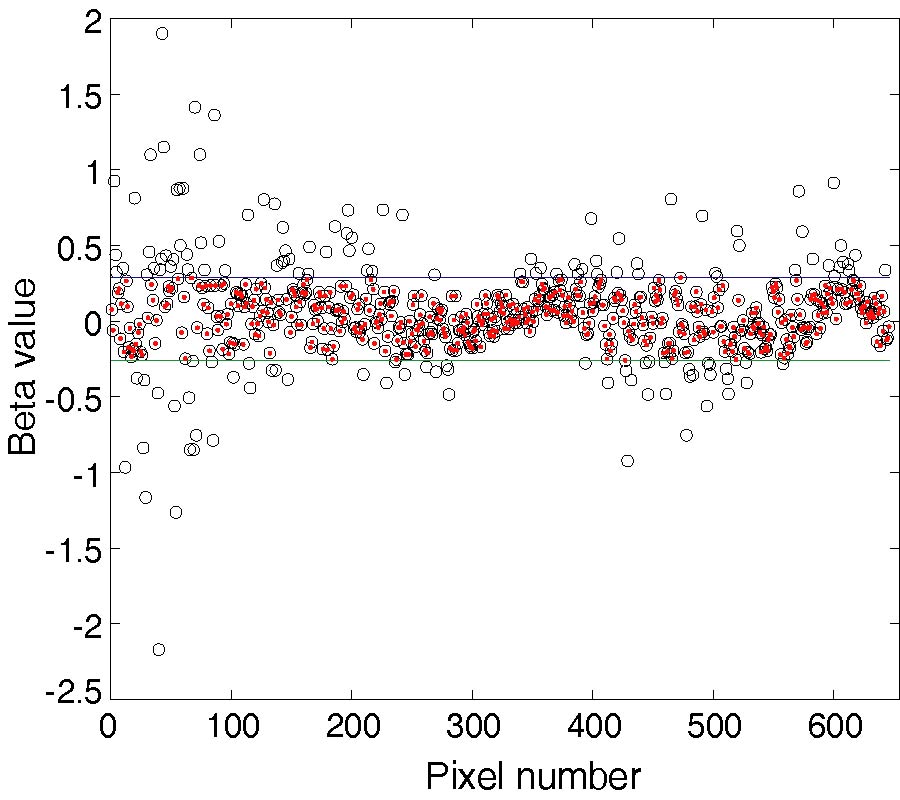
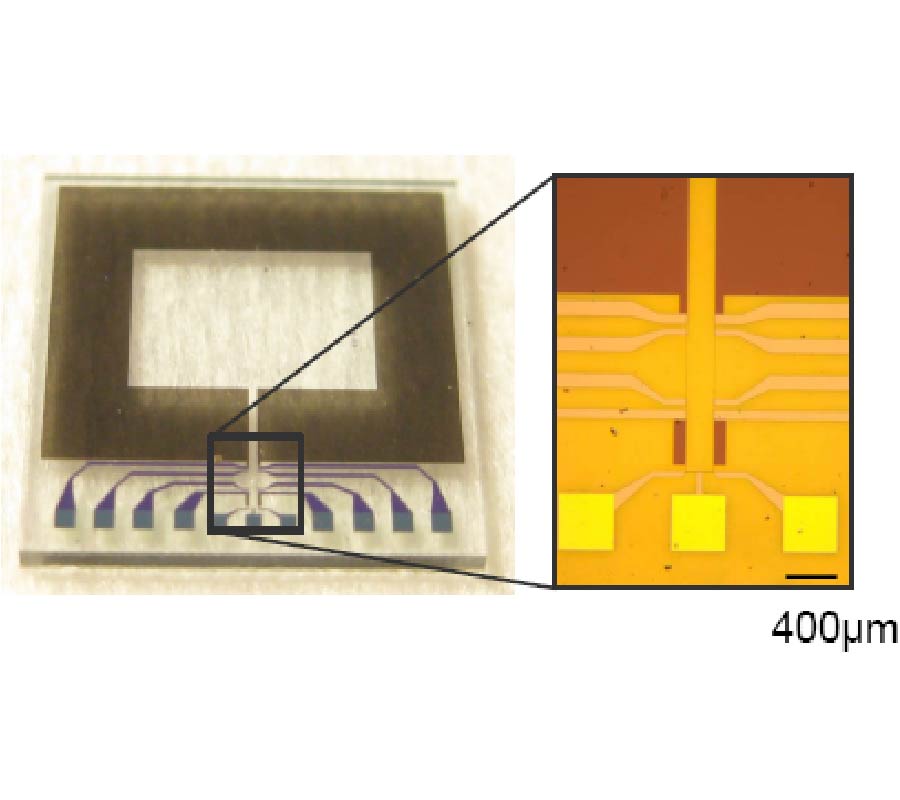
This study presents NMR signal detection by means of a superconducting channel consisting of a Nb surface detection coil inductively coupled to a YBCO mixed sensor. The NMR system operates at a low field (8.9 mT) in a magnetically shielded room suitable for magnetoencephalographic (MEG) recordings. The main field is generated by a compact solenoid and the geometry of the pickup coil has been optimized to provide high spatial sensitivity in the NMR field of view. The Nb detection coil is coupled to the mixed sensor through a Nb input coil. The mixed sensor consists of a superconducting YBCO loop with 2-μm constriction above which two Giant Magneto Resistance sensors are placed in a half-bridge configuration to detect changes of the bridge voltage as a function of the flux through the YBCO loop. The sensitivity of the receiving channel is calibrated experimentally. The measured spatial sensitivity is in agreement with the simulations and is ~10 times better than that of the stand-alone mixed sensor. A NMR echo at 375 kHz shows a SNR only a factor 4 smaller than a tuned room temperature coil tightly wound around the sample, with a noise level which is a factor 3 better than for the volume coil. Our results suggest that mixed sensors are suitable for the integration of low-field MRI and MEG in a hybrid apparatus, where MEG and MRI would be recorded by SQUIDs and mixed sensors, respectively.