Design and Fabrication of a Compact Quad-Band Bandpass Filter Using Two Different Parallel Positioned Resonators
Cheng-Fu Yang,
Yin-Chung Chen,
Cheng-Yuan Kung,
Jing-Jenn Lin and
Tai-Ping Sun
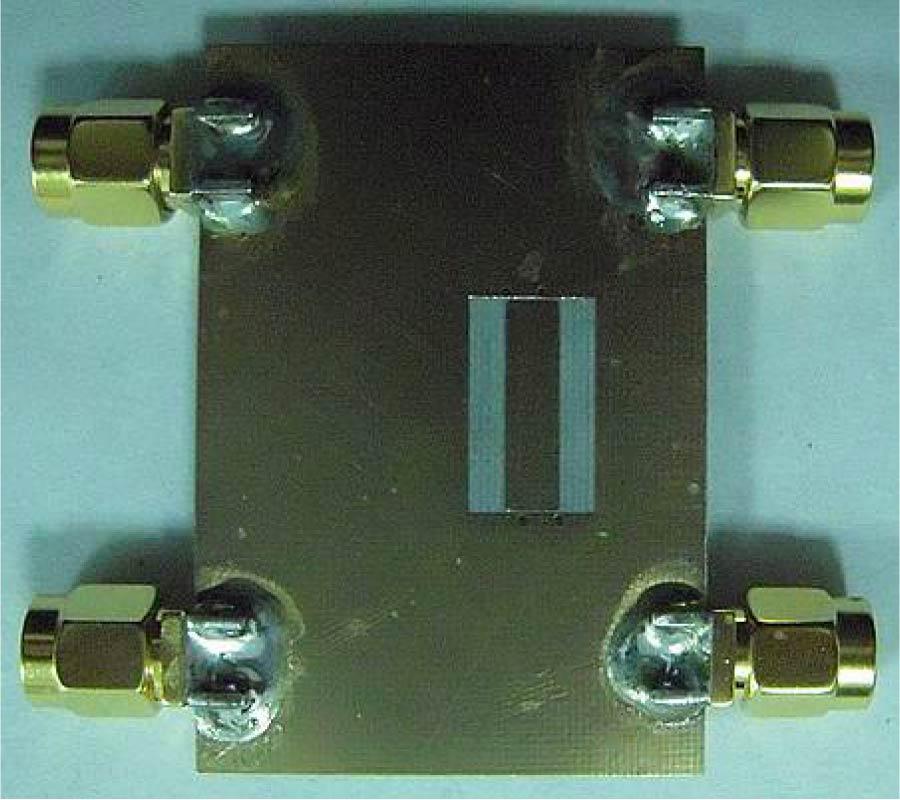
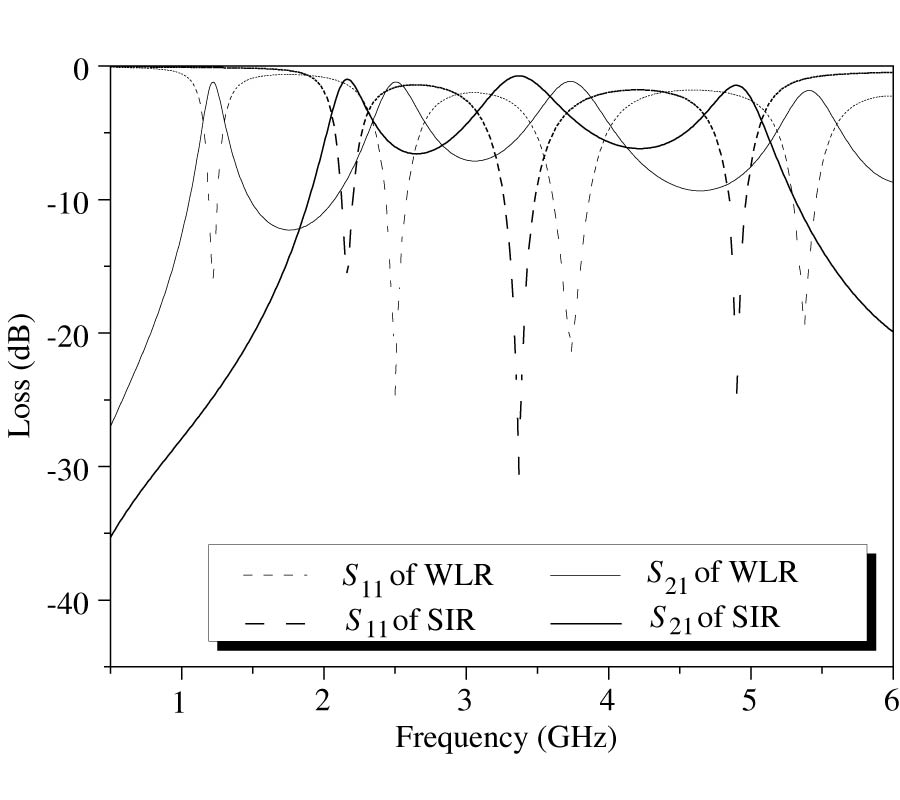
A novel microstrip quad-band bandpass filter was designed and fabricated on an Al2O3 ceramic substrate of 1 mm thick. Two different types of open-loop resonator --- a winding line-shaped resonator (WLR) and a stepped impedance resonator (SIR) --- were positioned in parallel at the two sides of input/output microstrip lines that had the same coupling lengths and coupling gap widths. The proposed filter was based on a WLR with four different resonant frequencies: 1.23 GHz, 2.49 GHz, 3.73 GHz, and 5.41 GHz. By carefully selecting the resonant frequencies of the two resonators to be slightly different, the phase difference for the signals in the two resonators was negative, indicating that energy cancellation occurred, resulting in wide bandwidths and deep transmission zeros. The spurious resonant frequencies of the SIR were designed to be non-integer multiples of the fundamental resonant frequency by adjusting the length, characteristic impedance ratio, and electrical length. The SIR was designed to have three resonant frequencies at around 2.27 GHz, 3.37 GHz, and 4.94 GHz, which had phase differences with the WLR's resonant frequencies of 2.49 GHz, 3.73 GHz, and 5.41 GHz. Finally, a novel quad-band filter with a narrow band in the L2-band (GPS, 1.227 GHz) and three wide bands in the WIMAX (3.5 GHz) and WLAN (2.4 GHz and 5.2 GHz) was achieved.